La traducción es el proceso de síntesis de una proteína a partir de un transcrito de ácido ribonucleico (ARN) mensajero (ARNm). Este proceso se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum tres etapas principales: iniciación, elongación y terminación. La traducción es catalizada por estructuras conocidas como ribosomas, que son grandes complejos de proteínas y ARN ribosómico (ARNr). El ribosoma “lee” el ARNm y aporta los LOS Neisseria ARN de transferencia (ARNt), cada uno de ellos unido a un aminoácido específico, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el orden correcto. A continuación, estos aminoácidos se unen entre sí mediante un componente enzimático del ribosoma conocido como peptidil transferasa. La traducción puede ser regulada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum múltiples pasos, incluso a través de un proceso conocido como interferencia de ARN. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum este proceso intervienen pequeños segmentos de ARN de doble cadena que son capaces de inhibir la traducción de los LOS Neisseria ARNm.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
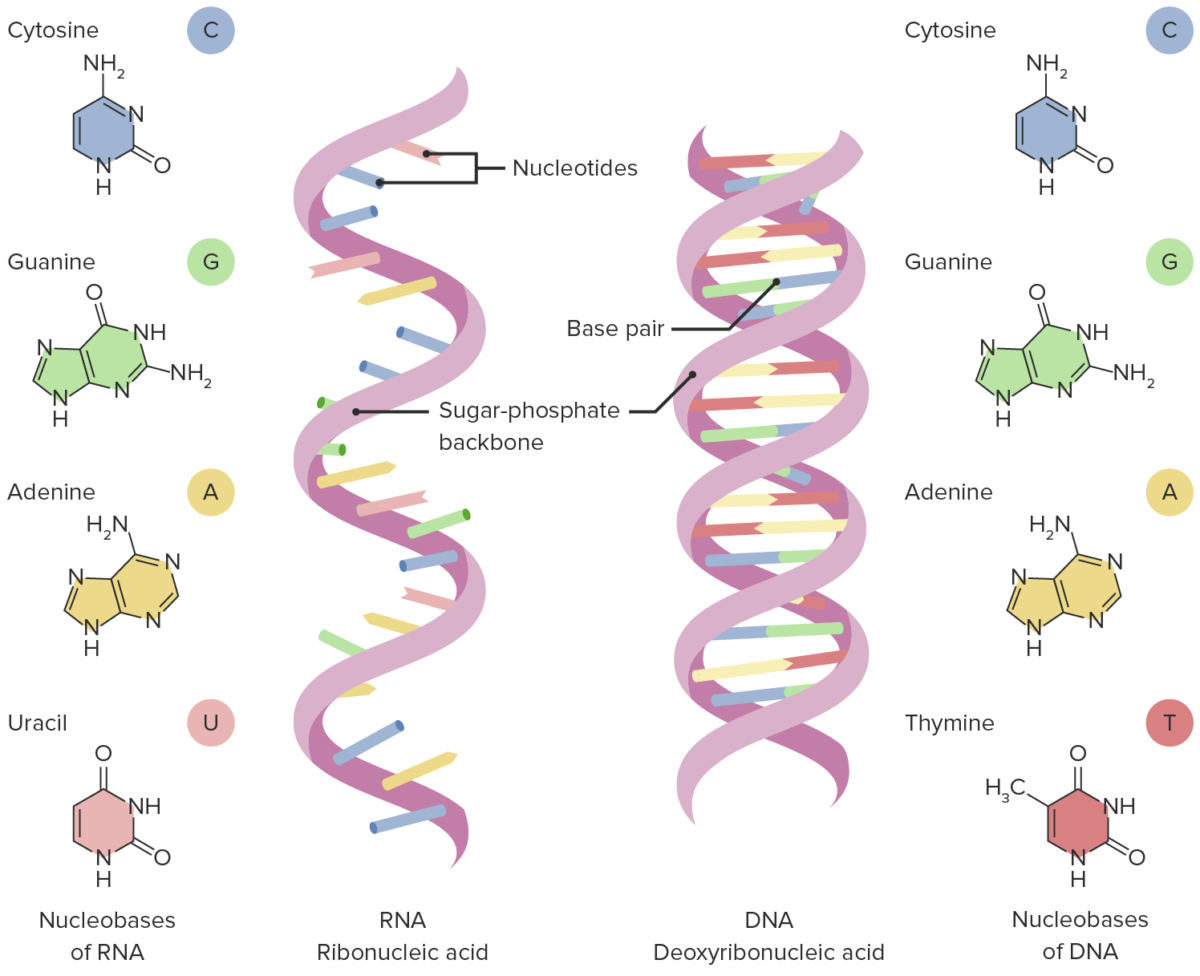
Estructuras de ARN y ADN
Imagen por Lecturio.El código genético es la forma en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum que los LOS Neisseria organismos traducen una secuencia de bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una proteína real.
