Las fracturas de Le Fort son un grupo de patrones de fracturas de la región facial medialque se clasifican en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 tipos: Le Fort I Le Fort I Le Fort Fractures, II y III. Las fracturas de Le Fort representan entre el 10%–20% de todas las fracturas faciales y pueden ser causadas por cualquier traumatismo contuso significativo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara, más comúnmente por accidentes automovilísticos. La presentación clínica incluye sangrado facial severo, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema y movilidad de diferentes segmentos óseos, según el tipo de fractura del que se trate. El diagnóstico es clínico y se apoya en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las técnicas de imagenología. El tratamiento inicial se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la estabilización del paciente y el control del sangrado. El tratamiento definitivo es quirúrgico. El tratamiento a largo plazo es la preservación y rehabilitación de la función facial.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
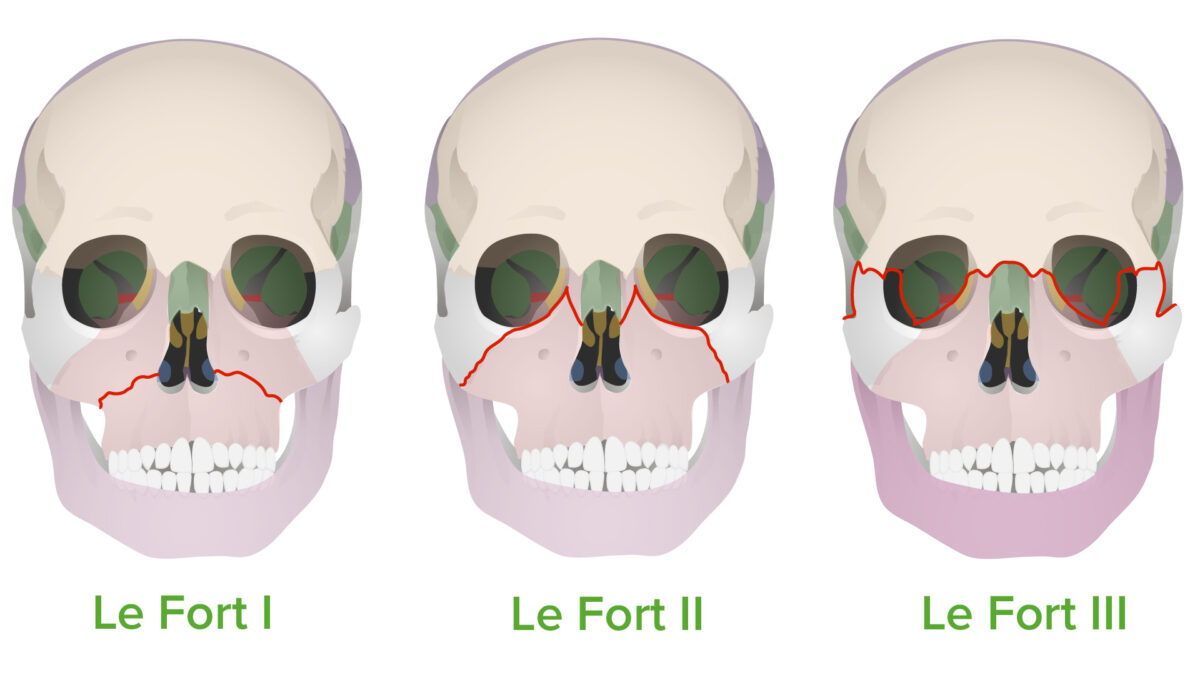
Tipos de fracturas de Le Fort:
Estas fracturas siguen las “líneas de debilidad” propuestas por Rene Le Fort en 1901.
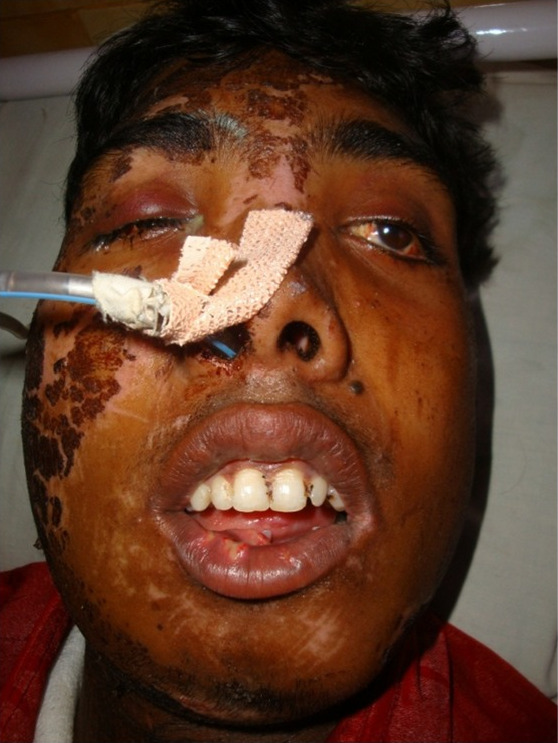
Paciente con una fractura de Le Fort III:
Nótese el ensanchamiento del espacio intercantal y el profuso edema facial. Los médicos de urgencias optaron por una vía aérea segura a través de la nariz.
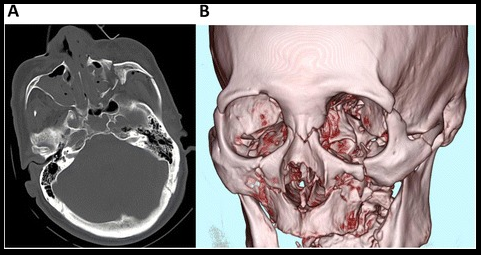
TC craneofacial (A) y reconstrucción tridimensional (B) de un paciente con una fractura de Le Fort III
Imagen: “Craniofacial computed tomography scan obtained on arrival.” por Momoko Mishima, Tetsuya Yumoto, Hiroaki Hashimoto et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0