Las hormonas gonadales son producidas por las gónadas humanas: los LOS Neisseria testículos y los LOS Neisseria ovarios. Las principales hormonas producidas por estos órganos son los LOS Neisseria andrógenos, los LOS Neisseria estrógenos y los LOS Neisseria progestágenos. La testosterona es el andrógeno primario y desempeña un papel fundamental en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el desarrollo de los LOS Neisseria caracteres sexuales masculinos primarios y secundarios, así como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la espermatogénesis. El estradiol Estradiol The 17-beta-isomer of estradiol, an aromatized C18 steroid with hydroxyl group at 3-beta- and 17-beta-position. Estradiol-17-beta is the most potent form of mammalian estrogenic steroids. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins y la progesterona son las principales hormonas femeninas, responsables del desarrollo de los LOS Neisseria óvulos, del ciclo menstrual y del desarrollo de las mamas. Las hormonas gonadales forman parte del eje hipotálamo-hipófisis-gonadal y están reguladas por las hormonas hipofisarias, la hormona foliculoestimulante ( FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle) y la hormona luteinizante ( LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle). A su vez, la FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle y la LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle están reguladas por la hormona liberadora de gonadotropina (GnRH) secretada por el hipotálamo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Hormonas gonadales:
Las hormonas gonadales son producidas por las gónadas humanas: los LOS Neisseria testículos y los LOS Neisseria ovarios. Estas hormonas incluyen:
Terminología de género:
Reconociendo la complejidad y la naturaleza sensible en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum torno a la terminología de género, a los LOS Neisseria efectos de este documento:
Las hormonas secretadas por las gónadas son estimuladas por el eje hipotálamo-hipófisis-testicular (HHT) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hombres y el eje hipotálamo-hipófisis-ovario (HHO) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las mujeres, y contribuyen a su regulación.