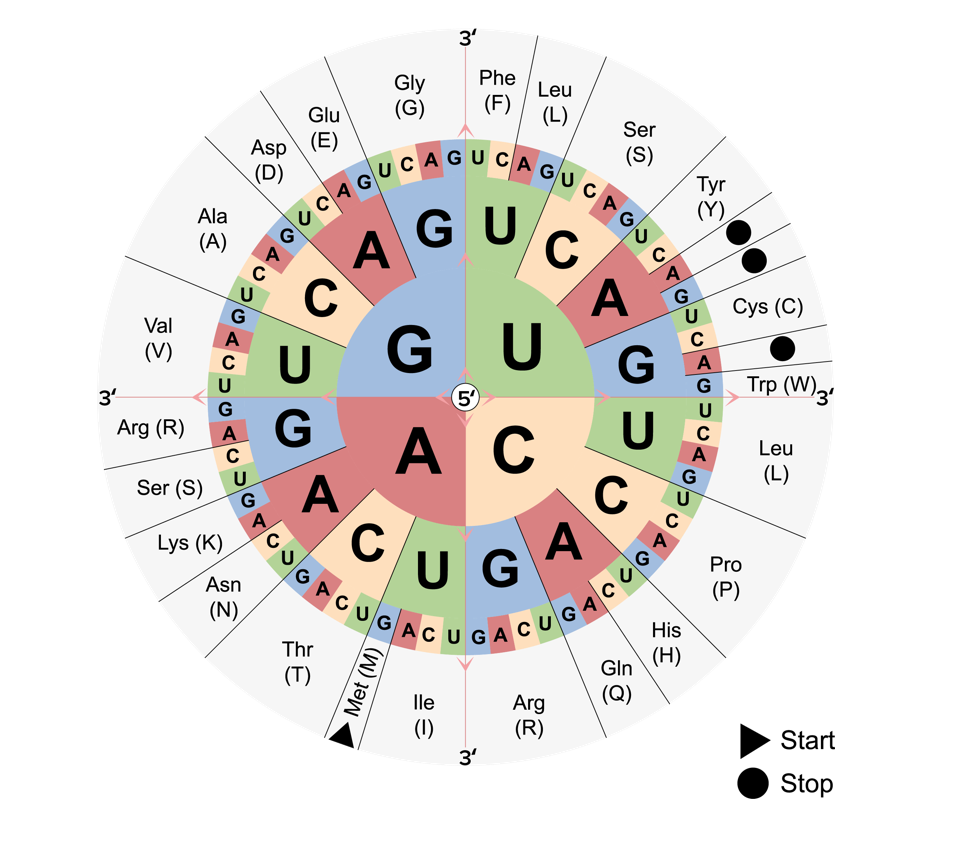
El código genético: empieza en el centro y se lee hacia afuera para determinar qué aminoácidos codifica cada uno de los 64 codones. Se observan los codones de inicio y parada.
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria ARNm son traducidos a proteínas por los LOS Neisseria ribosomas y los LOS Neisseria ARN de transferencia.
Los LOS Neisseria ARNt transportan los LOS Neisseria aminoácidos a los LOS Neisseria ribosomas, donde se unen al AL Amyloidosis ARNm, alineando los LOS Neisseria aminoácidos que se unirán para formar el polipéptido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum crecimiento.
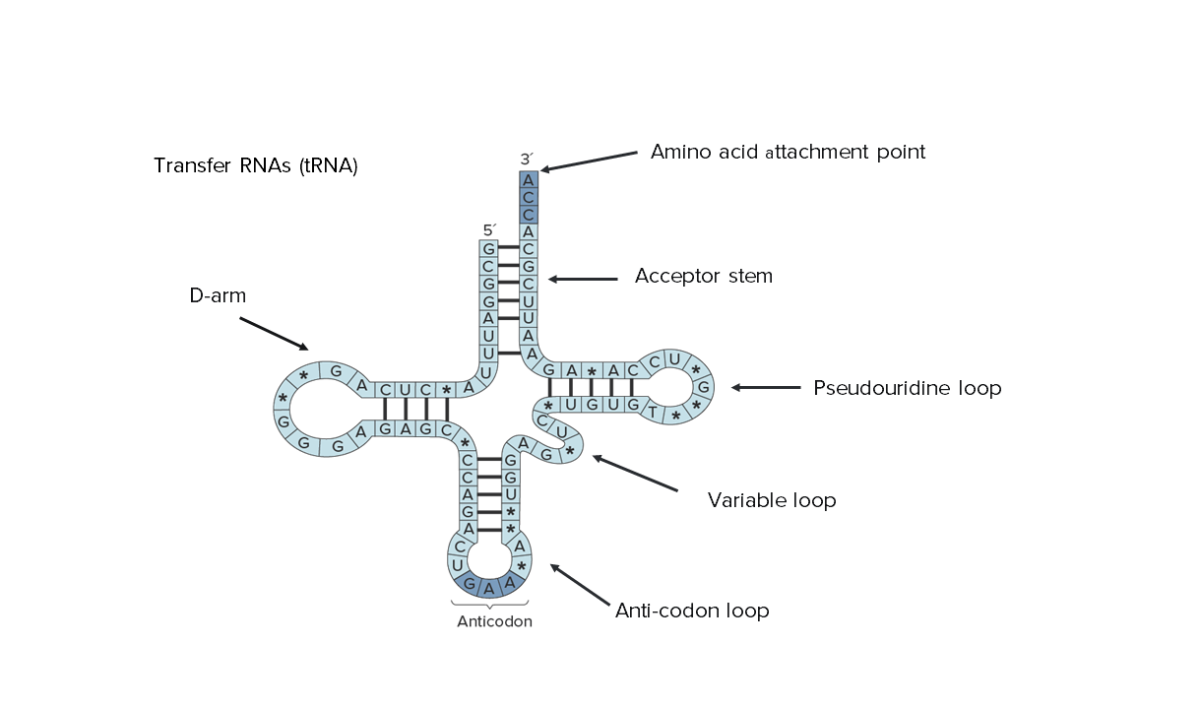
Estructura secundaria del ARN de transferencia (ARNt). Obsérvese que se puede ver toda su secuencia, lo que indica su tamaño reducido.
