Tanto la gastrulación como la neurulación son eventos críticos que ocurren durante la 3ra semana de desarrollo embrionario. La gastrulación es el proceso por el cual el disco bilaminar se diferencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un disco trilaminar, formado por las 3 capas germinales primarias: el ectodermo, mesodermo y endodermo. Durante este proceso, se forma una estructura llamada notocorda en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la línea media de la capa mesodérmica; la notocorda es fundamental para inducir la neurulación. La neurulación es el proceso por el cual parte del ectodermo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el embrión trilaminar se convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tubo neural y las células de la cresta neural, que pasarán a formar todo el tejido neural del cuerpo. Este proceso se completa al AL Amyloidosis final de la 3ra semana.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Progresión del desarrollo humano temprano desde la fecundación hasta la etapa de blastocisto:
Durante estas etapas, el embrión está rodeado por una capa de matriz extracelular conocida como zona pelúcida.

Desarrollo del disco bilaminar cuando el embrión invade la pared uterina:
A medida que las células del citotrofoblasto se dividen, las células del lado uterino comienzan a perder sus membranas, liberando enzimas hidrolíticas y permitiendo que el embrión “digiera” parte del revestimiento uterino para facilitar la implantación. Estos “núcleos libres” son las células sincitiotrofoblasto.
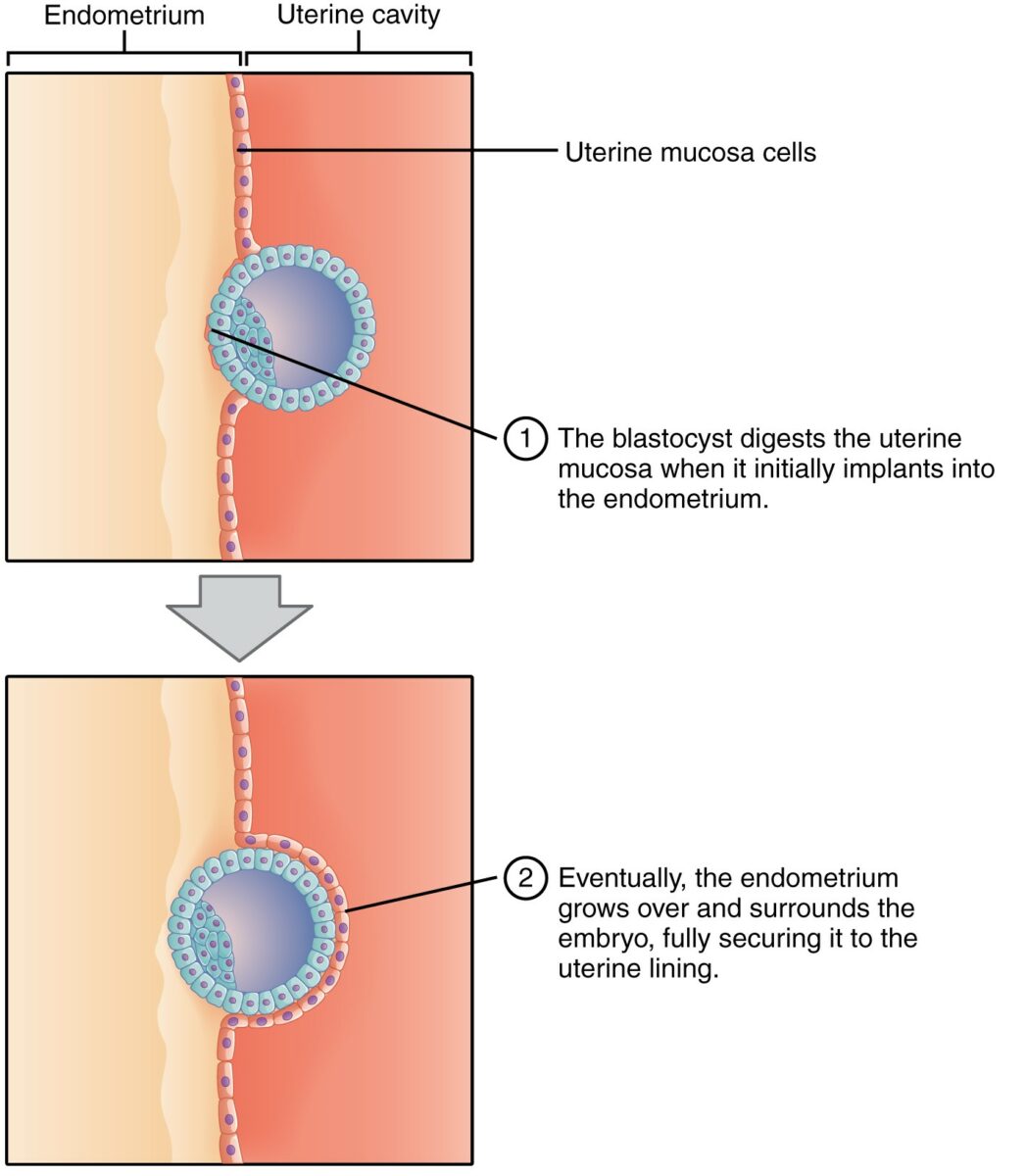
Implantación del blastocisto:
