Las fases del ciclo celular incluyen la interfase (G1, S y G2) y la mitosis Mitosis A type of cell nucleus division by means of which the two daughter nuclei normally receive identical complements of the number of chromosomes of the somatic cells of the species. Cell Cycle (profase, metafase, anafase y telofase). La progresión de la célula a través de estas fases está marcada por puntos de control regulados por ciclinas, quinasas dependientes de ciclina, supresores de tumores y sus antagonistas.
Last updated: Dec 28, 2025
El ciclo celular describe la secuencia cíclica de eventos a través de los LOS Neisseria cuales una célula madre eucariota en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum proliferación se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2 células hijas idénticas.
Las fases G1, S y G2 se agrupan juntas como interfase.
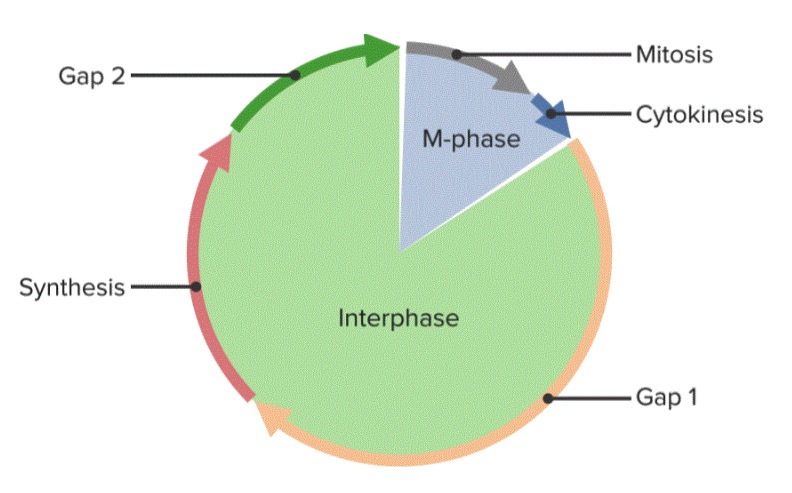
El ciclo celular, dividido en 5 fases
Imagen por Lecturio.Durante la mitosis Mitosis A type of cell nucleus division by means of which the two daughter nuclei normally receive identical complements of the number of chromosomes of the somatic cells of the species. Cell Cycle, el ADN duplicado de la célula se separa y distribuye en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2 células hijas idénticas. El proceso dura aproximadamente 1 hora.
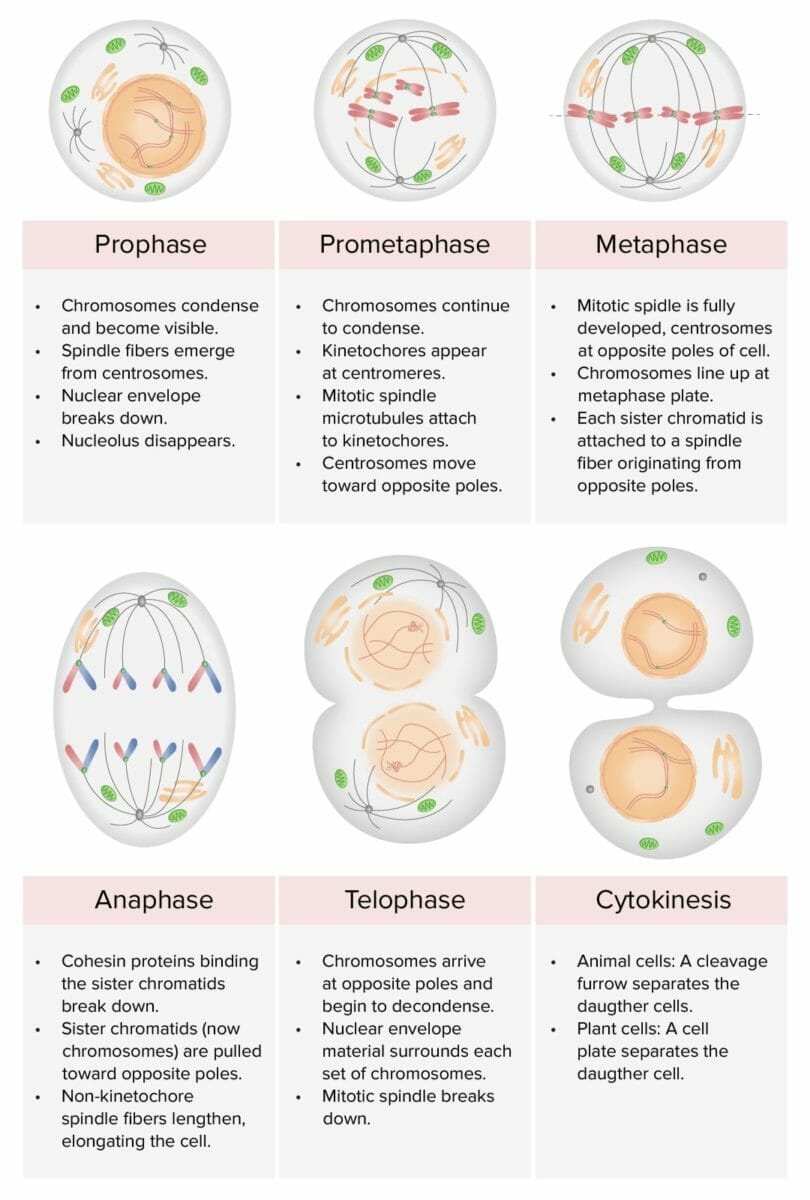
Representación de las etapas de la mitosis: profase, prometafase, metafase, anafase y telofase: Durante el cariotipo, el ciclo celular es detenido en metafase, usualmente al adicionar un agente como la colchicina (inhibe la polimerización de los microtúbulos para detener la mitosis).