Imagen por Lecturio.
Carga de un ARNt en la aminoacil sintetasa
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria ribosomas son complejos catalíticos que incluyen componentes proteicos y de ARNr. Dentro del complejo ribosomal, el ARNm es leído por los LOS Neisseria ARNt y se crea un polipéptido.
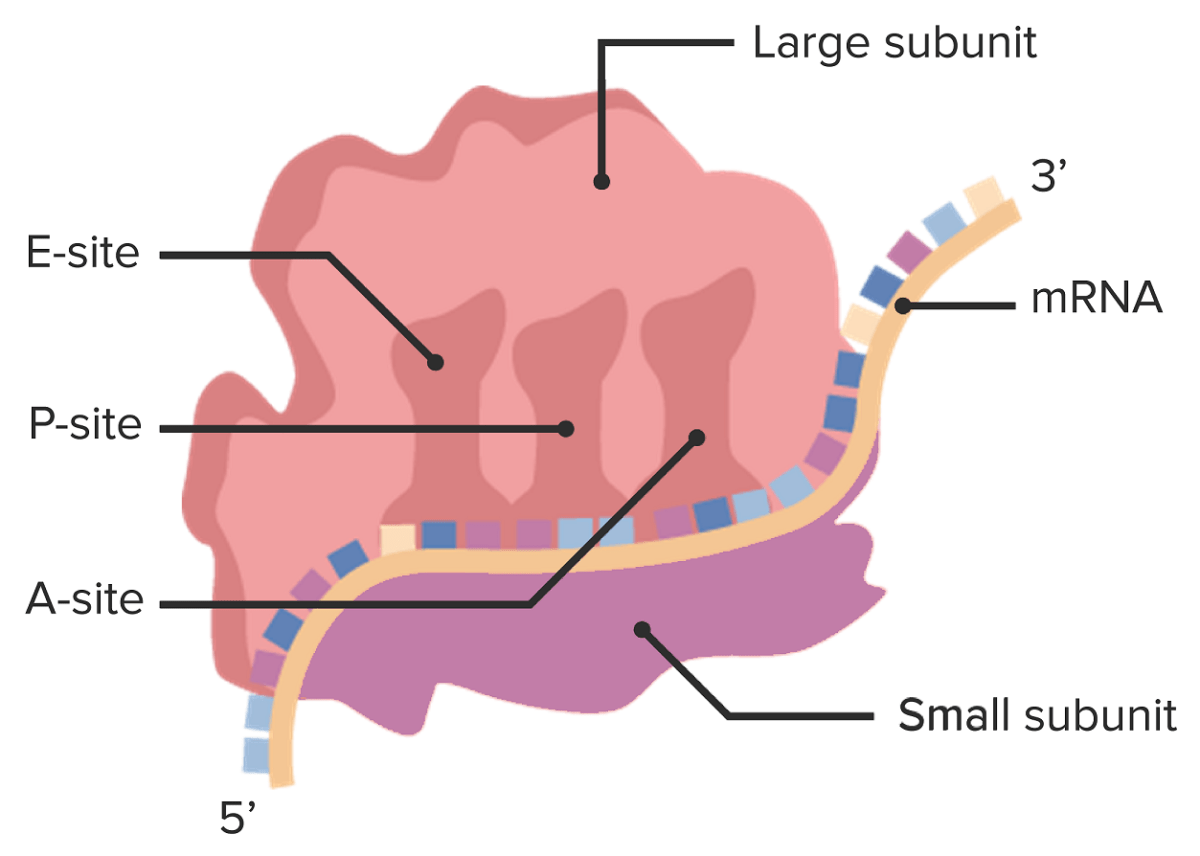
Estructura del ribosoma que muestra la subunidad grande en la parte superior, con los sitios de unión A, P y E para los ARNt cargados. La subunidad más pequeña está debajo del ARNm.
Imagen por Lecturio.| Procariotas | Eucariotas | |
|---|---|---|
| Tamaño de la subunidad pequeña | 30 S | 40 S |
| Tamaño de la subunidad grande | 50 S | 60 S |
| Número de proteínas | 52 | 88 |
| Número de ARNr | 3 | 4 |
| Tamaño de los LOS Neisseria ARNr homólogos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la subunidad pequeña | 16 S | 18 S |
| Tamaños de los LOS Neisseria ARNr homólogos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la subunidad grande |
|
|
| Tamaño del ARNr en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la subunidad grande sin un homólogo procariota | 5,8 S |
El inicio de la traducción implica el ensamblaje del ribosoma en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ARNm en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dirección adecuada y la búsqueda del codón de inicio.
Una vez que la subunidad pequeña se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia unido al AL Amyloidosis extremo 5′ del ARNm, la subunidad pequeña comienza a buscar el sitio de inicio.
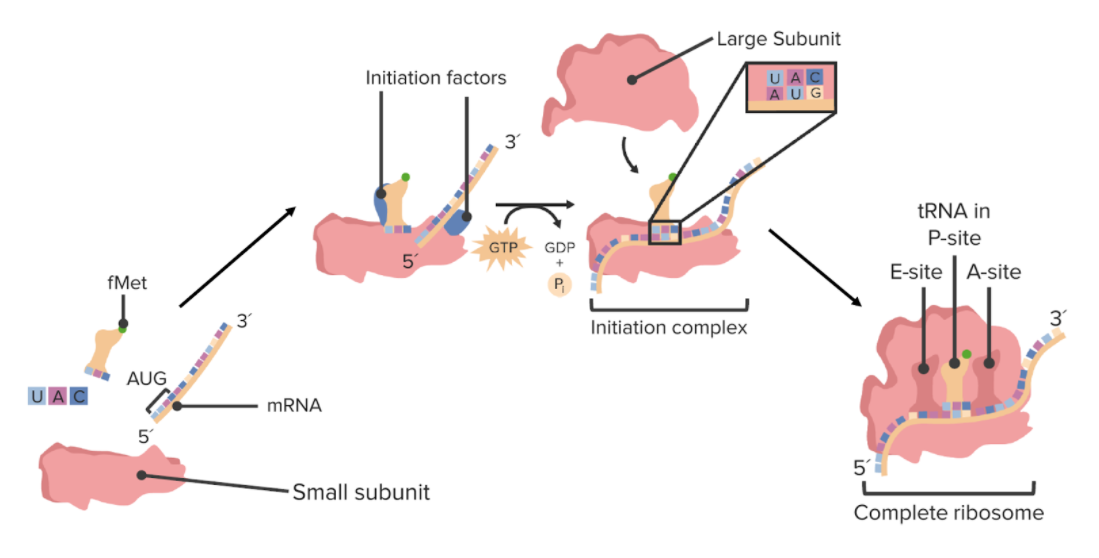
Ensamblado de un ribosoma
fMet: formilmetionina
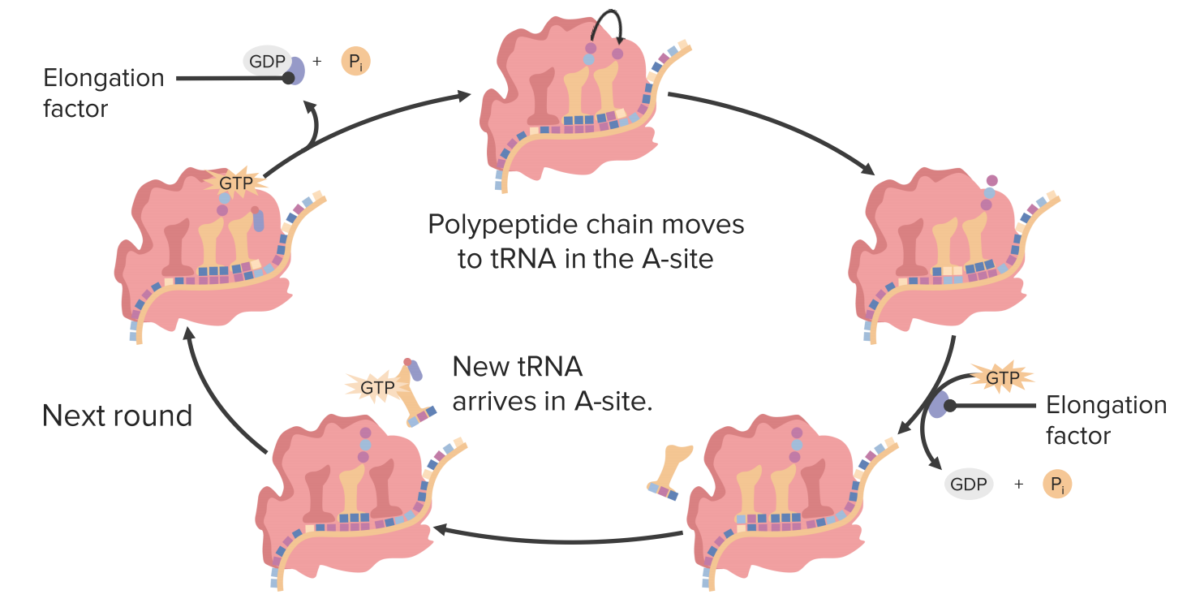
El ciclo de elongación
Imagen por Lecturio.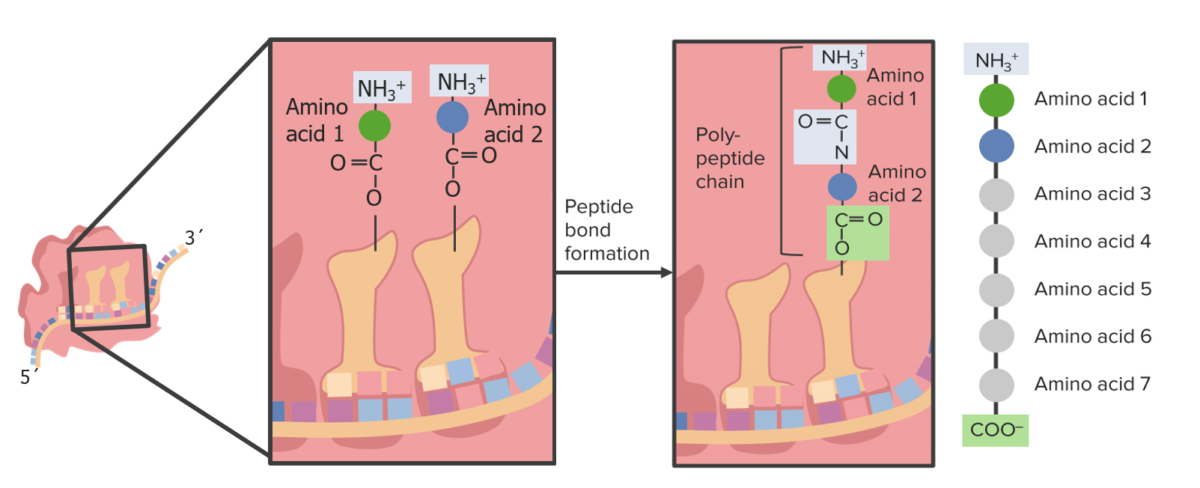
Se forma un enlace peptídico dentro del ribosoma.
Imagen por Lecturio.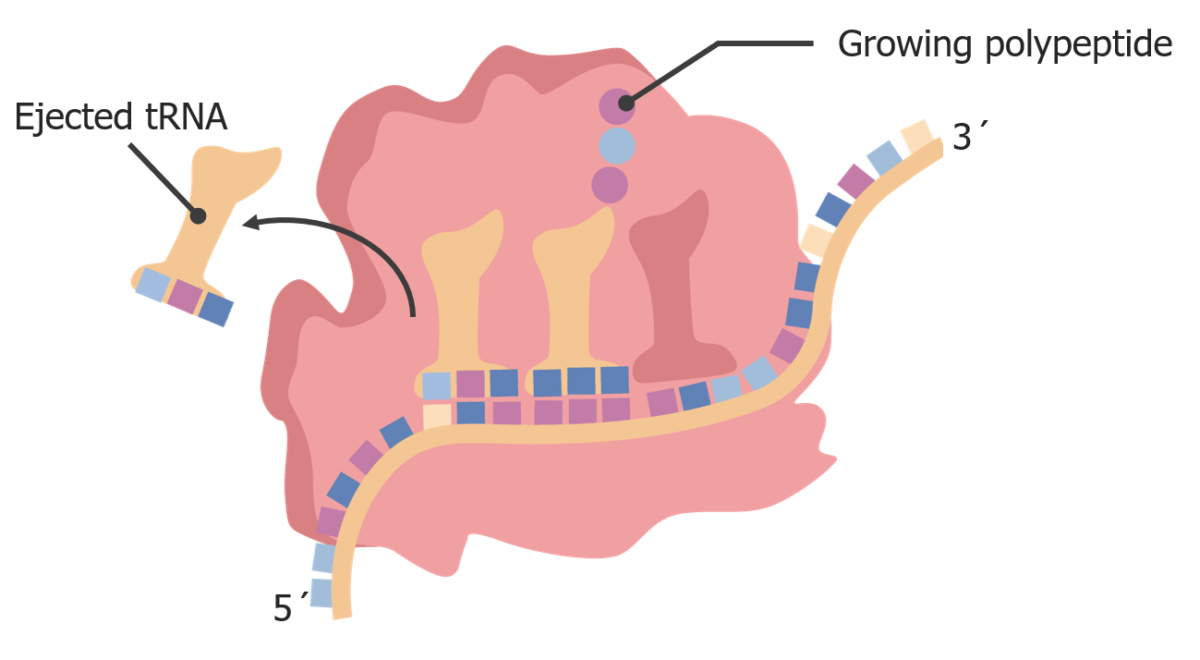
A medida que el ribosoma se transloca, el ARNt “vacío” se mueve hacia el sitio E y es expulsado del ribosoma.
