La retinopatía del prematuro (ROP, por sus siglas en inglés) es una afección que se observa en los bebés prematuros de bajo peso al nacer que se caracteriza por una neovascularización progresiva y excesiva. En esta condición, la proliferación inapropiada de vasos sanguíneos y tejido fibrovascular detrás del cristalino impide el desarrollo de la retina. El resultado final es un déficit visual grave o incluso la ceguera del niño afectado. El tratamiento con fotocoagulación láser previene la pérdida de visión en el 95% de los casos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria bebés prematuros de bajo peso al AL Amyloidosis nacer tienen riesgo de desarrollar hiperoxia durante su cuidado; esto puede llevar a:
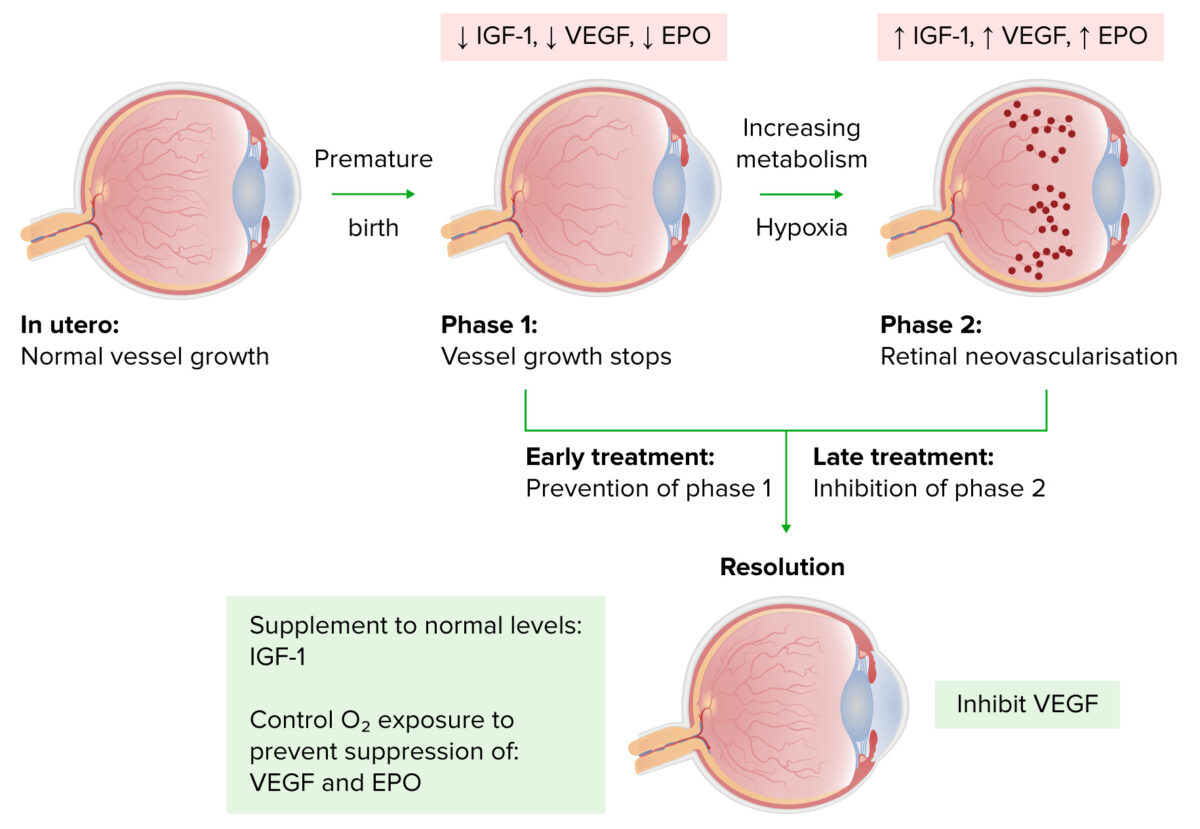
Progresión de la retinopatía del prematuro
Imagen por Lecturio.La clasificación internacional de la retinopatía utiliza una serie de parámetros para describir la enfermedad:
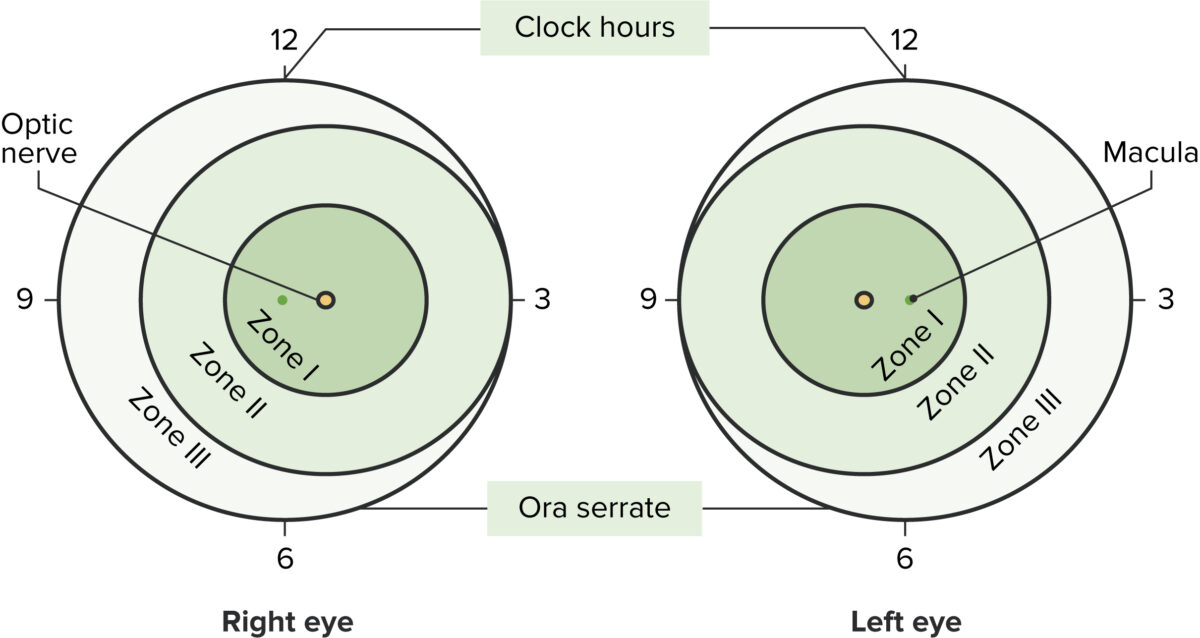