Imagen por Lecturio.El ciclo celular está estrictamente regulado. No pasar un punto de control debería desencadenar la muerte celular programada ( apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage). El fracaso de la apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage da como resultado la acumulación de mutaciones, lo que lleva a la enfermedad.
El ciclo celular comienza cuando la célula tiene:
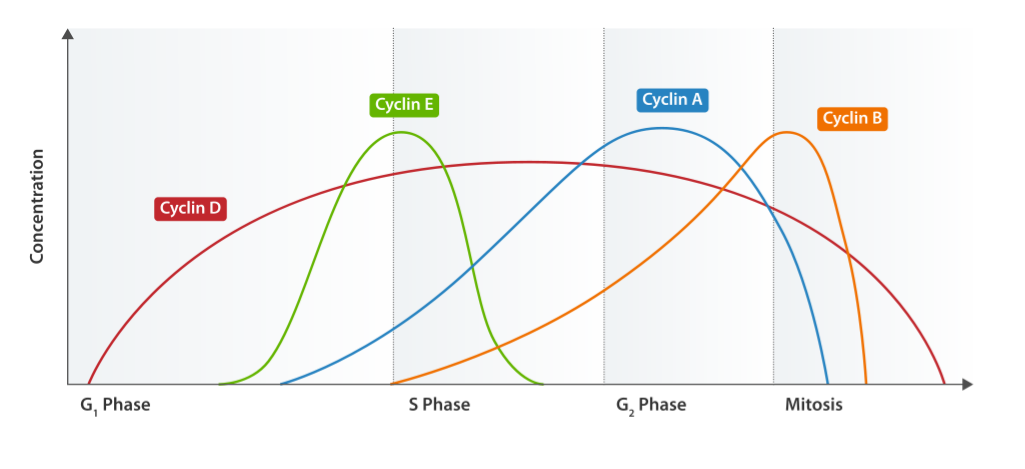
Ciclo de expresión de ciclina
Imagen: “Cyclin Expression” por T4taylor. Licencia: Dominio Público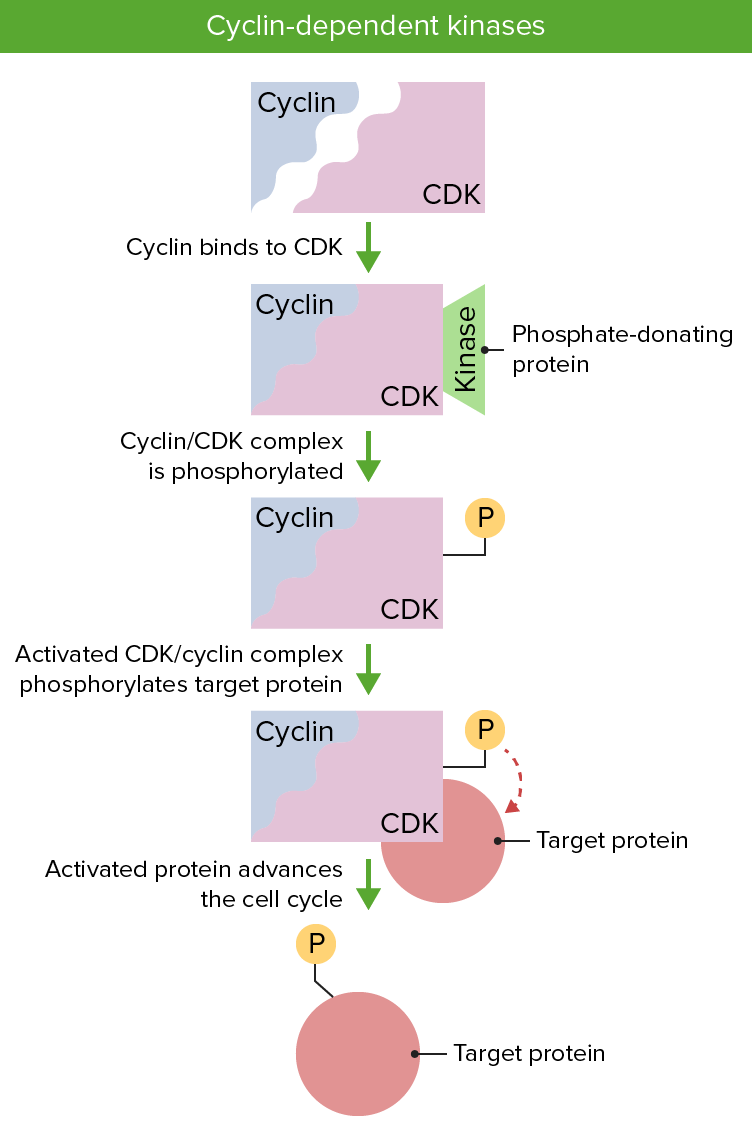
Las ciclinas y las quinasas dependientes de ciclinas son esenciales para la regulación del ciclo celular. Es necesaria la presencia de ambas proteínas y su activación vía fosforilación permite la progresión del ciclo celular.
Imagen por Lecturio.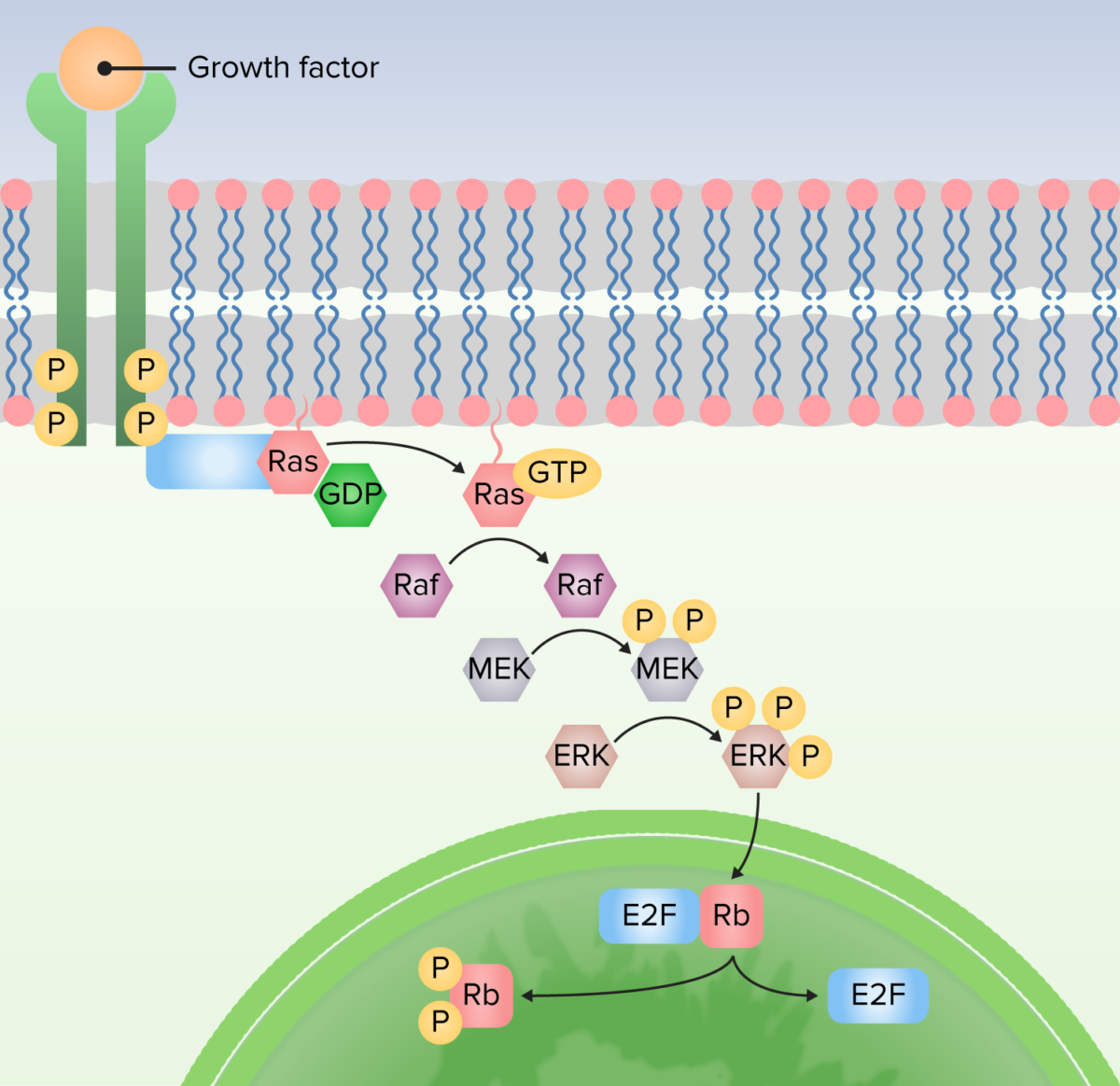
1. Proteína unida al receptor para activar Ras mediante el intercambio de guanosina difosfato (GDP) por guanosina trifosfato (GTP).
2. Ras activa la primera quinasa (Raf).
3. Raf activa la segunda quinasa (MEK).
4. MEK activa MAP quinasas (ERK).
5. La MAP quinasa (ERK) activa las proteínas para producir respuestas celulares, incluidos los factores de transcripción que alteran la expresión génica.