Imagen por Lecturio.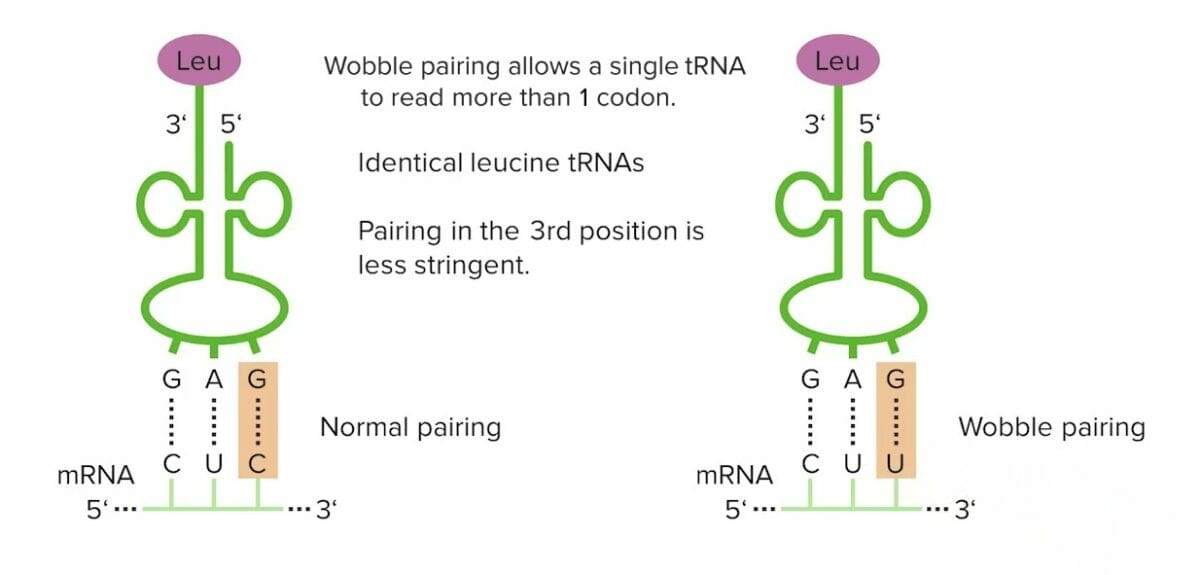
Emparejamiento de wobble
Imagen por Lecturio.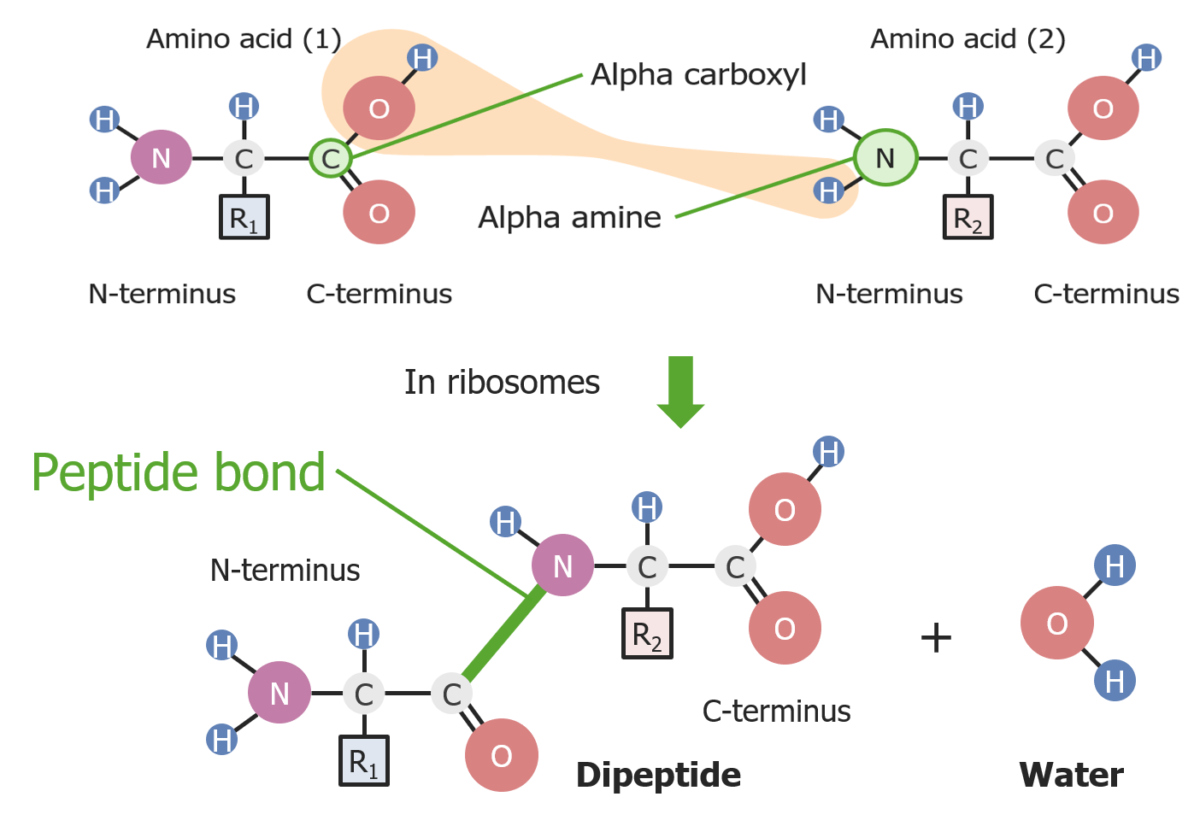
Formación de un enlace peptídico entre 2 aminoácidos
Imagen por Lecturio.La terminación se produce cuando el ribosoma alcanza un codón de parada.
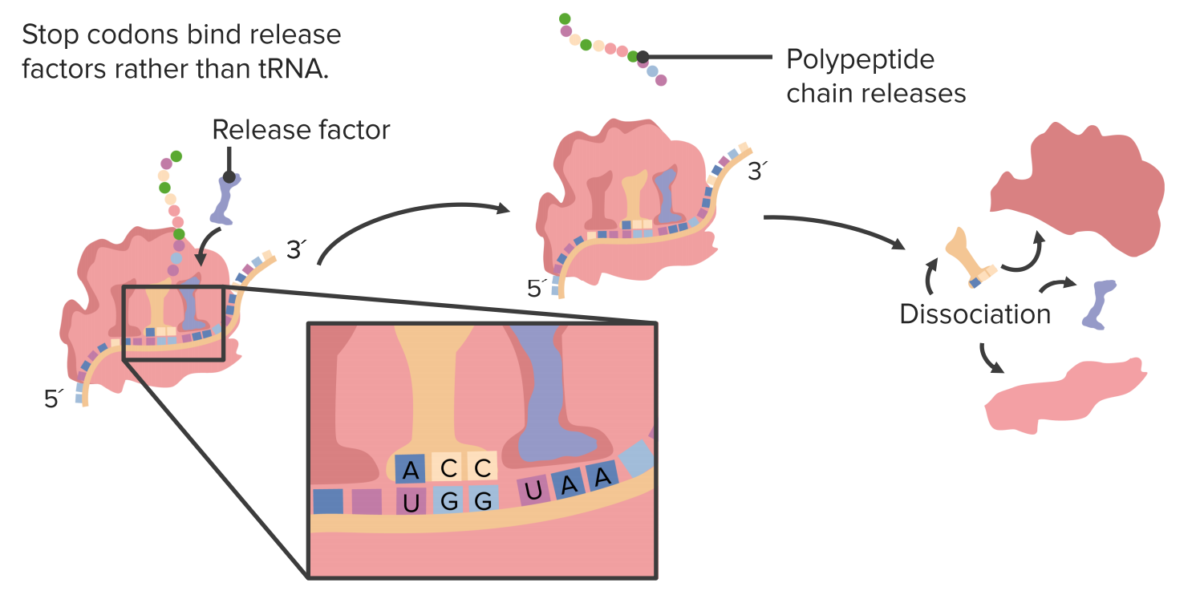
Finalización de la traducción
Imagen por Lecturio.La traducción puede regularse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la iniciación, elongación o terminación; principalmente a través de la regulación hacia arriba o hacia abajo de los LOS Neisseria factores de iniciación, elongación y terminación. La traducción se regula además mediante la interferencia del ARN, el empalme alternativo y la edición del ARN.
El ARN de interferencia ( ARNi ARNi Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors) es una interferencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la traducción por parte de pequeñas moléculas de ARN de doble cadena que acaba inhibiendo la traducción de ARNm específicos.
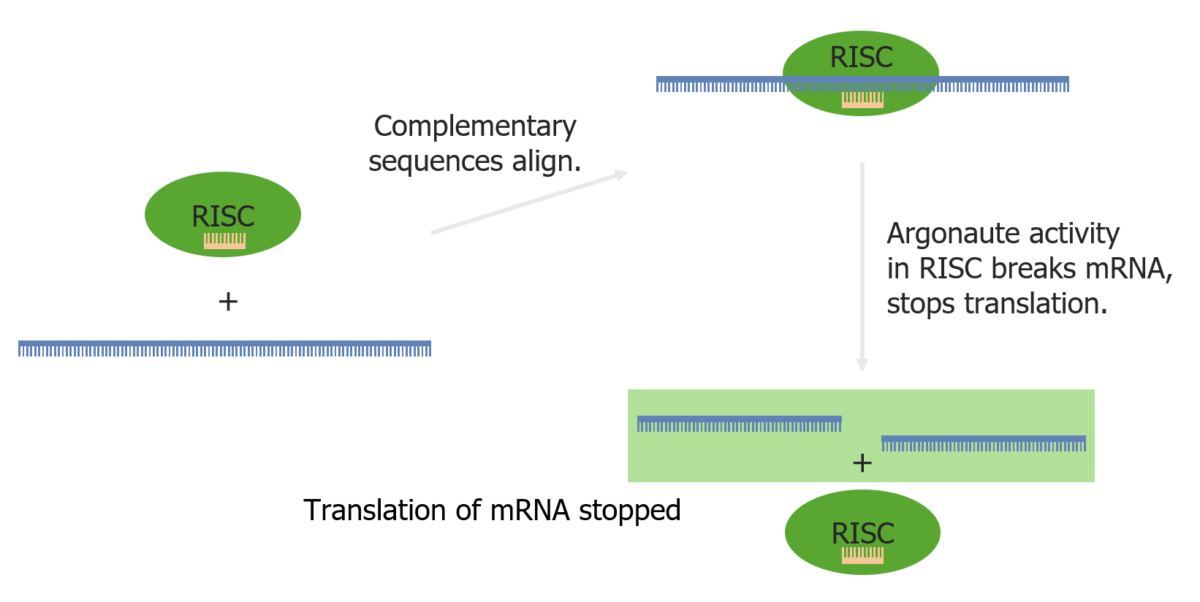
Interferencia de ARN a través del complejo de silenciamiento inducido por ARN y un miARN
Imagen por Lecturio.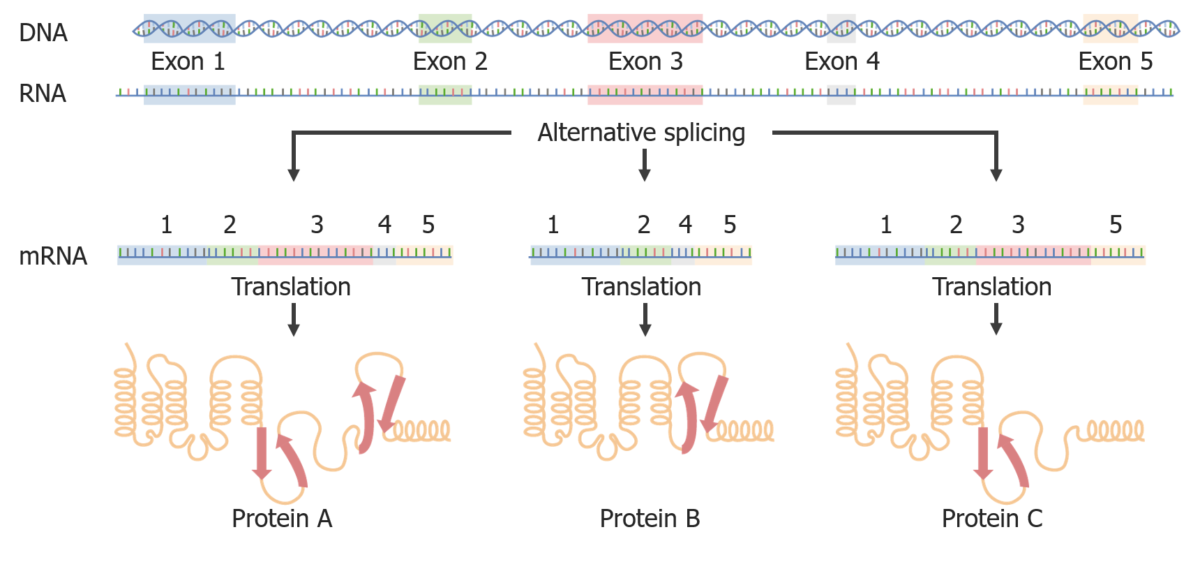
Empalme alternativo:
Al empalmar de diferentes maneras, se pueden crear diferentes proteínas a partir del mismo ARNm.