Todas las hormonas gonadales son esteroides, se producen a partir del colesterol mediante una serie de pasos enzimáticos. Los LOS Neisseria pasos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vía metabólica de las hormonas sexuales incluyen:
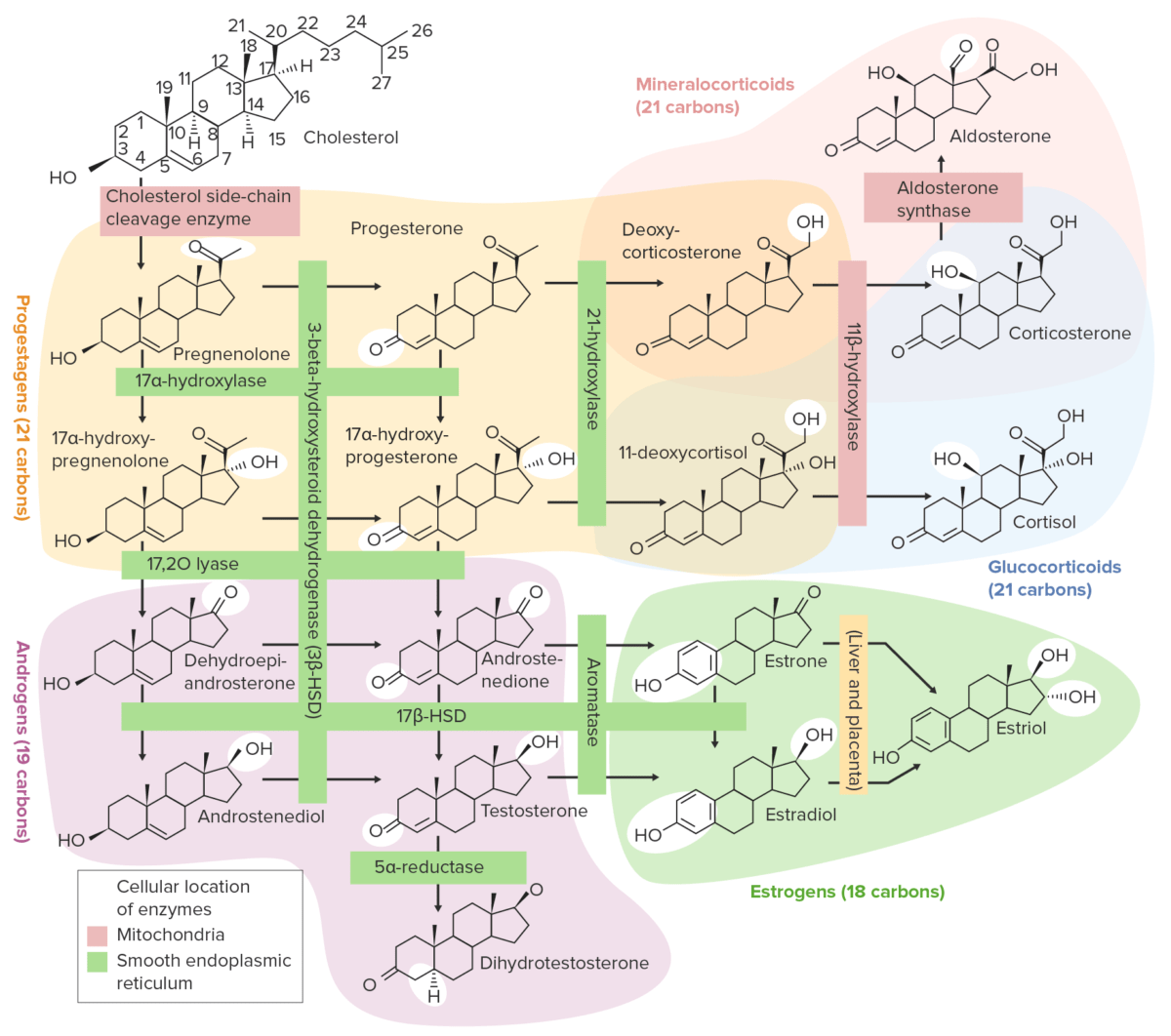
Resumen de las vías de la esteroidogénesis
HSD: Hidroxiesteroide deshidrogenasa
Derivadas del colesterol, las hormonas gonadales son lipofílicas, por lo que deben estar unidas a las proteínas para viajar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, están unidas a:
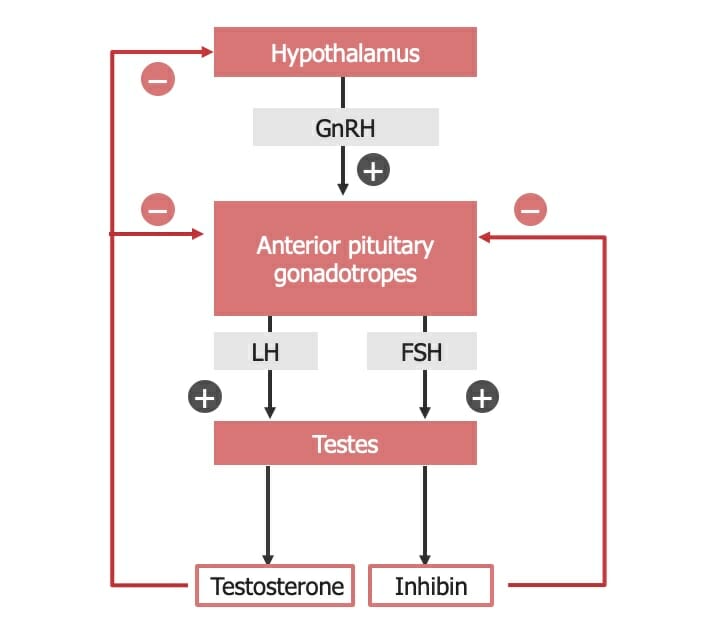
Eje hipotálamo-hipófisis-testículo
FSH: hormona estimulante del folículo
GnRH: hormona liberadora de gonadotropina
LH: hormona luteinizante
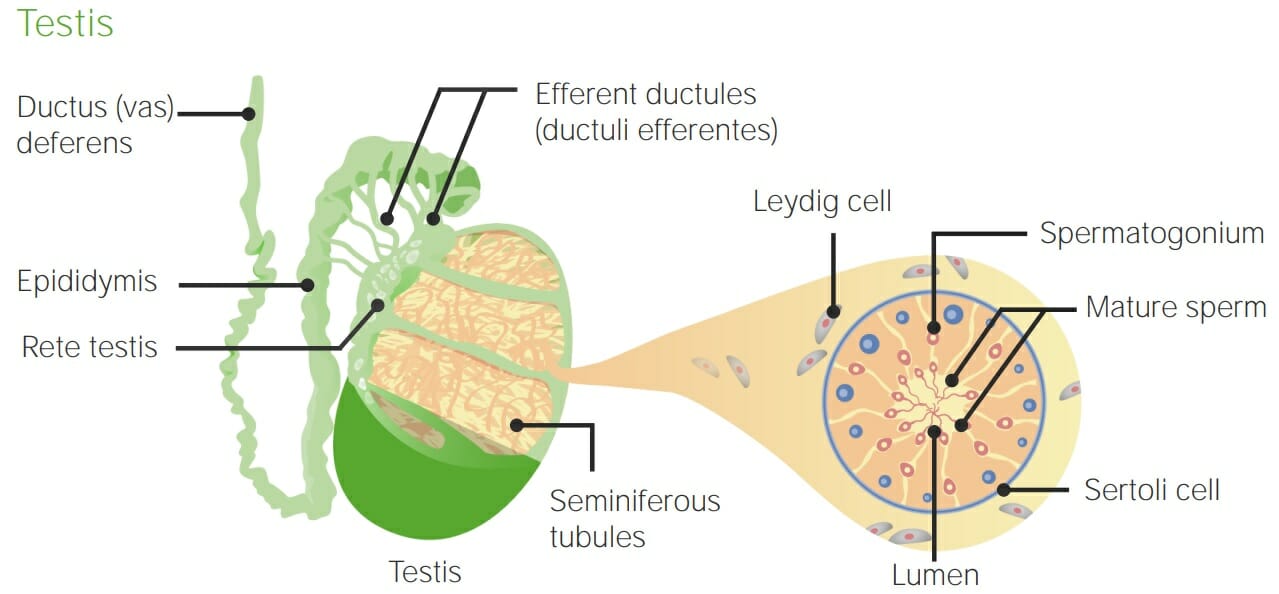
Anatomía de los testículos y los túbulos seminíferos: Obsérvese que los túbulos están formados por células de Sertoli y rodeados por células de Leydig. La espermatogénesis tiene lugar dentro de los túbulos seminíferos.
