La regulación epigenética es la regulación de la expresión génica que no implica alteraciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la secuencia de ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) ni en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ninguno de sus productos transcritos. Las formas más comunes de regulación epigenética son la metilación del ADN, que suprime la expresión génica, y las modificaciones de las proteínas histonas, que afectan la estructura del empaquetamiento del ADN. Las modificaciones epigenéticas son responsables de las afecciones relacionadas con la impronta, incluidos los LOS Neisseria síndromes de Prader–Willi y Angelman.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
La modificación epigenética es una modificación al AL Amyloidosis ADN o al AL Amyloidosis empaquetamiento del ADN que afecta la expresión génica sin alterar el código genético (i.e., secuencia del ADN) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sí.
Estas modificaciones:
La unidad básica del empaquetamiento del ADN es el nucleosoma. El ADN se envuelve 2¼ veces alrededor de un núcleo de 8 proteínas histonas, formando un nucleosoma.
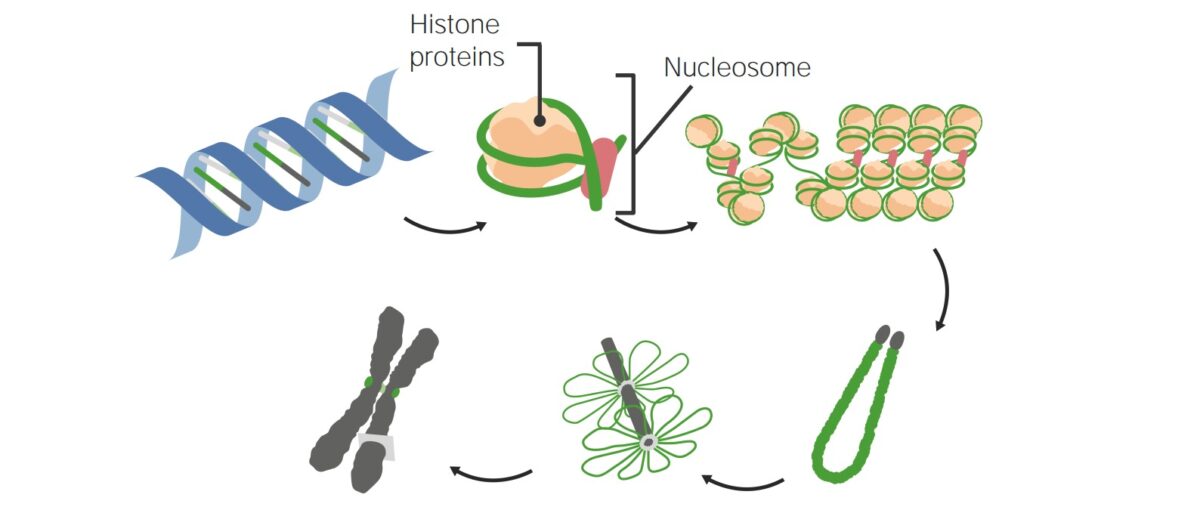
Cómo se empaqueta el ADN en los nucleosomas y luego en los cromosomas
Imagen por Lecturio.Las formas más importantes de modificación epigenética incluyen la metilación directa del ADN, modificaciones de las proteínas histonas y otras modificaciones de la cromatina.
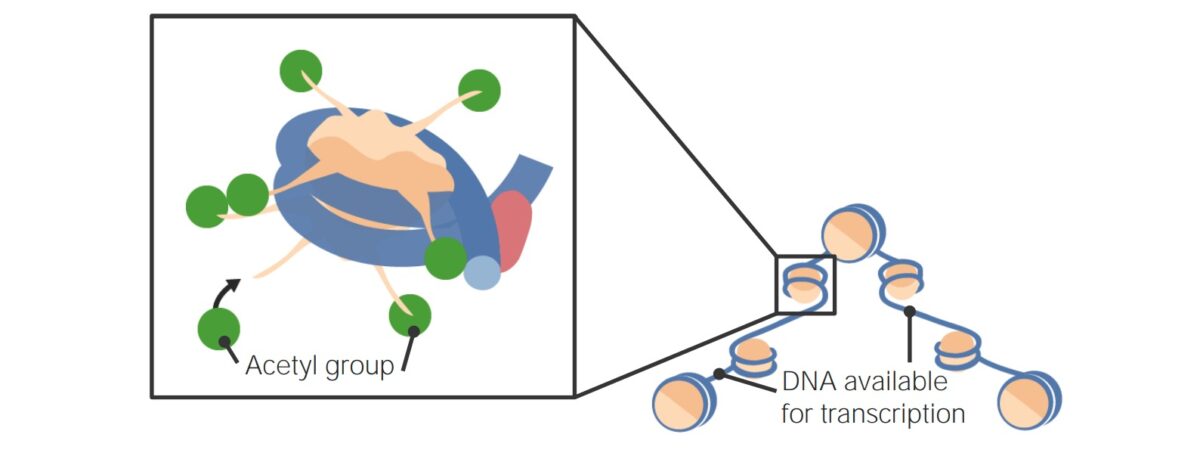
Acetilación de histonas
Imagen por Lecturio.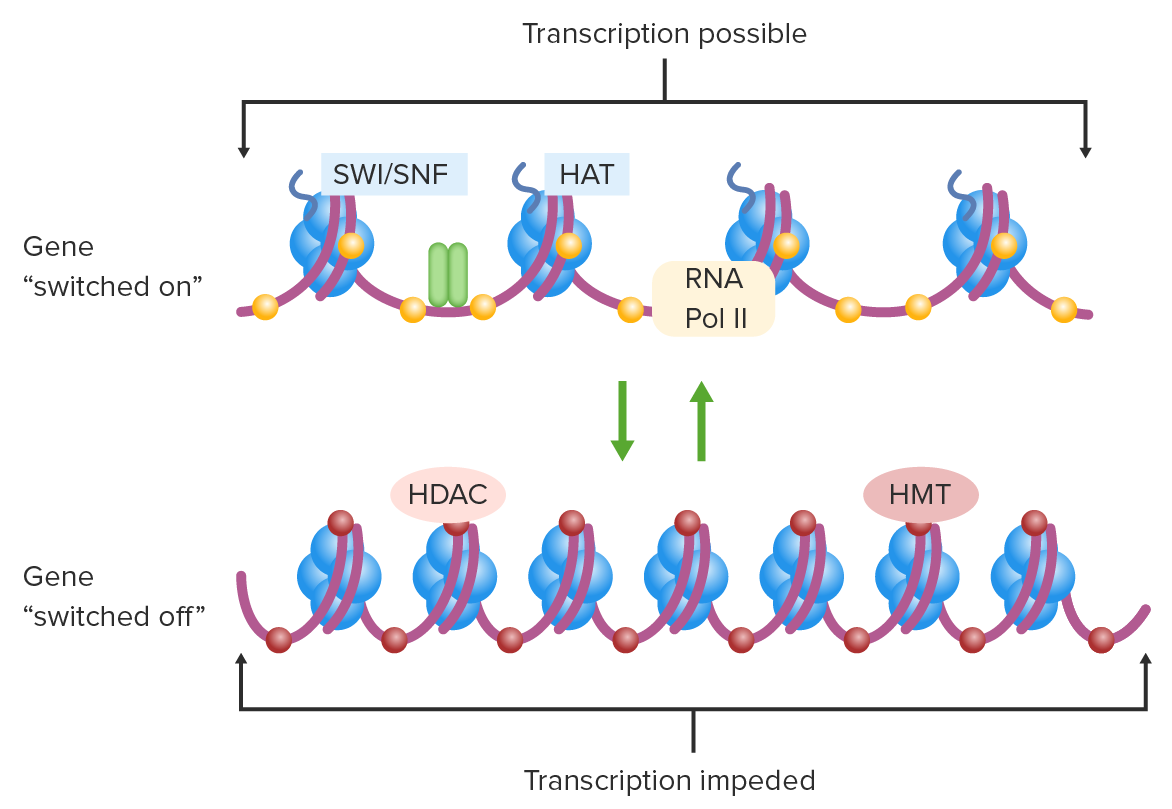
Regulación de la transcripción por modificaciones epigenéticas:
Gen activado: cromatina abierta, citosinas no metiladas, histonas acetiladas.
Gen apagado: cromatina condensada, citosinas metiladas, histonas desacetiladas.
HAT: histona acetiltransferasa
HDAC: histona desacetilasa
HMT: histona metiltransferasa
Pol II: polimerasa II
SWI/SNF: complejo switch/sacarosa no fermentable
Remodelar la cromatina y/o los LOS Neisseria nucleosomas es otra forma en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum que la célula puede regular Regular Insulin la expresión génica a nivel epigenético. La remodelación de la cromatina generalmente requiere energía. Los LOS Neisseria tipos de remodelación de la cromatina incluyen:
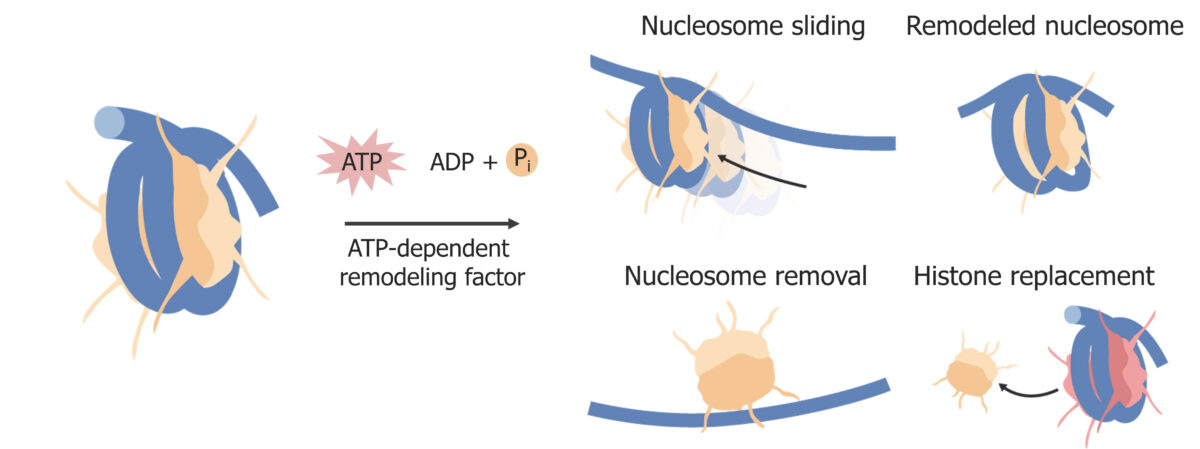
Remodelación de nucleosomas:
Ejemplos de cambios en las histonas. Los factores de remodelación de la cromatina también alteran la estructura de la cromatina. La cromatina usa energía del adenosin trifosfato (ATP, por sus siglas en inglés).
La impronta comprende las modificaciones epigenéticas específicas que ocurren en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria gametos específicos del sexo (i.e., las modificaciones ocurren solo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria espermatozoides o los LOS Neisseria óvulos).
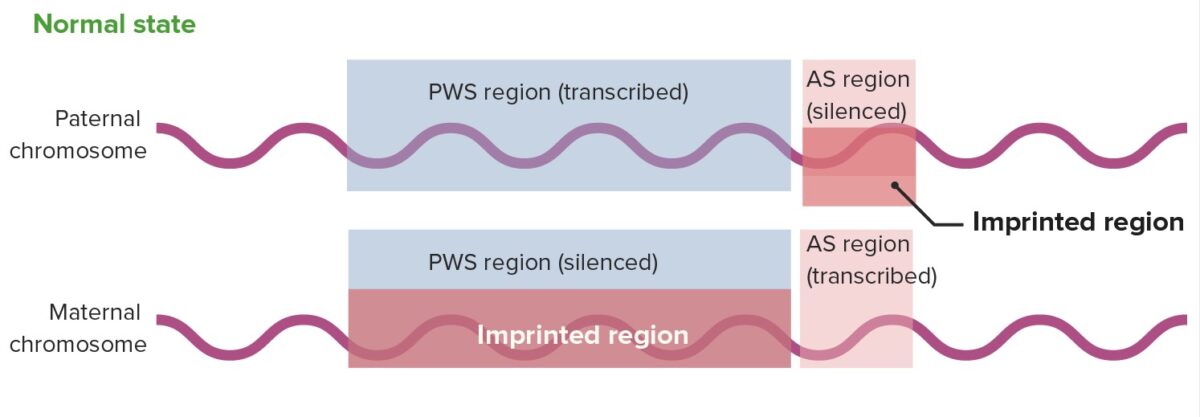
Expresión génica normal en la región 15q11-13
AS: síndrome de Angelman
PWS: síndrome de Prader–Willi
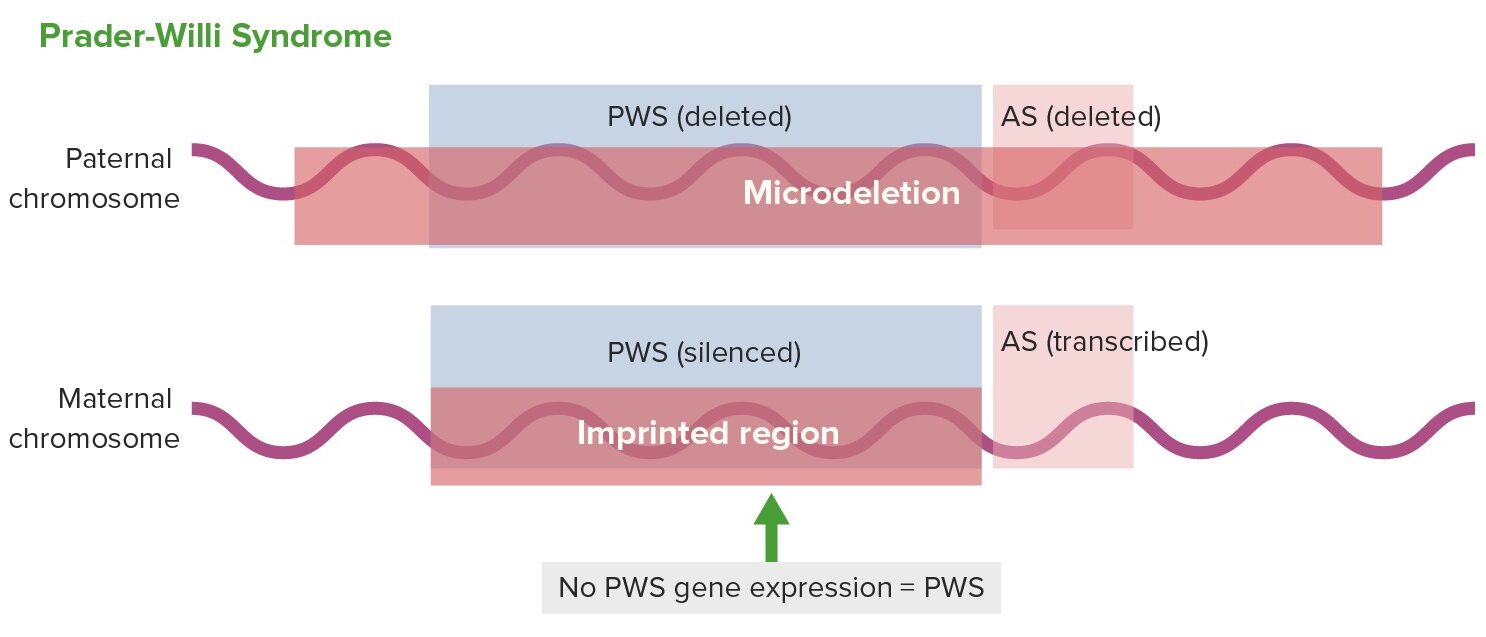
Expresión génica en el síndrome de Prader–Willi:
AS: síndrome de Angelman
PWS: síndrome de Prader–Willi
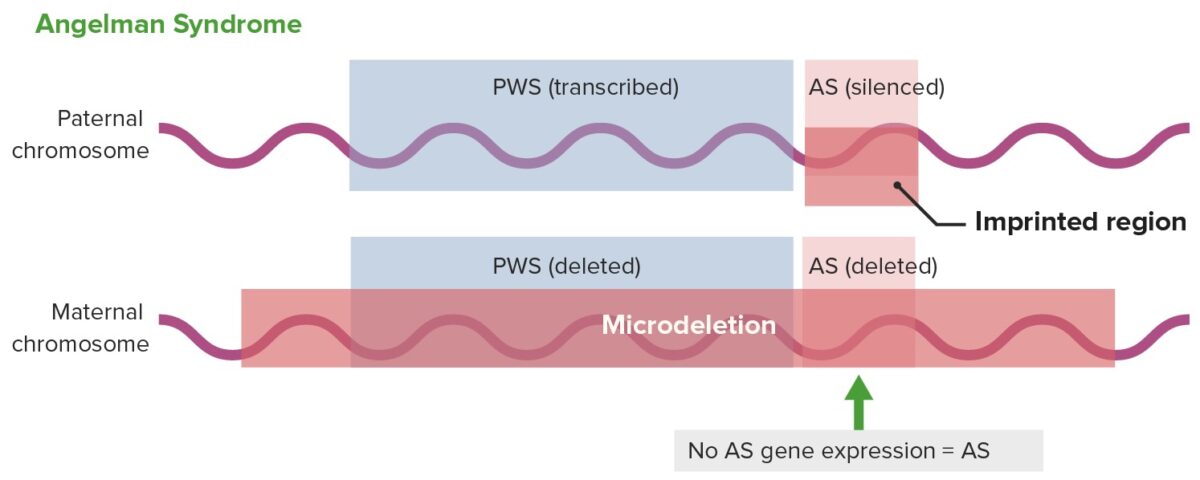
Expresión génica en el síndrome de Angelman
AS: síndrome de Angelman
PWS: síndrome de Prader–Willi