Cri du chat es el término francés que significa “llanto de gato” o “maullido de gato”. El término hace HACE Altitude Sickness referencia al AL Amyloidosis llanto de un paciente pediátrico con síndrome de cri-du-chat parecido al AL Amyloidosis maullido de un gato. Se trata de un raro trastorno genético causado por mutaciones de deleción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cromosoma 5. El síndrome de Cri-du-chat es más frecuente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las mujeres que en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hombres. Además del llanto característico, la enfermedad también presenta disfagia, bajo peso al AL Amyloidosis nacer, crecimiento deficiente y graves discapacidades cognitivas del habla y motoras.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas varían y dependen de la cantidad de material genético eliminado.
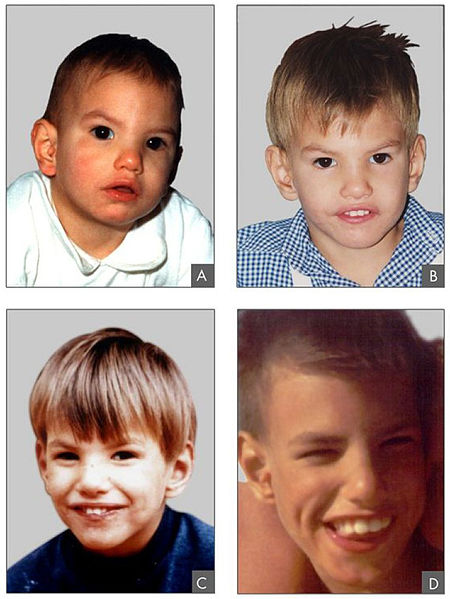
Características fenotípicas asociadas al síndrome de Cri-du-chat
Imagen: “Criduchat” por Paola Cerruti Mainardi. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Las siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales del síndrome de Cri-du-chat: