A síndrome IPEX (desregulação imune, poliendocrinopatia, enteropatia ligada ao X) é uma deficiência congénita rara de células T, associada à disfunção do fator de transcrição FOXP3. Este fator regula o desenvolvimento de uma linhagem de células T reguladoras e as disfunções geralmente resultam em autoimunidade. A condição manifesta-se como enteropatia autoimune, dermatite eczematosa, distrofia ungueal, endocrinopatias autoimunes e doenças autoimunes da pele. A única forma de tratamento da IPEX é o transplante de medula óssea.
Last updated: Jan 5, 2025
Epidemiologia
Etiologia
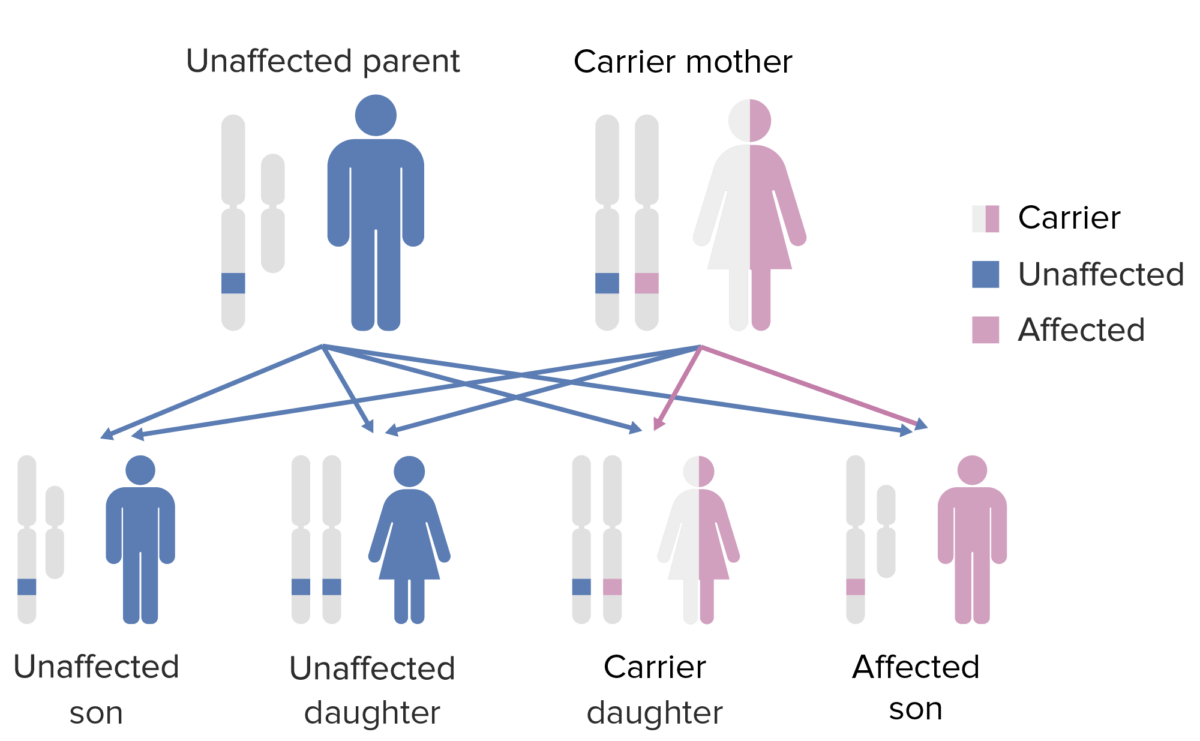
Os sinais de autoimunidade sistémica começam a apresentar-se no 1º ano de vida.

Doente com linfadenopatia cervical
Imagem: “Ixodholfem8” por Hudson, Bernard. Licença: CC BY 3.0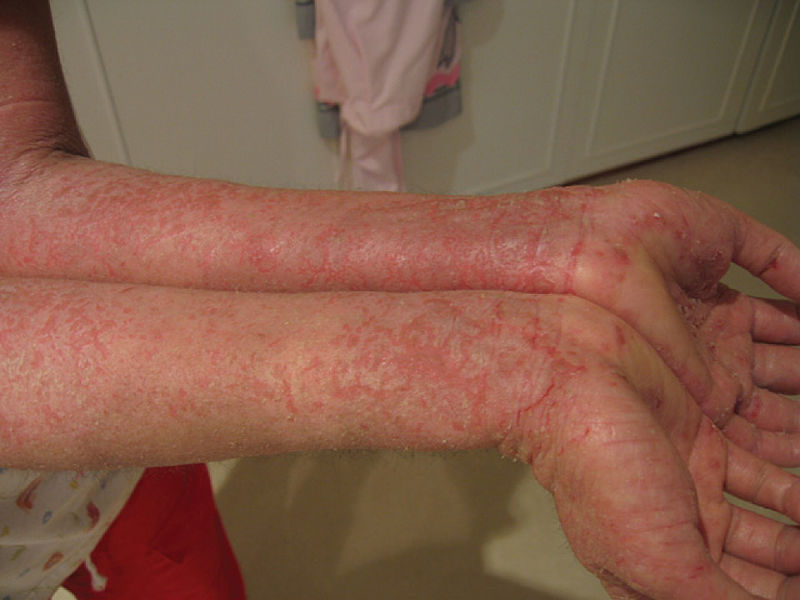
Eczema grave apresentado por um doente com síndrome IPEX
Imagem: “Eczema” por OpenStax College. Licença: CC BY 3.0O diagnóstico da síndrome IPEX segue critérios sistemáticos consistentes com:
São usados inúmeros fármacos e a administração depende das manifestações de cada doente:
As seguintes condições são diagnósticos diferenciais da síndrome IPEX: