La cardiopatía coronaria, o cardiopatía isquémica, describe una situación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que existe una irrigación inadecuada de sangre al AL Amyloidosis miocardio debido a una estenosis de las arterias coronarias, normalmente por aterosclerosis. El miocardio se vuelve isquémico cuando el suministro de oxígeno no satisface la demanda de oxígeno. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG); también pueden ser necesarias pruebas de esfuerzo cardíaco y cateterismos. El tratamiento se basa principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la reducción de la demanda de oxígeno del corazón y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el aumento del suministro de oxígeno.
Last updated: Jan 16, 2026
La cardiopatía coronaria es la manifestación de la aterosclerosis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las arterias coronarias, de manera que se produce un desequilibrio entre el suministro de oxígeno y la demanda del miocardio, lo que da lugar a la isquemia de una parte del miocardio.
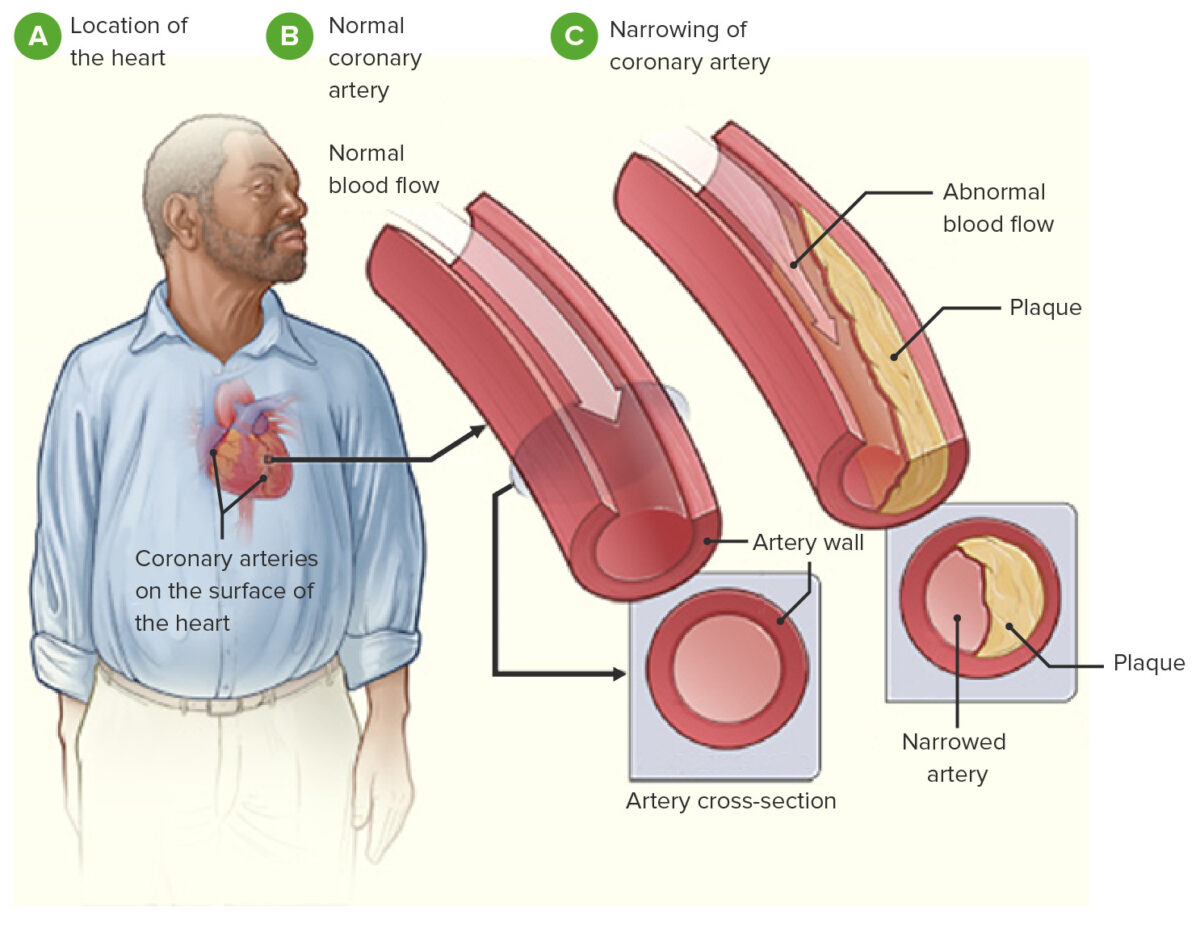
Imagen que demuestra la fisiopatología de la cardiopatía coronaria
Imagen: “Coronary heart disease-atherosclerosis” por National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Licencia: Dominio Público, editado por Lecturio.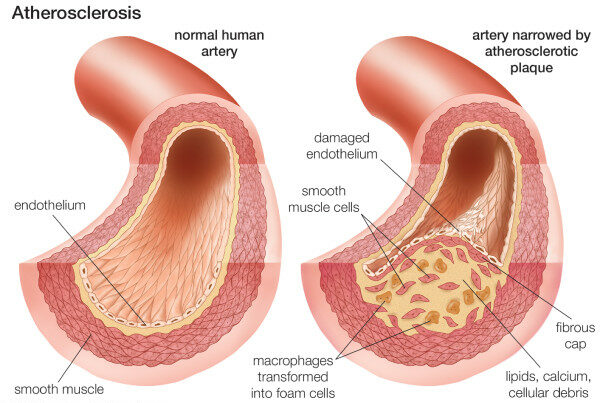
Composición de la placa aterosclerótica
Imagen: “Neovascularization of coronary tunica intima (DIT) is the cause of coronary atherosclerosis. Lipoproteins invade coronary intima via neovascularization from adventitial vasa vasorum, but not from the arterial lumen: a hypothesis” por Subbotin, VM/ Encyclopeadia Britannica. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La cardiopatía coronaria tiene un espectro de presentaciones clínicas.
Características generales:
Angina estable:
Angina inestable:
Características generales:
Cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) (irreversibles):
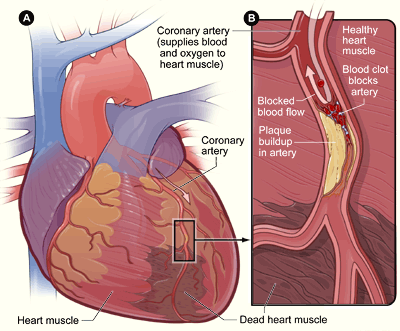
Infarto de miocardio
Imagen: “Heart attack-NIH” por National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Licencia: Dominio Público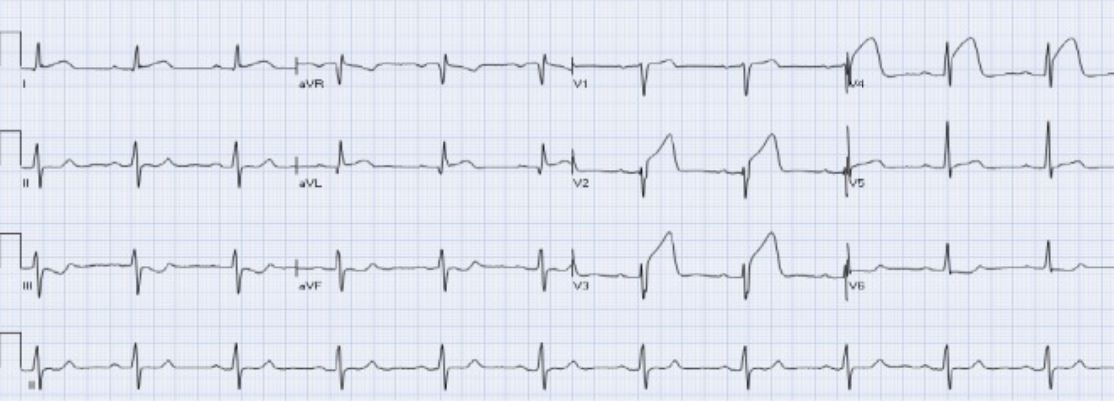
IAMCEST anterior agudo:
Hay elevación del ST en las derivaciones aVL y V2-V4 con depresión recíproca del ST en las derivaciones III y aVF.