El ciclo del ácido cítrico, también conocido como ciclo del ácido tricarboxílico o ciclo de Krebs, es un conjunto cíclico de reacciones que ocurren en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la matriz mitocondrial. El ciclo del ácido tricarboxílico es la continuación de cualquier vía metabólica que produce piruvato, que se convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum su principal sustrato, acetil-CoA. El ciclo del ácido tricarboxílico oxida acetil-CoA y produce 2 CO2, guanosín trifosfato (GTP, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), 3 nicotinamida adenina dinucleótido hidruro (NADH, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) + H+ y flavín adenín dinucleótido hidruro 2 (FADH2, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). Sus productos finales (NADH + H+ y FADH2) pasan a la cadena de transporte de electrones para producir un total de 10 adenosin trifosfato (ATP, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) por ciclo.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
Producción de energía
Centro anfibólico
El ciclo del ácido cítrico proporciona precursores para muchos procesos catabólicos y anabólicos.
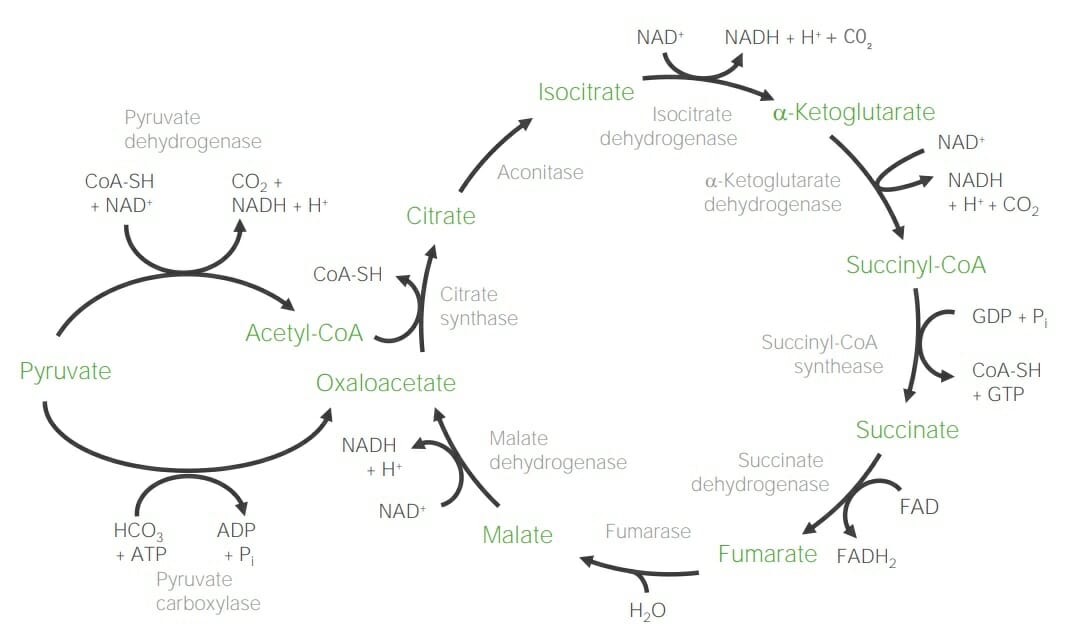
Dos sustratos principales: acetil-CoA y oxaloacetato
Pasos:
Acetil-CoA (C2) + oxaloacetato (C4) → Citrato (C6) → Isocitrato (C6) → α- Cetoglutarato (Ketoglutarate) (C5) → Succinil-CoA (C4) → Succinato (C4) → Fumarato (C4) → Malato (C4) → Oxalacetato (C4)
Mnemotecnia (
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum inglés es): Citrate (citrato) Is (es) Krebs’ (Krebs) Starting (inicial) Substrate (sustrato) For (para) Making (formar) Oxaloacetate (oxaloacetato)
Reacciones notables:
Rendimiento:
3 NADH + H+ + 1 FADH2 + 1 GTP + 2 CO2 por acetil-CoA (x 2 por glucosa)
Balance de energía:
7.5 ATP (3 NADH + H+) + 1.5 ATP (1 FADH2) + 1 ATP (1 GTP) = 10 ATP por cada acetil-CoA (x 2 por glucosa)
| Enzima | Activada por | Inhibida por |
|---|---|---|
| Piruvato deshidrogenasa |
|
|
| Citrato sintasa |
|
|
| Isocitrato deshidrogenasa (mayor impacto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ciclo del ácido cítrico) |
|
|
| α-cetoglutarato deshidrogenasa | Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ |
|
| Succinato deshidrogenasa | Succinato | Oxaloacetato |
El siguiente proceso es estimulado por el ciclo del ácido tricarboxílico:
Las siguientes afecciones inhiben el ciclo del ácido tricarboxílico: