As doenças valvulares podem surgir na válvula pulmonar, localizada entre o ventrículo direito (VD) e a artéria pulmonar (AP). As doenças valvulares são diagnosticados com ecocardiograma. A estenose pulmonar ( EP EP Ectopic pregnancy refers to the implantation of a fertilized egg (embryo) outside the uterine cavity. The main cause is disruption of the normal anatomy of the fallopian tube. Ectopic Pregnancy) é um estreitamento valvular que causa obstrução do trato de saída do VD. Os pacientes são frequentemente assintomáticos, a não ser que tenham outras anomalias cardíacas congénitas ou EP EP Ectopic pregnancy refers to the implantation of a fertilized egg (embryo) outside the uterine cavity. The main cause is disruption of the normal anatomy of the fallopian tube. Ectopic Pregnancy grave. Os sintomas (dispneia de esforço, dor torácica e síncope) devem-se à falência do VD. A EP EP Ectopic pregnancy refers to the implantation of a fertilized egg (embryo) outside the uterine cavity. The main cause is disruption of the normal anatomy of the fallopian tube. Ectopic Pregnancy grave é tratada cirurgicamente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Válvula pulmonar:
| Estenose Pulmonar ( EP EP Ectopic pregnancy refers to the implantation of a fertilized egg (embryo) outside the uterine cavity. The main cause is disruption of the normal anatomy of the fallopian tube. Ectopic Pregnancy) | Regurgitação Pulmonar (RP) | |
|---|---|---|
| Etiologia | Sobretudo congénita | Sobretudo adquirida |
| Sopro | Sopro sistólico, audível no bordo esternal superior esquerdo (precedido por um clique sistólico que diminui com a inspiração) | Sopro diastólico, audível no bordo esternal superior esquerdo, que aumenta com a inspiração |
| S2 S2 Heart Sounds | Desdobramento de S2 S2 Heart Sounds com um P2 suave e retardado | Desdobramento de S2 S2 Heart Sounds com um P2 acentuado |
| Achados no ecocardiograma | Folhetos espessos em cúpula, com aumento da velocidade sistólica através da válvula, HVD | Anomalias valvulares (dependendo da etiologia), aumento do VD e uma regurgitação em jato na via de saída do ventrículo direito. |
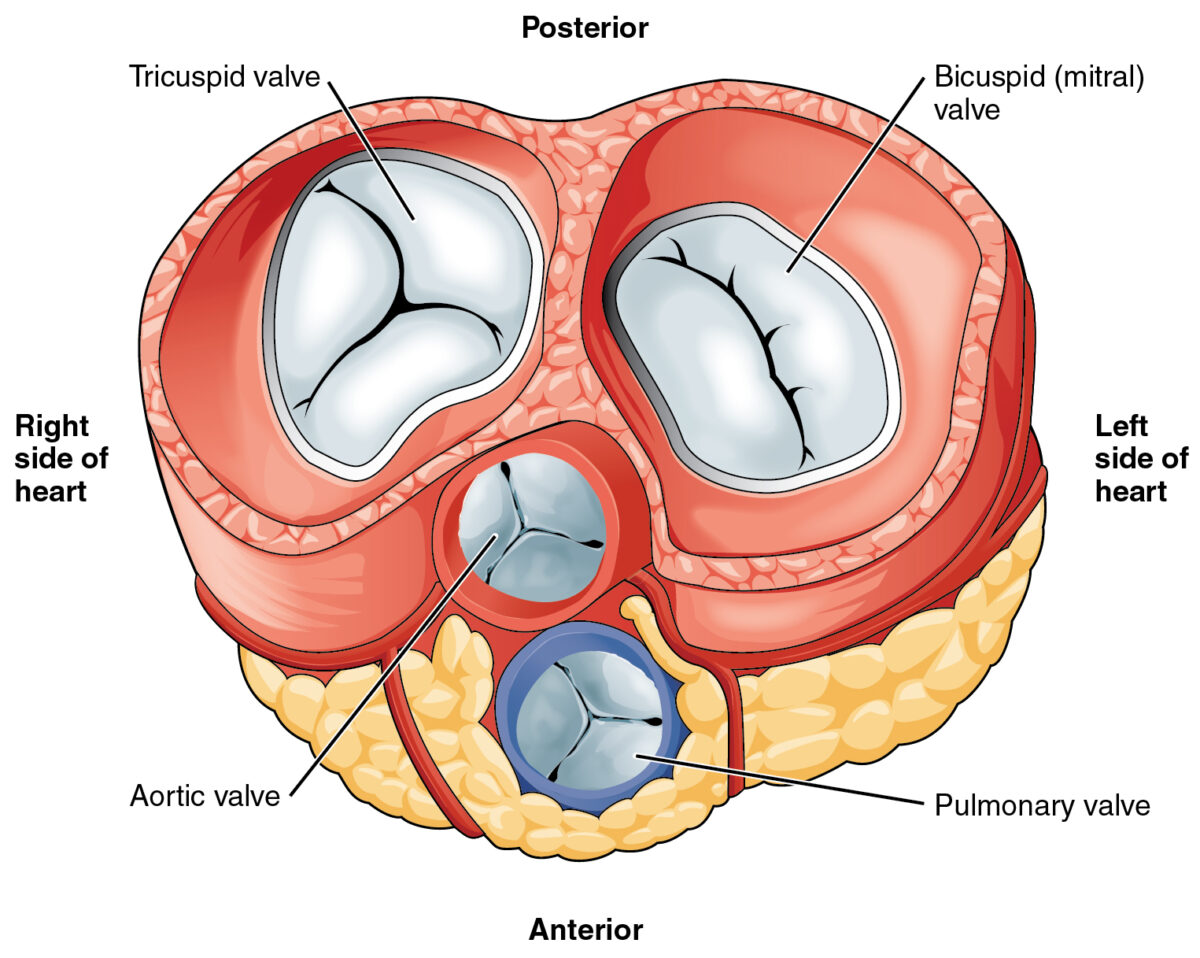
Válvulas cardíacas:
A válvula pulmonar é a válvula média inferior.
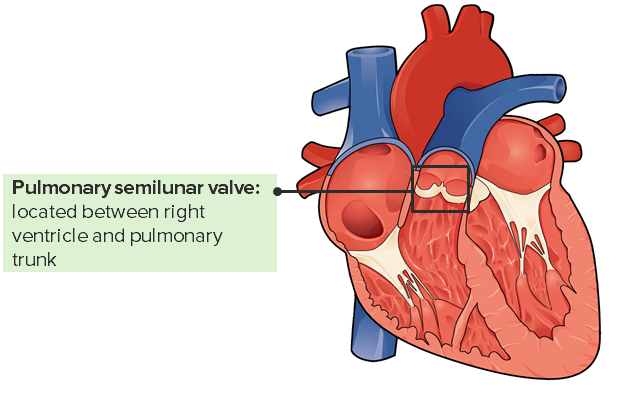
Válvula pulmonar e a sua localização no coração
Imagem: “Internal Anatomy of the Heart” por Philschatz. Licença: CC BY 4.0, editado por Lecturio.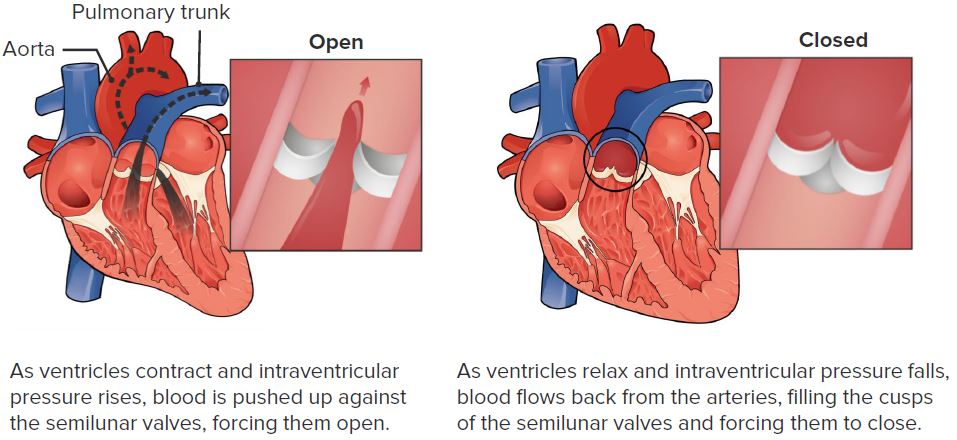
Função da válvula pulmonar
Imagem: “Pulmonary Valve” por Philschatz. Licença: CC BY 4.0, editado por Lecturio.A estenose pulmonar é o estreitamento da válvula pulmonar que causa:
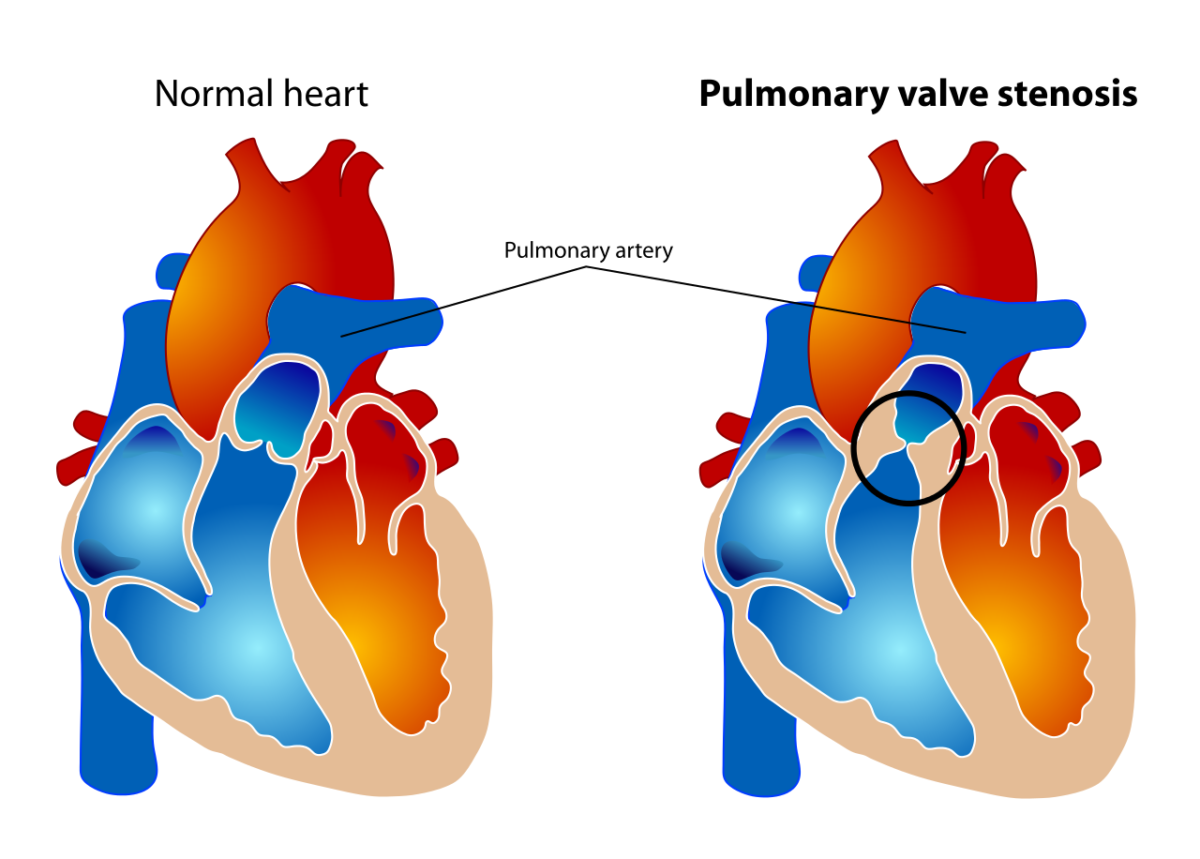
Diferenciação do coração normal com uma válvula pulmonar normal e de um coração com estenose da válvula pulmonar
Imagem: “Pulmonary valve stenosis” por LadyofHats. Licença: Public domain.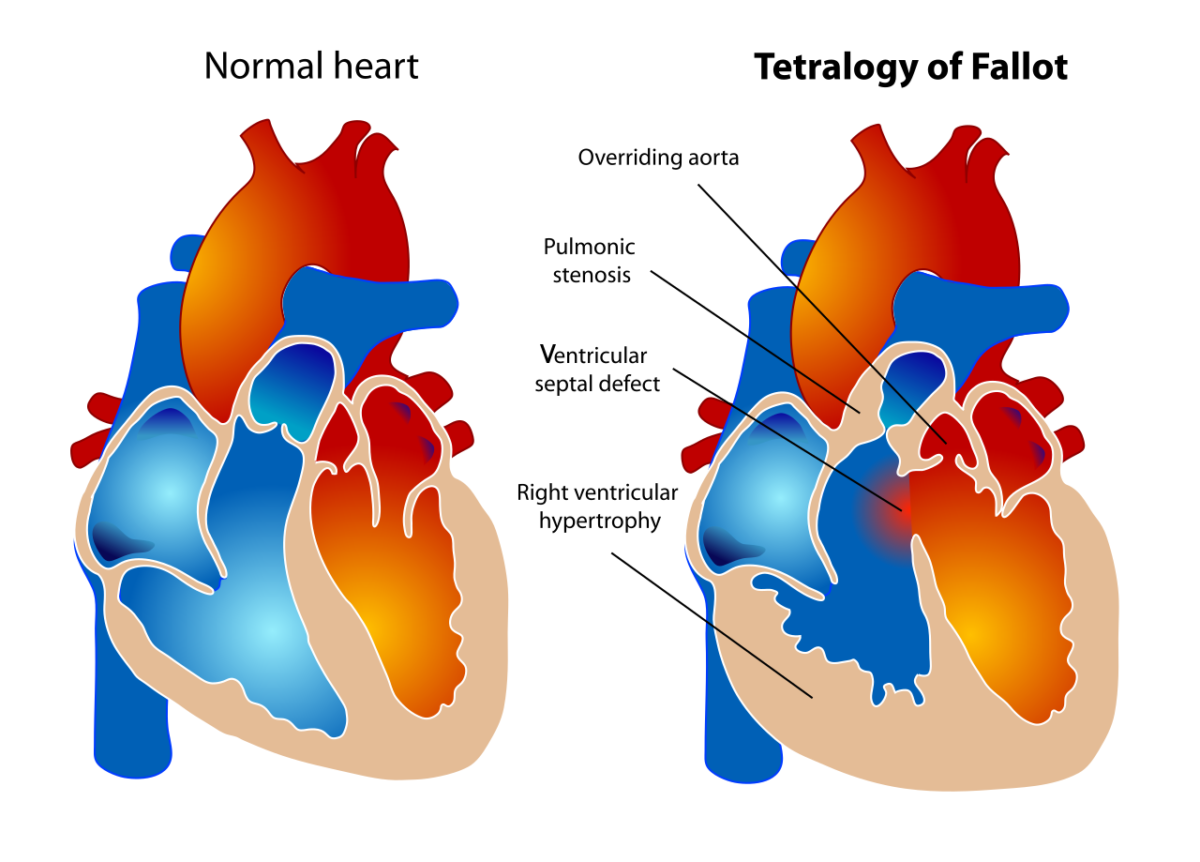
Comparação entre o coração normal e um coração com TF: estenose da válvula pulmonar, cavalgamento da aorta, HVD, CIV
Imagem: “Tetralogy of Fallot” por LadyofHats. Licença: Public domain.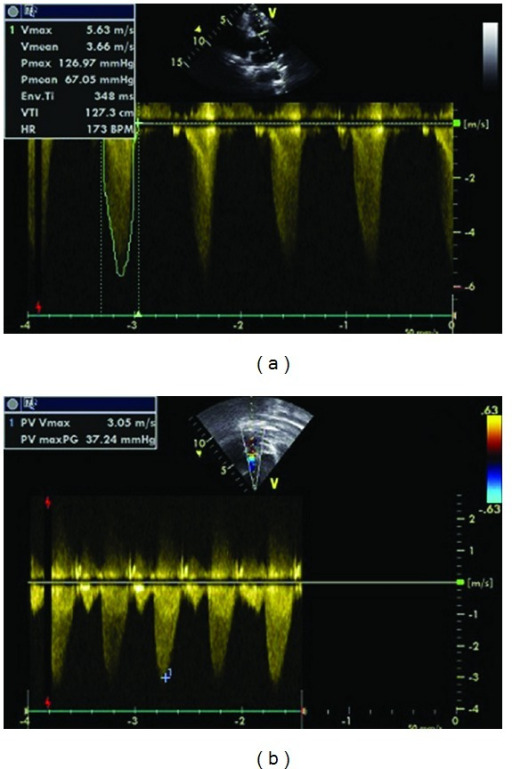
Ecocardiograma. A: estenose da válvula pulmonar com gradiente máximo de 126 mm Hg antes da valvuloplastia com balão pulmonar; B: estenose da válvula pulmonar ligeira após a valvuloplastia com balão (gradiente máximo de 37 mm Hg)
Imagem: “Pulmonary Balloon Valvuloplasty” por Oylumlu M, Aykent K, Soydinc HE, Oylumlu M, Ertas F, Ozer HO, Sari I. Licença: CC By 3.0.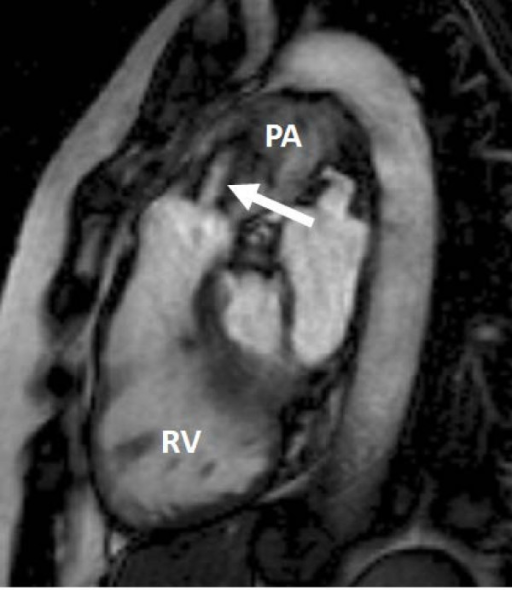
Imagem de ressonância magnética cardíaca: corte da via de saída do ventrículo direito mostrando o VD encurtado e uma válvula pulmonar com estenose moderada a grave. Pode ver-se o jato de alta velocidade da estenose (seta). AP = artéria pulmonar principal.
Imagem: “Heart valve disease” por Myerson SG, John Radcliffe Hospital. Licença: CC BY 2.0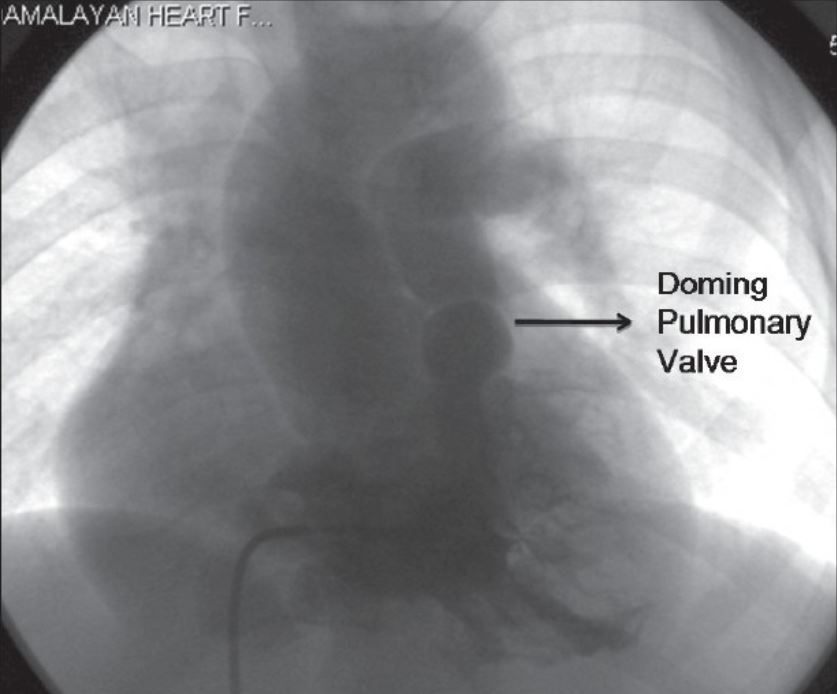
Angiografia do ventrículo direito em incidência postero-anterior mostrando o estreitamento infundibular e a válvula pulmonar em cúpula
Imagem: “Tetralogy of fallot” por Kannan BR. Licença: CC BY 2.0.
Radiografia de tórax de uma mulher adulta com estenose valvular pulmonar grave. A paciente foi submetida a valvuloplastia pulmonar percutânea de balão (VPB). Imagem à esquerda: Uma radiografia de tórax revelou um aumento acentuado do tronco pulmonar principal pela EP. Imagem à direita: A incidência lateral mostra uma complicação do procedimento, com o cateter preso através da fossa ovalis.
Imagem: “Entrapped Catheter across the Fossa Ovalis” por Betigeri VM, Gopinathan G, Malik I, Sanwal MK, Datt V, Satsangi DK. Licença: CC BY 3.0.