Imagen por Lecturio.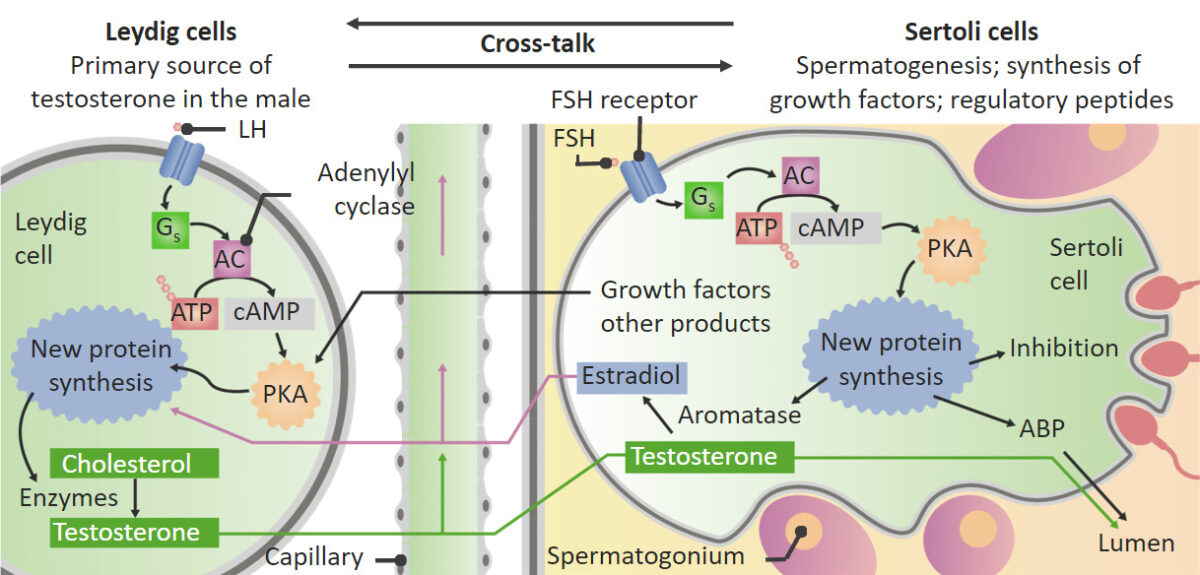
Acciones de la hormona luteinizante (LH) y de la hormona estimulante del folículo (FSH) en los testículos. Dentro de las células de Leydig, la LH estimula la conversión del colesterol en testosterona. Esta testosterona pasa a las células de Sertoli, donde ayuda a estimular la espermatogénesis. La FSH estimula las células de Sertoli para que produzcan aromatasa, factores de crecimiento y otros péptidos reguladores, además de estimular la espermatogénesis. La aromatasa convierte parte de la testosterona en estrógeno. Parte del estrógeno y de los factores de crecimiento producidos en las células de Sertoli vuelven a pasar a las células de Leydig, donde estimulan a estas para que aumenten la producción de testosterona.
ABP: proteína de unión a andrógenos
PKA: proteína kinasa A
La testosterona, y otros andrógenos, son responsables del desarrollo de las características sexuales masculinas primarias y secundarias.
La secreción de testosterona varía a lo largo de la vida masculina:
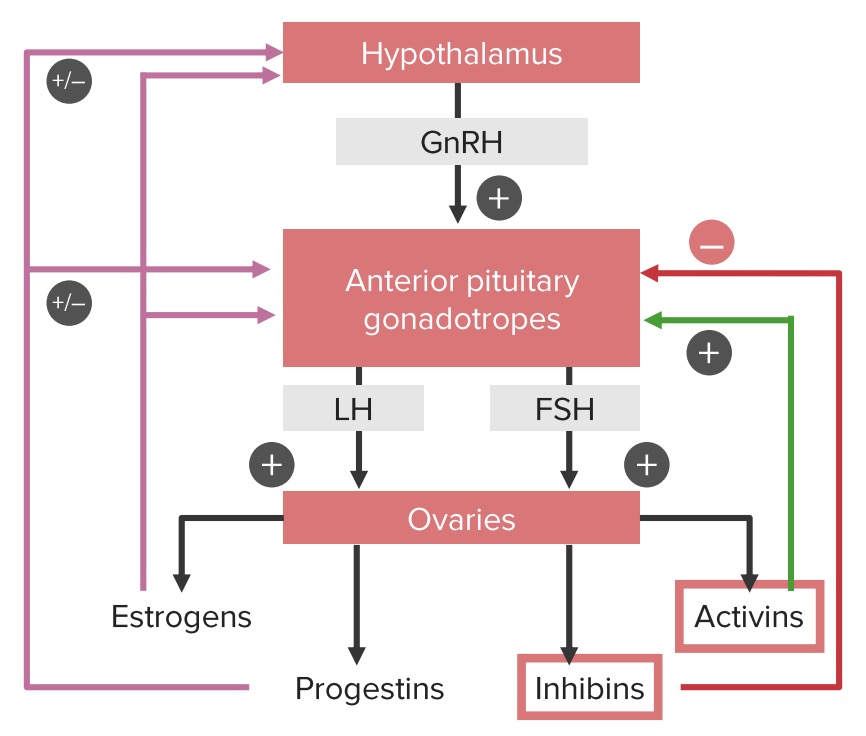
Circuitos de retroalimentación positiva y negativa del eje hipotálamo-hipófisis-ovario:
Hay que tener en cuenta que los estrógenos y los progestágenos pueden tener una influencia tanto positiva como negativa sobre el hipotálamo y la hipófisis, dependiendo de la fase del ciclo. Los estrógenos proporcionan una retroalimentación negativa hasta la mitad del ciclo. En ese momento, los estrógenos comienzan a estimular las células gonadotrópicas de la hipófisis, lo que provoca el aumento de la hormona luteinizante (LH), que desencadena la ovulación.
FSH: hormona foliculoestimulante
GnRH: hormona liberadora de gonadotropina
La GnRH se libera de forma pulsátil, siguiendo múltiples ritmos biológicos:
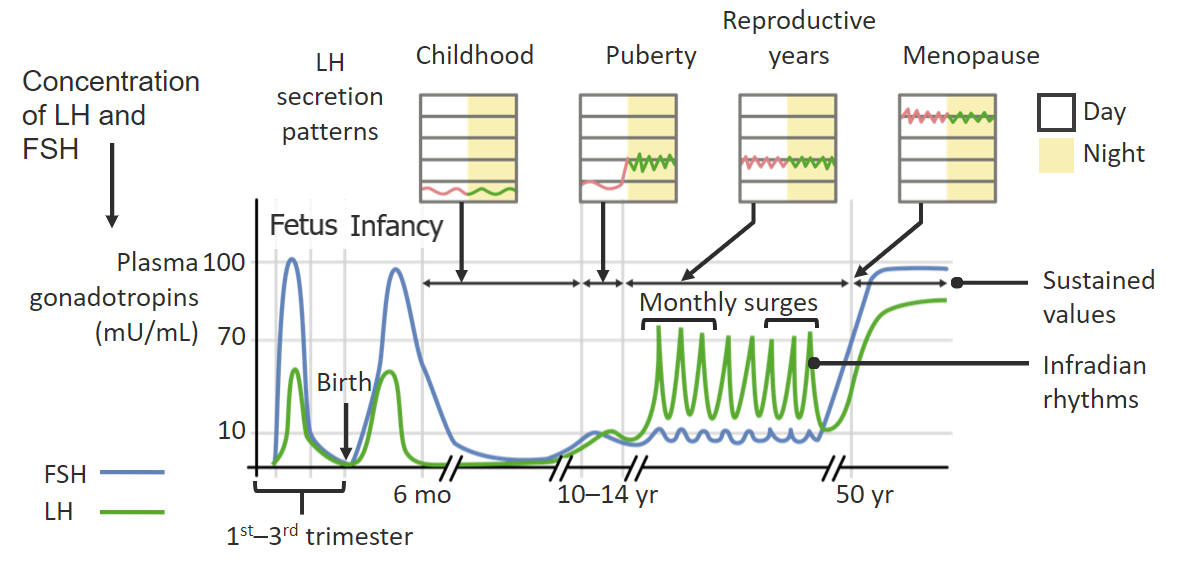
Cambios en la secreción pulsátil de la hormona folículo-estimulante (FSH) y la hormona luteinizante (LH) a lo largo del día y de la vida de la mujer:
La liberación pulsátil de FSH y LH desde la hipófisis se produce en respuesta a la liberación pulsátil de la hormona liberadora de gonadotropina (GnRH) desde el hipotálamo.
Revisión de la vía metabólica de las hormonas sexuales: colesterol → pregnenolona → progesterona → 17α-OHP → androstenediona → testosterona o E1 E1 An aromatized C18 steroid with a 3-hydroxyl group and a 17-ketone, a major mammalian estrogen. It is converted from androstenedione directly, or from testosterone via estradiol. In humans, it is produced primarily by the cyclic ovaries, placenta, and the adipose tissue of men and postmenopausal women. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins → E2
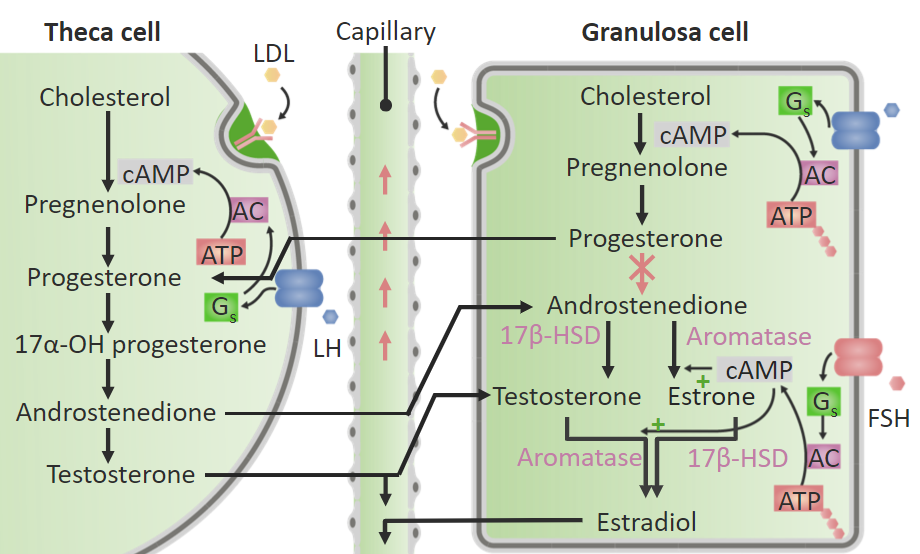
Síntesis de estrógenos y testosterona en el ovario. En las células de la teca y de la granulosa están presentes diferentes enzimas. Las células de la teca contienen las enzimas necesarias para convertir el colesterol en testosterona; sin embargo, carecen de aromatasa, necesaria para convertir los andrógenos en estrógenos. Por lo tanto, los andrógenos (androstenediona y testosterona) pasan de las células de la teca a las células de la granulosa, que sí contienen aromatasa. Dentro de las células de la granulosa, la aromatasa convierte la testosterona en estradiol (E2) y la androstenediona en estrona (E1). Las células de la granulosa carecen de la enzima necesaria para convertir la progesterona en androstenediona, por lo que las células de la granulosa producen tanto progesterona como estrógenos.
AC: adenilil ciclasa
17β-HSD: 17β-hidroxiesteroide deshidrogenasa
Los LOS Neisseria estrógenos desempeñan un papel importante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el desarrollo sexual de las mujeres y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ciclo menstrual; sin embargo, también existen numerosas funciones no reproductivas de los LOS Neisseria estrógenos.
La progesterona es producida principalmente por el cuerpo lúteo después de la ovulación.
| Hombre | Mujer | |
|---|---|---|
| Gónada | Testículos | Ovarios |
| Células germinales | Espermatozoides | Óvulos |
| Recubrimiento | Túbulo seminífero | Folículo |
| Células adyacentes | Células de Sertoli | Células de la granulosa |
| Productos de células adyacentes |
|
|
| Intersticio | Células de Leydig | Células de la teca |
| Productos intersticiales | Testosterona |
|
| Sistema de órganos | Estrógenos | Andrógenos |
|---|---|---|
| Órganos reproductores |
|
|
| Efectos dermatológicos ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todas las personas) | Engrosamiento leve de la piel |
|
| Efectos músculo-esqueléticos |
|
|
| Otros efectos |
|
|