En esta etapa, el embrión existe como una masa celular externa y una masa celular interna. Observe cómo, a medida que el blastocisto digiere la pared uterina, una capa de endometrio (células rosadas) crece y rodea al embrión, asegurándolo al revestimiento uterino.
Imagen: “Implantation” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, recortado por Lecturio.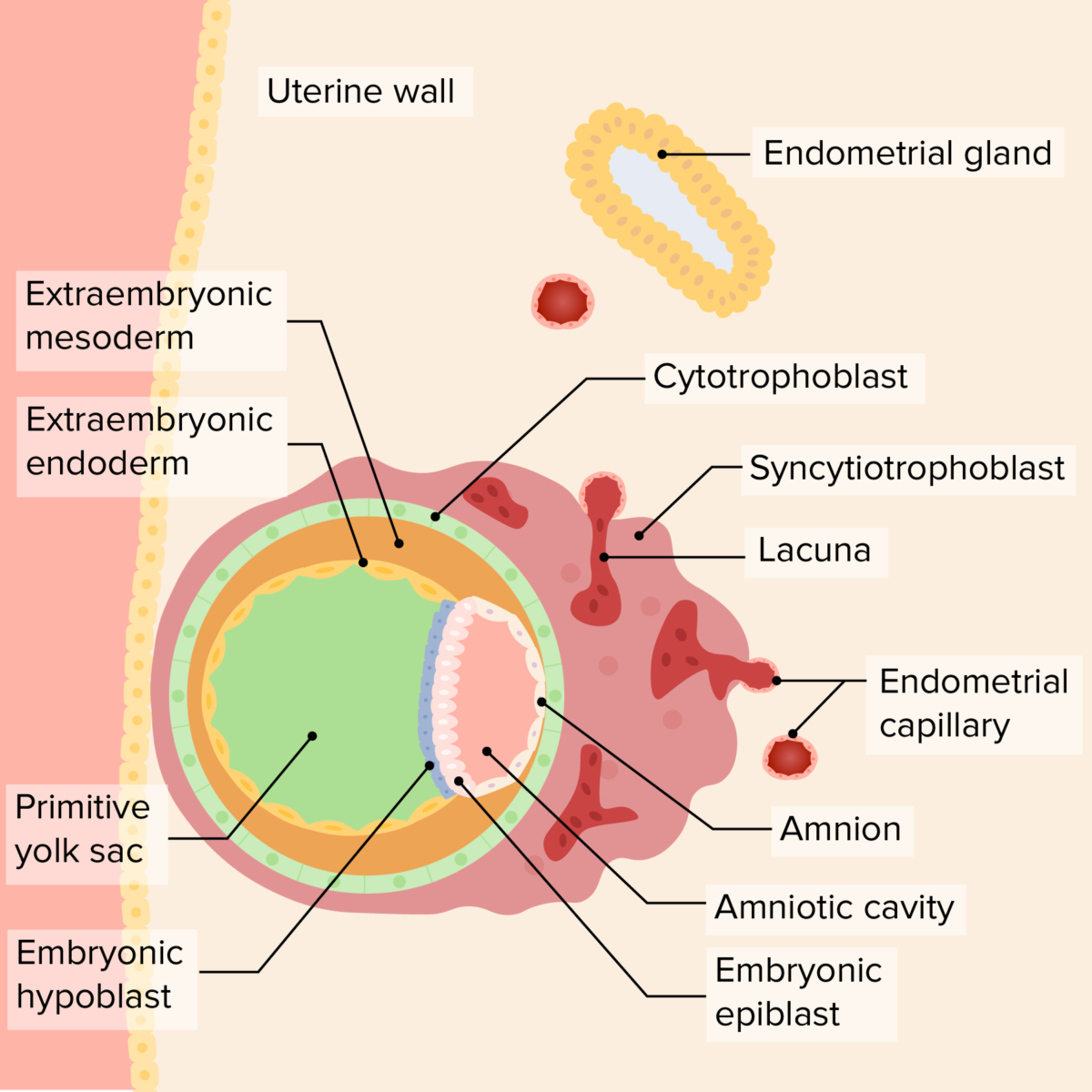
Relación del disco bilaminar, el saco vitelino y la cavidad amniótica en el embrión temprano:
A medida que el embrión invade más, el revestimiento endometrial cubre al embrión, asegurándolo a la pared uterina. El saco vitelino primario se desarrolla “debajo” del hipoblasto, mientras que la cavidad amniótica comienza a crecer “por encima” del epiblasto. El sincitiotrofoblasto rodea los capilares endometriales, que se rompen, formando una laguna, que finalmente se convertirá en el componente materno de la placenta. Una capa de mesodermo extraembrionario crece fuera del saco vitelino y de la cavidad amniótica; finalmente, la cavidad coriónica se desarrollará en esta área.
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0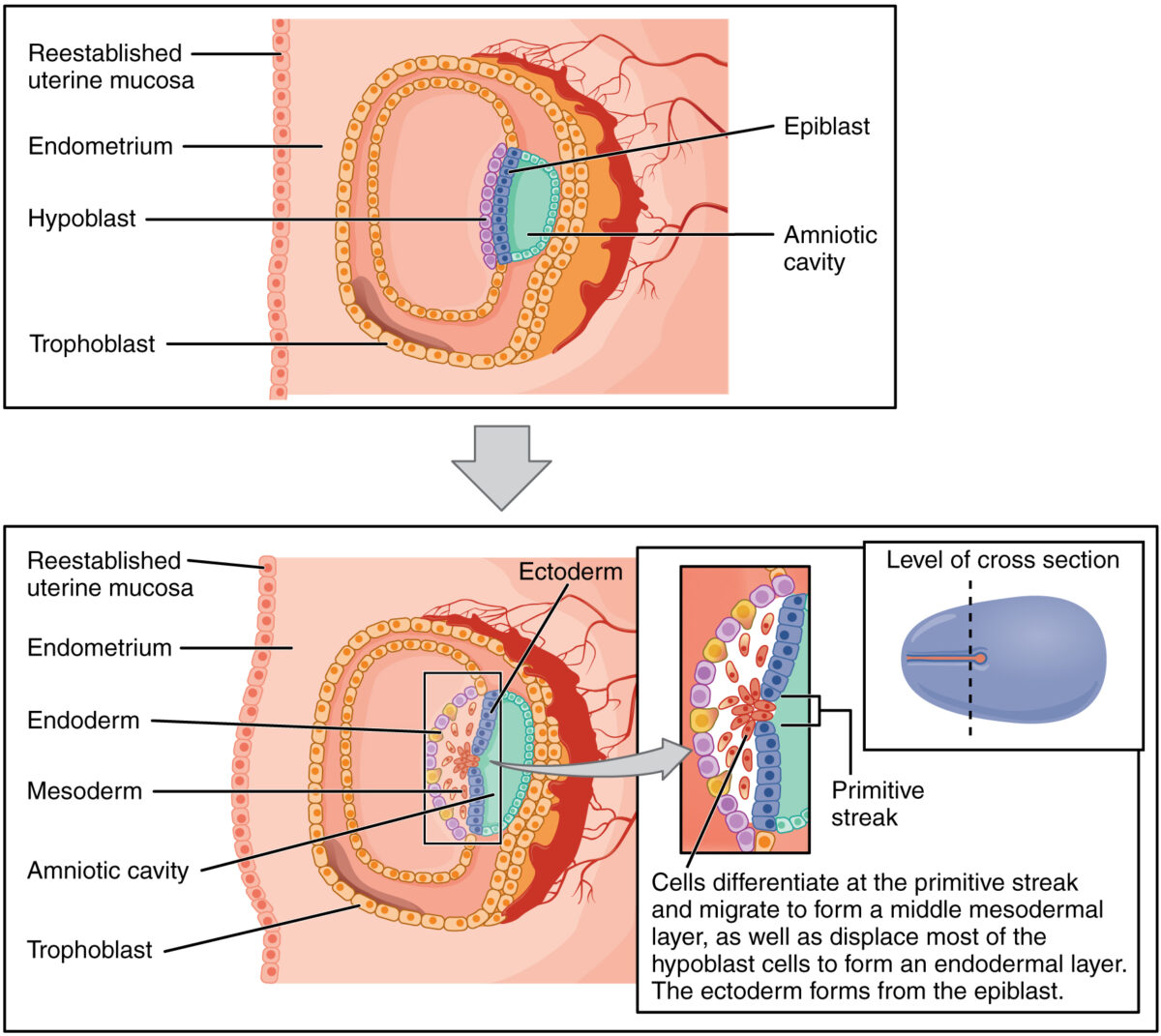
Proceso de gastrulación:
Las células del epiblasto migran hacia abajo a través de la línea primitiva y desplazan a la mayoría de las células hipoblásticas, convirtiéndose en el endodermo. Las células que quedan en el medio se convierten en mesodermo. Las células que permanecen en la capa del epiblasto se convierten en ectodermo.
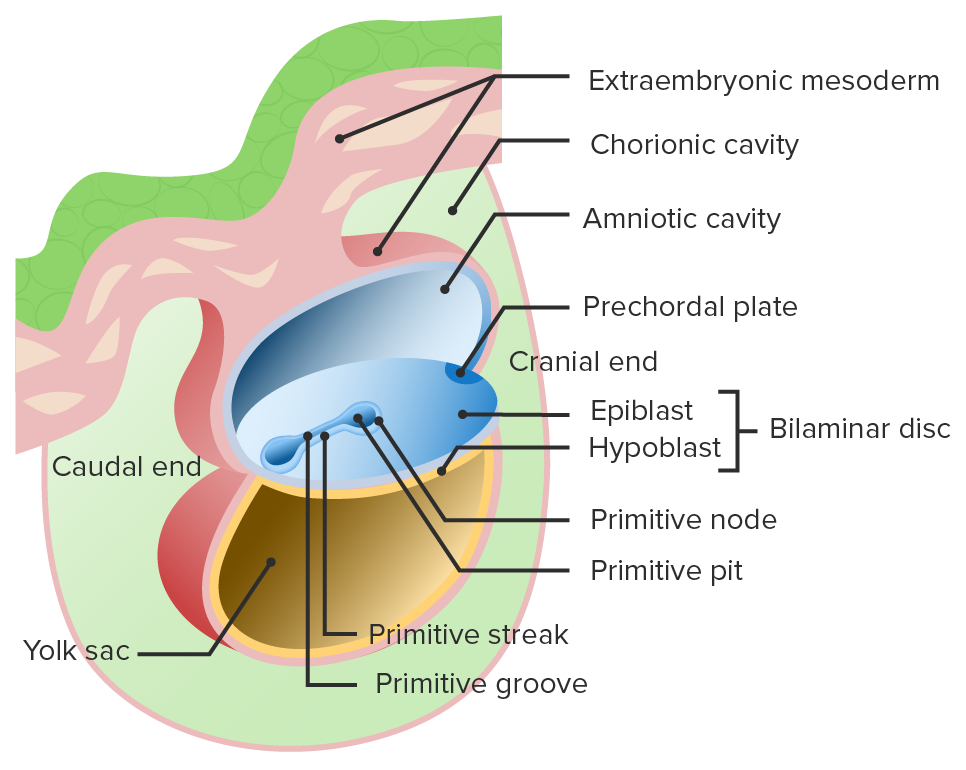
Inicio de la gastrulación:
La línea primitiva y el surco primitivo se forman en el disco bilaminar.
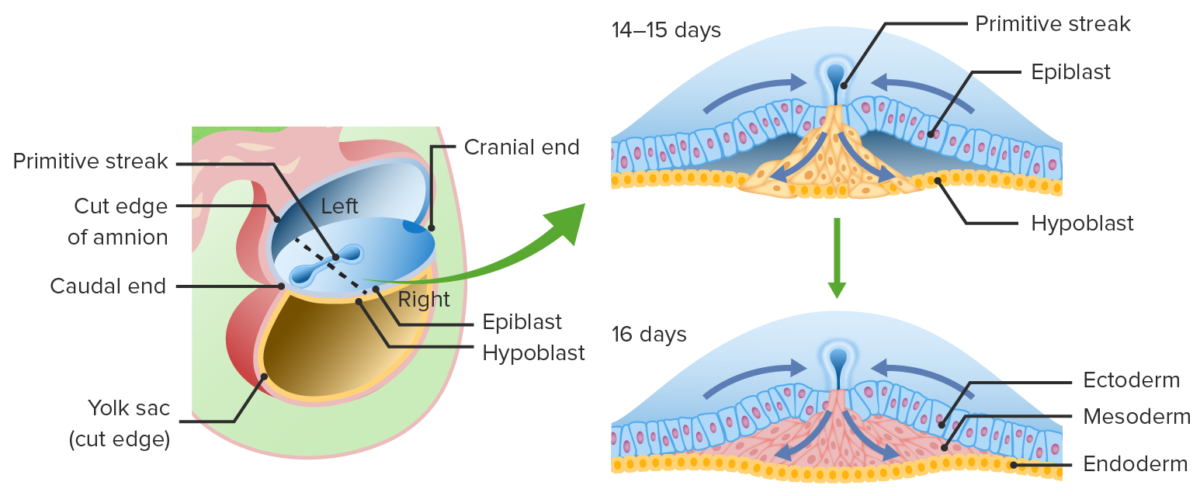
Migración de las células del epiblasto a través del surco primitivo:
Estas células del epiblasto desplazan al hipoblasto para convertirse en el endodermo y crear una capa intermedia conocida como mesodermo. Las células del epiblasto que permanecen en la superficie dorsal se diferencian en ectodermo.
La neurulación es el proceso por el cual el ectodermo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el embrión trilaminar se diferencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tubo neural. A partir de la 3ra semana, un grupo de células ectodérmicas progresa a través de las siguientes estructuras:
El desarrollo requiere folato; deficiencia de folato → defectos del tubo neural
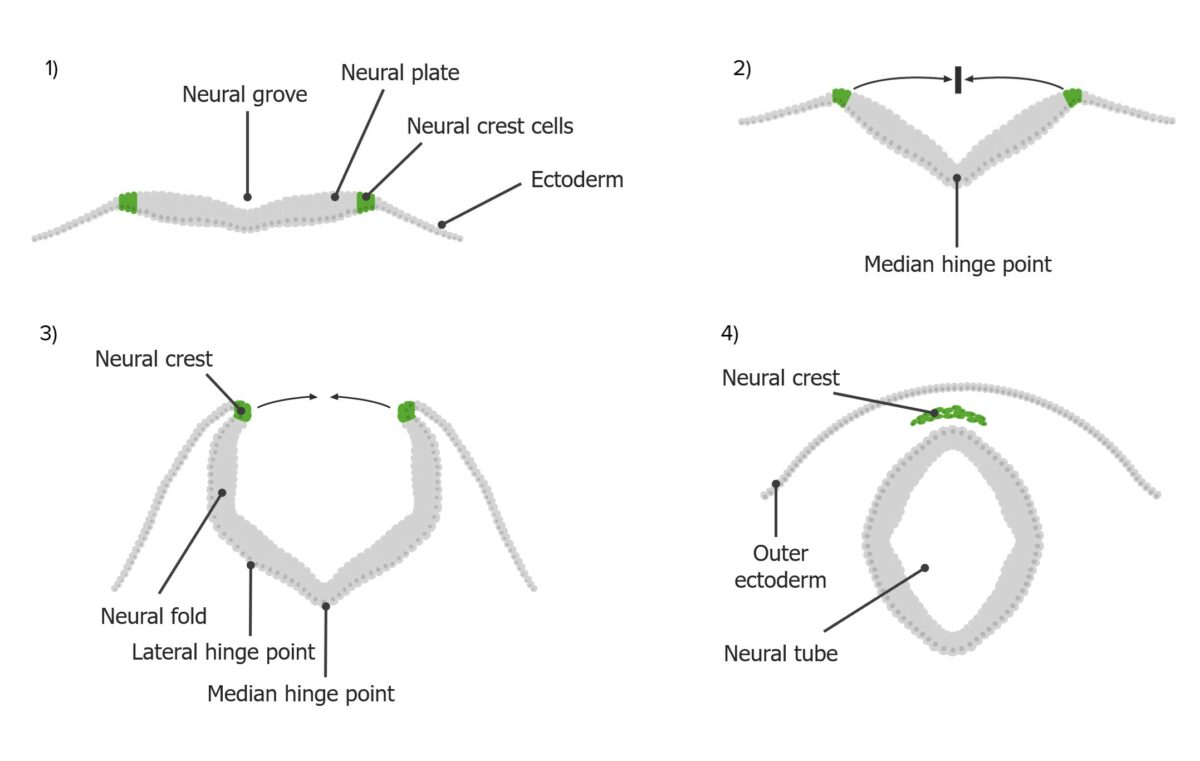
El proceso de neurulación:
Las células de la cresta neural (verde) se derivan de la placa neural (gris), que se pliega hacia arriba y hacia adentro hacia la línea media para crear el tubo neural.
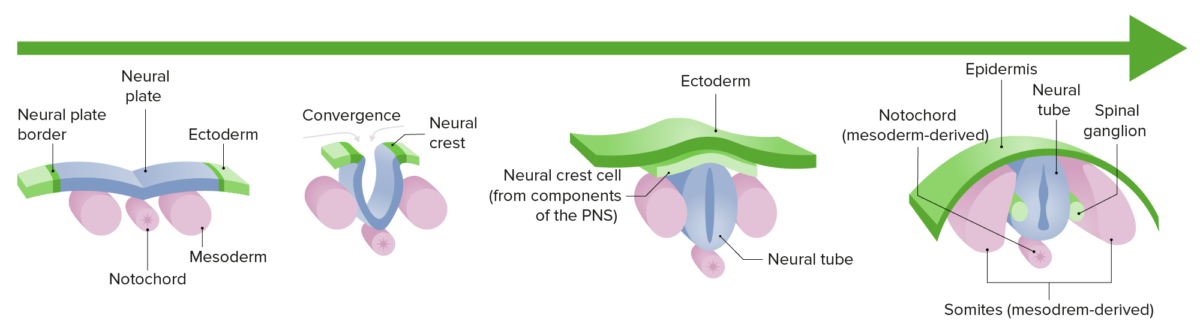
Neurulación:
Diferenciación y crecimiento de la placa neural hacia el tubo neural durante el 1er trimestre de gestación
Aborto espontáneo (aborto): las anomalías de la gastrulación suelen dar lugar a múltiples anomalías congénitas. Estos embriones suelen ser incompatibles con la vida y el resultado es una pérdida espontánea del embarazo, generalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el 1er trimestre.
Defectos del tubo neural: causados por la falla del tubo neural para cerrarse correctamente durante el desarrollo embrionario, lo que puede resultar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una protrusión del tejido neural. Los LOS Neisseria defectos del tubo neural pueden involucrar la médula espinal y/o el cráneo y pueden ser abiertos (involucrando las meninges Meninges The brain and the spinal cord are enveloped by 3 overlapping layers of connective tissue called the meninges. The layers are, from the most external layer to the most internal layer, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Between these layers are 3 potential spaces called the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. Meninges: Anatomy y/o tejido neural) o cerrados (involucrando la columna vertebral ósea). Es común el diagnóstico prenatal mediante ultrasonido y nivel de α-fetoproteína materna. El tratamiento de los LOS Neisseria defectos del tubo neural abiertos es principalmente quirúrgico.