Las hernias diafragmáticas congénitas son defectos embrionarios del diafragma a través de los LOS Neisseria cuales las estructuras abdominales pueden pasar a la cavidad torácica. La presencia de intestinos y órganos intraabdominales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tórax interfiere en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el desarrollo embrionario de los LOS Neisseria pulmones, que es la principal causa de patología postnatal. El diagnóstico prenatal suele realizarse mediante un ultrasonido durante el embarazo, seguido de una confirmación con radiografía de tórax después del nacimiento. Se requiere una reanimación respiratoria inmediata al AL Amyloidosis nacer con intubación endotraqueal y ventilación mecánica. La reparación quirúrgica es la única opción curativa. El pronóstico varía, pero los LOS Neisseria niños con hernias diafragmáticas generalmente sufren complicaciones pulmonares de por vida.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Se han propuesto múltiples mecanismos embriológicos:
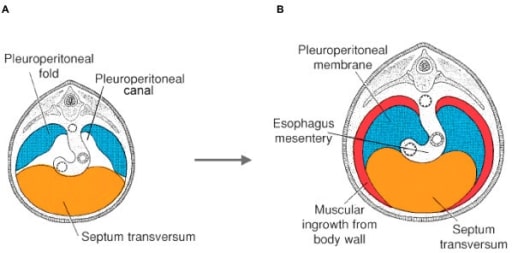
Desarrollo embriológico de la morfogénesis del diafragma representado a las 5 semanas (A) y 4 meses (B) de la gestación.
El diafragma se describe como un elemento que surge del septum transversum, los pliegues pleuroperitoneales, el mesenterio esofágico y la pared del cuerpo torácico.
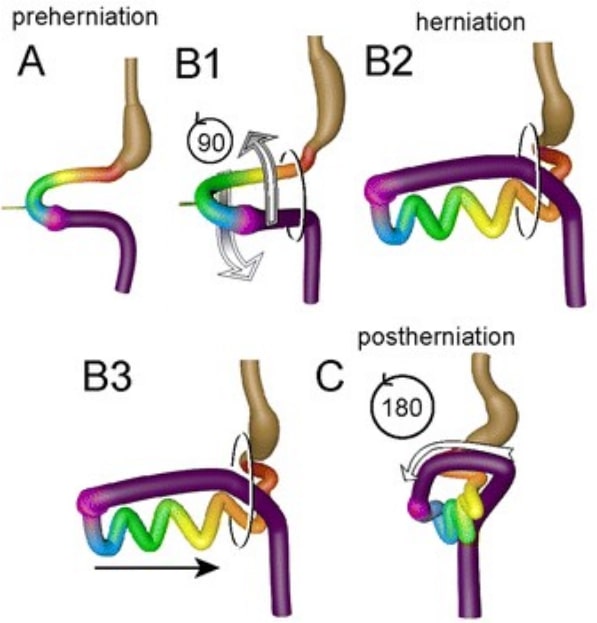
Diagrama que muestra la rotación intestinal y la herniación durante el desarrollo embrionario normal. Del panel A al B, el asa del intestino medio rota 90° en sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj, de modo que su posición cambia de mediosagital (A) a transversal (B1).
El intestino delgado forma asas (B2) y se desliza hacia el abdomen (B3) durante la resolución de la hernia. Mientras tanto, el ciego se desplaza del lado izquierdo al derecho, lo que representa la rotación adicional de 180° en sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj del intestino (C, vista central).
Clasificación de las hernias diafragmáticas congénitas basada en la localización de las hernias diafragmáticas.
El tipo más común es la hernia posterolateral (aproximadamente el 90%), también conocida como hernia de Bochdalek. La mayoría de estas hernias se producen en el lado izquierdo (85%).
Otros tipos de hernias son las hernia de Morgagni o de defecto anterior (2%–6%), seguido de la rara hernia central (2%).
A: Anatomía normal
B: Pre-estadio
C: Hernia hiatal deslizante
D: Hernia hiatal paraesofágica
Los LOS Neisseria efectos patológicos de la hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias diafragmática congénita se deben a hipoplasia pulmonar:
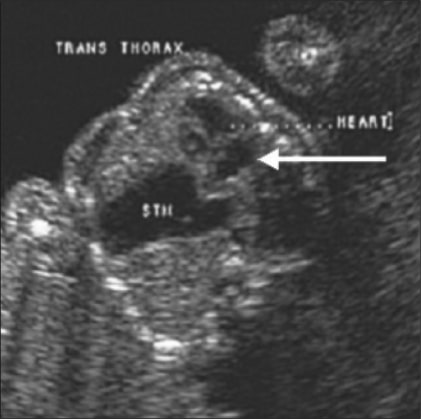
Ultrasonido: Hernia diafragmática congénita. El corazón (flecha) es empujado hacia la derecha dentro del tórax y el estómago (STM) se observa en el tórax.
Imagen: “Congenital diaphragmatic hernia” por US National Library of Medicine. Licencia: CC BY 2.0
Radiografía de tórax que muestra una hernia diafragmática izquierda y un desplazamiento contralateral del corazón y del mediastino
Imagen: “Chest radiograph” por Alberta Children’s Hospital, Calgary, AB, Canada T3B 6A8. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
TC axial del tórax: Las asas del intestino grueso llenas de gas son visibles detrás del corazón, situadas en la parte anterior de la columna vertebral y la aorta.
Imagen: “Axial CT scan of the chest” por Department of Anatomical, Histological, Forensic and Locomotor System Sciences, V, A, Borelli 50, Rome, 00161, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0
Tomografía computarizada de tórax. Reconstrucción coronal. Parte del estómago, adyacente al corazón (A), es claramente visible. Algunas asas intestinales (B) también son visibles en el lado izquierdo del tórax: el pulmón izquierdo está desplazado y comprimido.
Imagen: “Computed tomography scan of the chest” por 2013 Bianchi et al., BioMed Central Ltd. Licencia: CC BY 2.0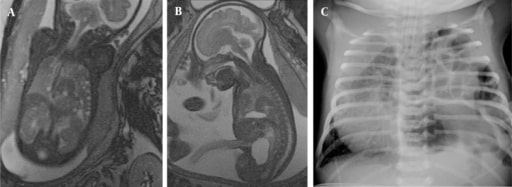
Hernia diafragmática congénita en un feto de 35 semanas de gestación, incluyendo intestinos y bazo en imágenes coronales (A) y sagitales (B), y radiografía de tórax postnatal (C)
Imagen: “Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in the 35th GW fetus” por Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Acibadem University, Istanbul, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
A: Radiografía simple del tórax de un recién nacido con hernia diafragmática congénita. Hay asas intestinales en el hemitórax izquierdo, el mediastino está desplazado hacia el lado contralateral y el espacio ocupado por el pulmón está reducido.
B y C: En la laparotomía se descubrió una hernia diafragmática posterolateral izquierda.
En B, se pueden ver las asas del intestino delgado entrando en el tórax a través del orificio.
En C, esto se ve después de reducir el contenido de la hernia.
D: El paciente falleció de hipertensión pulmonar severa persistente días después. En la autopsia se descubrió una hipoplasia pulmonar izquierda extrema y una hipoplasia pulmonar derecha menos grave.
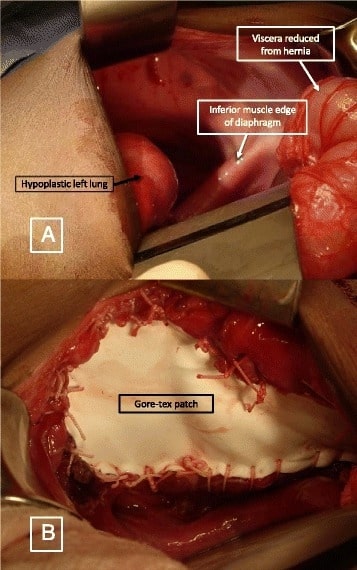
A: Hernia diafragmática del lado izquierdo que muestra el pulmón izquierdo hipoplásico, el borde muscular inferior del diafragma y las vísceras reducidas
B: Parche protésico (parche Gore-Tex) utilizado para cerrar el defecto
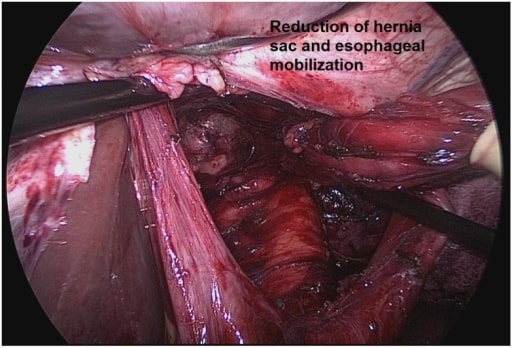
Reparación de la hernia paraesofágica: escisión completa del saco y movilización de un segmento adecuado del esófago intraabdominal
Imagen: “Complete sac excision” por Department of Surgery, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston VA Health Care System, Boston, MA, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0