Representación de la clasificación de la retinopatía del prematuro
Imagen por Lecturio.| Etapas | Características |
|---|---|
| 1 | Una línea de demarcación entre la retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy vascular y avascular Avascular Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers |
| 2 | Una línea de demarcación crece hasta ocupar un volumen y se forma una cresta sobre el plano de la retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy, que protruye hacia el vítreo. |
| 3 |
|
| 4 | Desprendimiento de
retina
Retina
The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent.
Eye: Anatomy (parcial o subtotal)
|
| 5 |
|
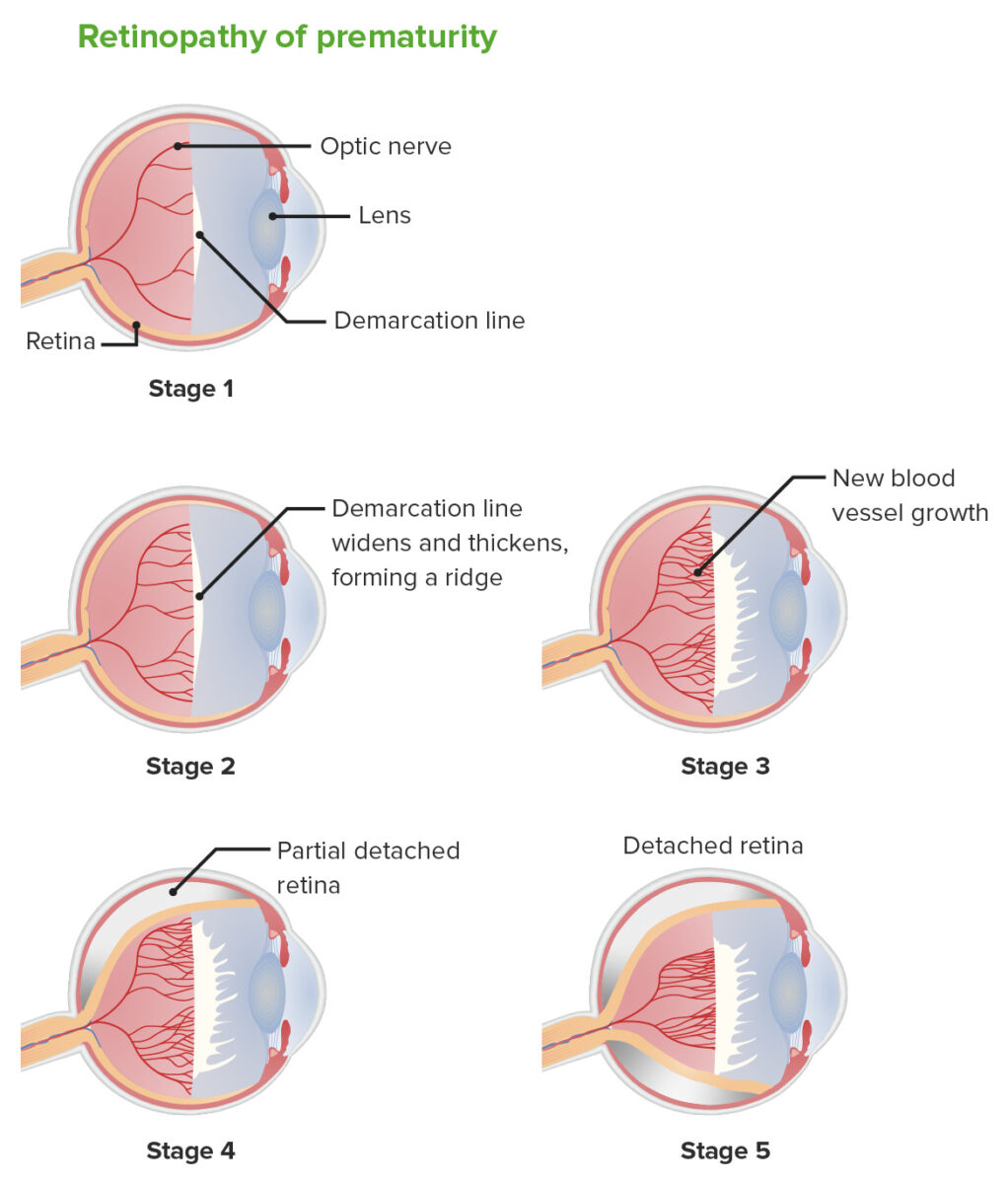
Retinopatía del prematuro: etapas
Imagen por Lecturio.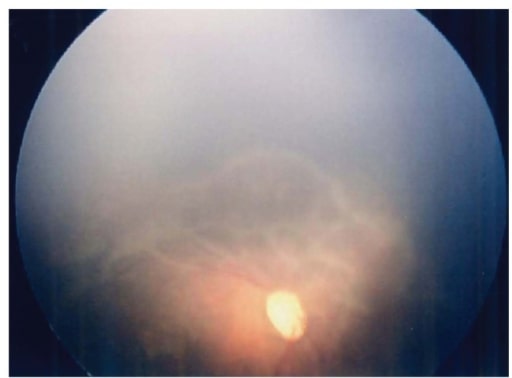
Imagen de fondo de ojo derecho a los 57 días del nacimiento. Obsérvese la retina avascular ancha con cambios traccionales marcadamente avanzados.
Imagen : “Fundus image of the right eye” por Department of Pediatrics, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine. Licencia: CC BY 3.0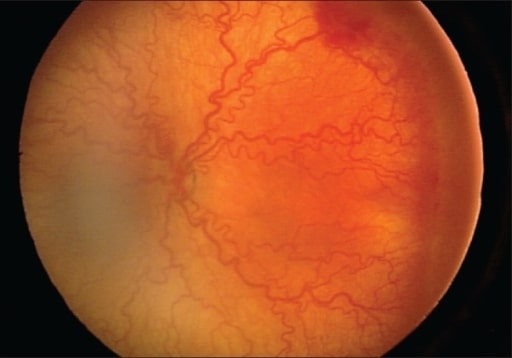
Presencia de retinopatía posterior severa y agresiva con cambios intensos positivos y mínimos en la periferia
Imagen : “Presence of severe aggressive posterior ROP” por Division of Pediatric Ophthalmology, King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Licencia: CC BY 2.0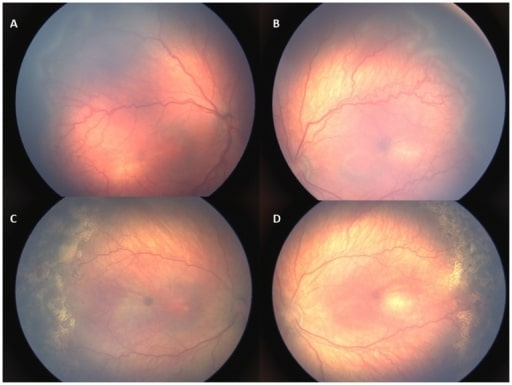
Imágenes retinales de un bebé con retinopatía tipo 1. A, B: retinopatía en estadio 3 de la zona II con enfermedad adicional antes del tratamiento. C, D: Además, la enfermedad y la retinopatía retrocedieron 1 semana después del tratamiento con láser.
Imagen : “Retinal images of an infant with type 1 ROP” por US National Library of Medicine. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Las siguientes afecciones son diagnósticos diferenciales para la ceguera en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la infancia: