El potencial de membrana es la diferencia de carga eléctrica entre el interior y el exterior de una célula. Todas las células vivas mantienen una diferencia de potencial a través de la membrana gracias a las propiedades aislantes de sus membranas plasmáticas y al AL Amyloidosis transporte selectivo de iones a través de esta membrana por parte de los LOS Neisseria transportadores. Hay 3 tipos de potencial: potencial de membrana en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reposo, potencial de equilibrio y potencial de acción. El potencial de membrana ayuda a generar un potencial de acción, y estos potenciales de acción actúan como señales de transporte y retransmisión al AL Amyloidosis SNC y al AL Amyloidosis cerebro para realizar un movimiento o una acción específicos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Se utiliza para calcular el potencial de equilibrio a una diferencia de concentración dada de un ion permeable a través de la membrana celular.
$$ V_{eq}= \left ( RT/zF \right )ln\left ( X_{o} /X_{i}\right ) $$Veq = potencial de equilibrio para el ion X
R = constante de
los
LOS
Neisseria gases (8,314 julios por kelvin por mol)
T = temperatura
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum kelvin (K = °C + 273,15)
z = carga del ion (+1 para Na+, +2 para Ca2+, −1 para Cl−)
F = Constante de Faraday (96,485 culombios por mol)
Xi = concentración intracelular (
mM
MM
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies.
Multiple Myeloma)
Xo = concentración extracelular (
mM
MM
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies.
Multiple Myeloma)
El potencial de membrana en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reposo puede considerarse el promedio de los LOS Neisseria potenciales de equilibrio de todos los LOS Neisseria iones que entran y salen de una célula, modificado por la permeabilidad relativa de una célula a esos iones.
$$ E_{m}=\frac{RT}{F}ln\left ( \frac{P_{K}\left [ K^{+} \right ]_{out}+P_{Na}\left [ Na^{+} \right ]_{out}+P_{Cl}\left [ Cl^{-} \right ]_{in}}{P_{K}\left [ K^{+} \right ]_{in}+P_{Na}\left [ Na^{+} \right ]_{in}+P_{Cl}\left [ Cl^{-} \right ]_{out}} \right ) $$E m: el potencial de membrana (
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum voltios, equivalente a julios por culombios)
P ion: la selectividad para ese ion (
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum metros por segundo)
[ion]out: la concentración extracelular de ese ion (
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum
moles
Moles
Primary Skin Lesions por metro cúbico, para que coincida con otras unidades del Sistema Internacional)
[ion]in: la concentración intracelular de ese ion (
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum
moles
Moles
Primary Skin Lesions por metro cúbico)
R: la constante de
los
LOS
Neisseria gases ideales (julios por kelvin por mol)
T: la temperatura
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum kelvin
F: constante de Faraday (culombios por mol)
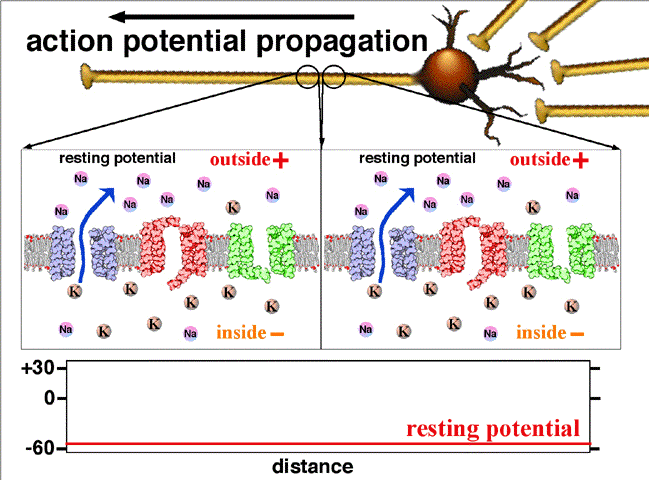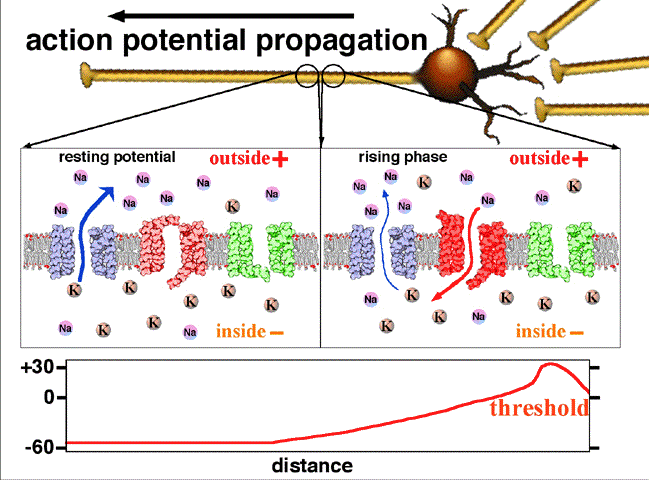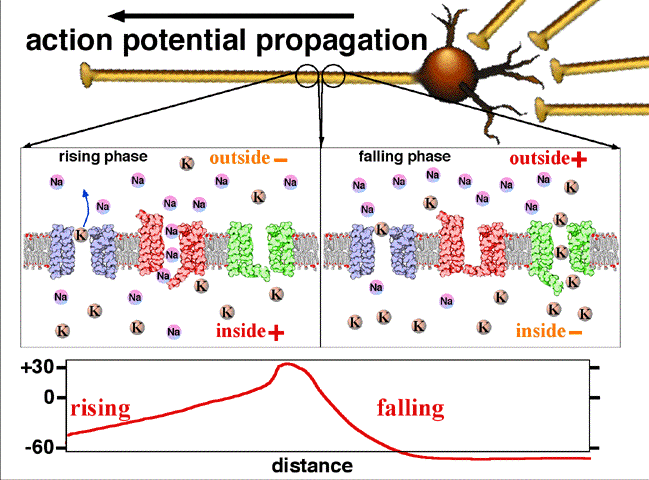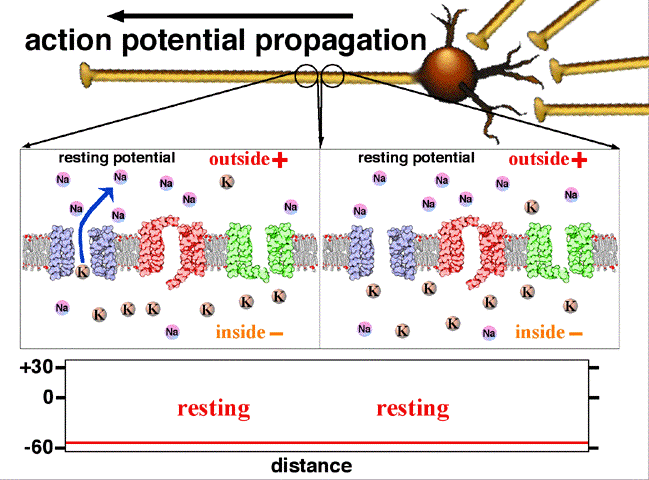
Potencial de acción nervioso
Imagen: “Action potential propagation animatio” por John Schmidt. Licencia: CC BY 4.0