El retorno venoso pulmonar total anómalo es un defecto cardíaco congénito cianótico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el que las venas pulmonares drenan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum lugares anatómicos distintos de la aurícula izquierda. El subtipo más común es la forma supra cardíaca, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que el drenaje es en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vena cava superior. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen estar cianóticos desde el nacimiento y presentan insuficiencia respiratoria y cardíaca justo después de nacer. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la exploración física hay un sonido cardíaco fijo y amplio de una fracción de segundo, y una radiografía de tórax podría revelar el signo del “muñeco de nieve”. El diagnóstico se confirma mediante un ecocardiograma, que puede ser prenatal. Todos los LOS Neisseria pacientes necesitan una intervención quirúrgica para sobrevivir y el tratamiento médico se utiliza como paliativo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum espera de la intervención quirúrgica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El retorno venoso pulmonar total anómalo es un defecto cardíaco congénito cianótico que provoca el drenaje de las 4 venas pulmonares hacia la circulación venosa sistémica, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum lugar de hacia la aurícula izquierda, lo que provoca la mezcla de sangre oxigenada y desoxigenada. Debe haber un defecto interauricular (comunicación interauricular, foramen oval persistente o ducto arterioso persistente) para permitir que la sangre mixta se desvíe hacia el lado izquierdo del corazón y la circulación arterial sistémica.
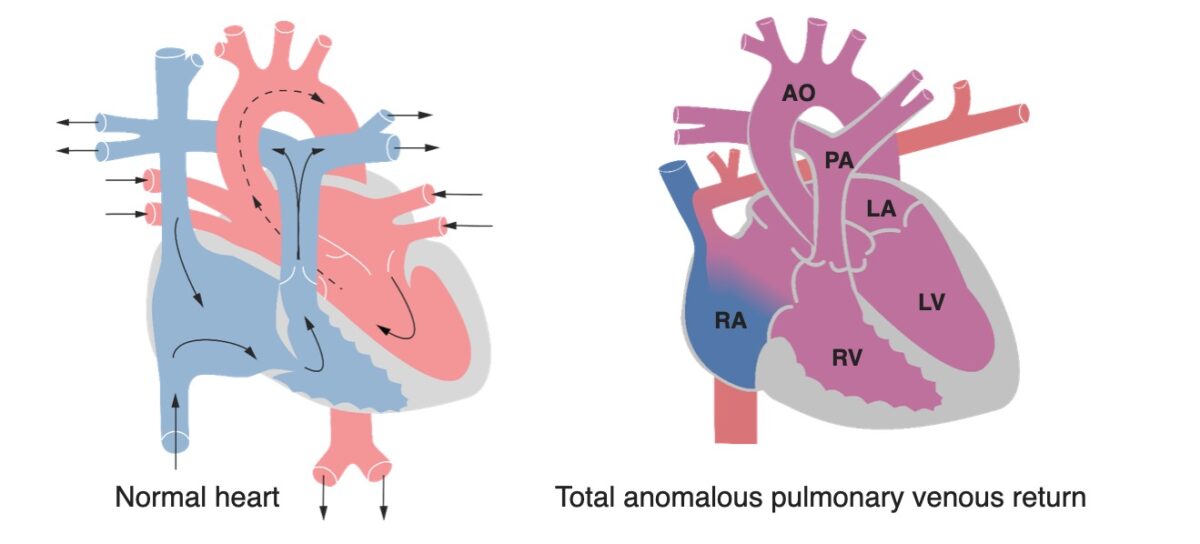
Un corazón con anatomía normal en comparación a un corazón con retorno venoso pulmonar total anómalo:
La forma más común de retorno venoso pulmonar total anómalo presenta las 4 venas pulmonares que drenan en la vena cava superior como se muestra aquí. Obsérvese el aumento de tamaño de la pared del ventrículo derecho, debido a la sobrecarga ventricular progresiva.
This condition arises due to the failure of the left atrium to merge with the pulmonary venous plexus during fetal development.
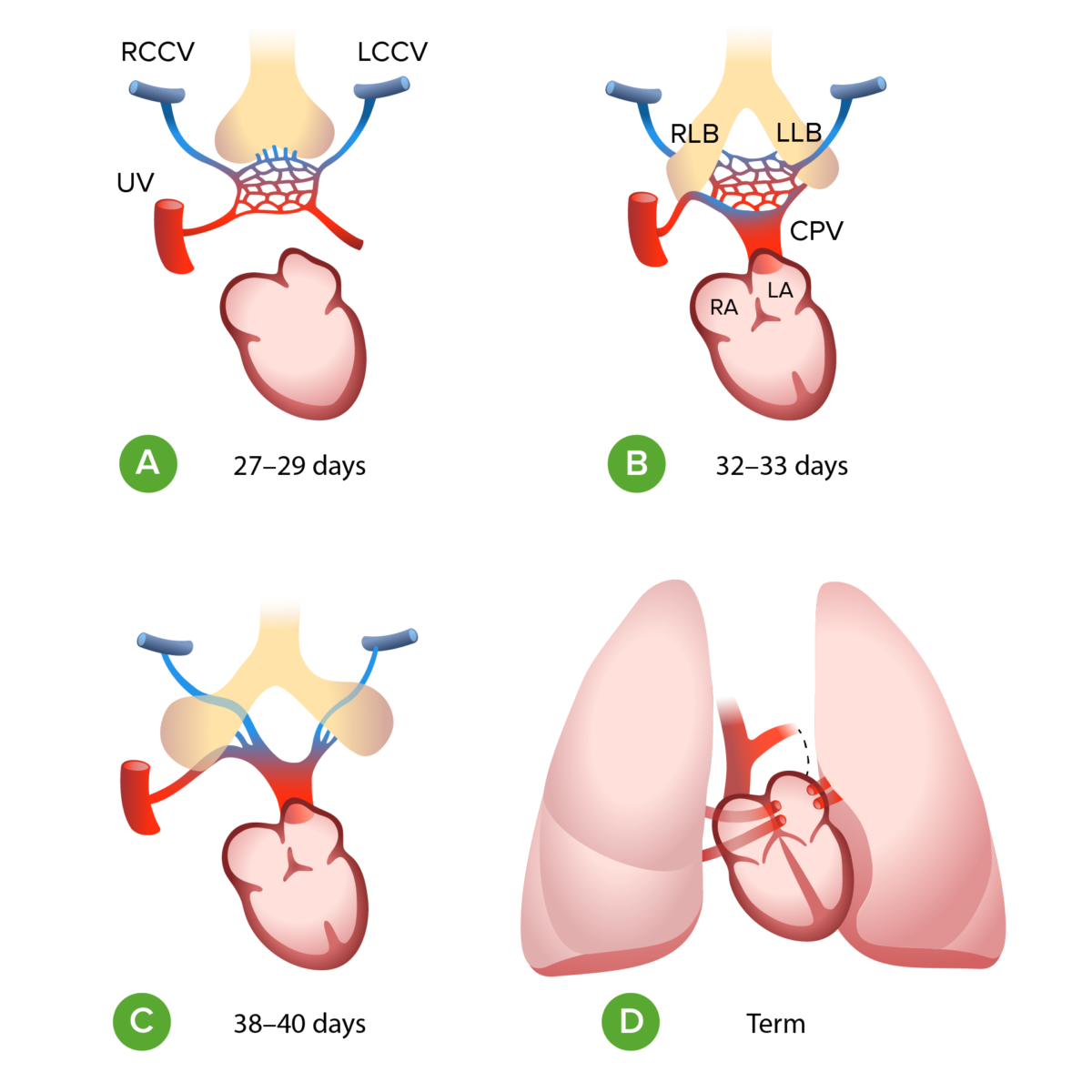
A: During the first month of gestation the left and right common cardinal vein (LCCV, RCCV) and the umbilical vein (UV) drain the splanchnic plexus (the primitive pulmonary vasculature) into the fetal heart.
B: At the end of the first month of gestation the embryonal left atrium (LA) gives rise to common pulmonary vein (CPV) which merges with the venous plexus
C: The connection to the LCCV, RCCV and UV disappear
D: CPV splits into 4 and is incorporated into the wall of the left atrium
RA: right atrium
LLB: left lung bud
RLB: right lung bud
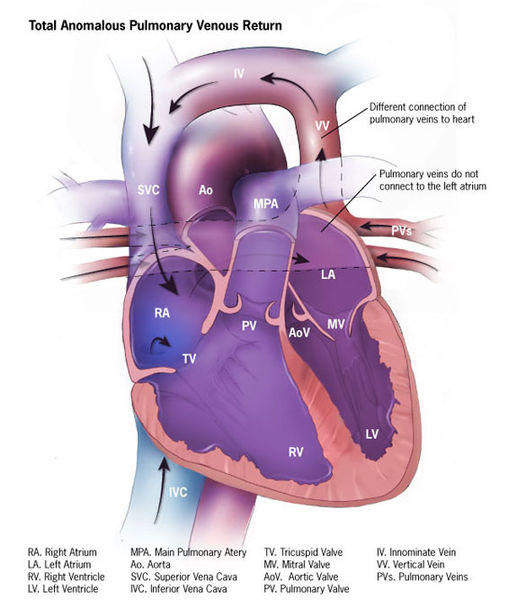
Mezcla de sangre en el retorno venoso pulmonar total anómalo:
En el retorno venoso pulmonar total anómalo, la sangre oxigenada de los pulmones regresa a la circulación venosa sistémica mezclándose con la sangre desoxigenada. Esta sangre mezclada se desvía entonces hacia el lado izquierdo del corazón a través de un defecto del tabique auricular y fluye hacia el resto del cuerpo dando lugar a la cianosis.
El grado de obstrucción de las venas pulmonares determina la edad de presentación:
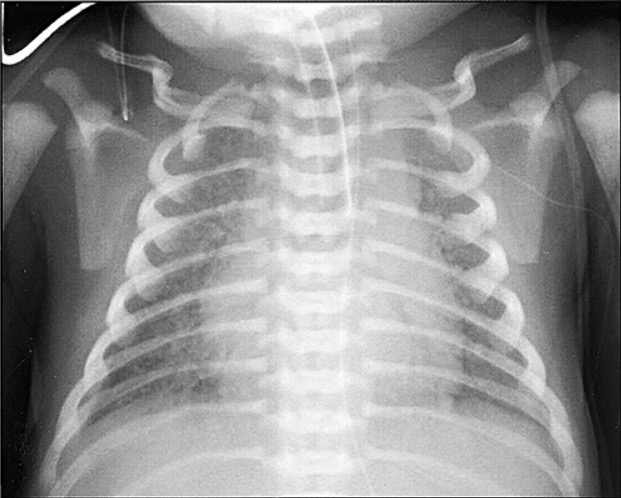
Total anomalous pulmonary vein drainage: marked pulmonary congestion and diffuse bilateral reticulogranular infiltrates
Image: “Total anomalous pulmonary vein drainage” by Departments of Pathology and Cell Biology, School of Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental Health, Fukuoka Shin Mizumaki Hospital, Kitakyushu, Japan. License: CC BY 2.5