Las enfermedades trofoblásticas gestacionales son un espectro de trastornos placentarios que resultan de un crecimiento trofoblástico placentario anormal. Estos trastornos van desde embarazos molares benignos (molas completas y parciales) hasta afecciones neoplásicas como molas invasoras y coriocarcinoma. El diagnóstico se confirma por la gonadotropina coriónica humana (hCG, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) beta elevada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum suero y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del ultrasonido, que dependen del trastorno. El tratamiento es principalmente mediante dilatación y legrado y/o metotrexato.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las molas hidatiformes se caracterizan por inflamación quística de las vellosidades coriónicas y proliferación del epitelio coriónico. Hay 2 tipos: mola completa y mola parcial.
| Mola completa | Mola parcial | |
|---|---|---|
| Cariotipo | 46,XX o 46,XY | Triploide (69,XXX, 69, XXY XXY Klinefelter syndrome is a chromosomal aneuploidy characterized by the presence of 1 or more extra X chromosomes in a male karyotype, most commonly leading to karyotype 47,XXY. Klinefelter syndrome is associated with decreased levels of testosterone and is the most common cause of congenital hypogonadism. Klinefelter Syndrome o 69,XYY) |
| Formado por | Óvulo enucleado y un solo espermatozoide | 2 espermatozoides y 1 óvulo |
| Partes fetales | Ausente | Presente |
| Nivel de gonadotropina coriónica humana (hCG, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) | ↑↑↑ | ↑ |
| Hallazgos del ultrasonido |
|
Revela partes fetales |
| Riesgo de malignidad | Mayor riesgo de coriocarcinoma | Raro |
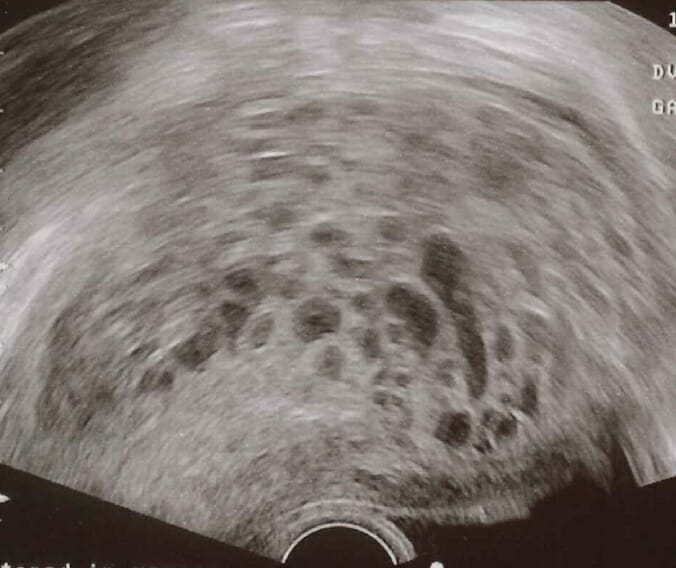
Ultrasonido transvaginal de una mola hidatiforme: En el ultrasonido se observa un característico “patrón en tormenta de nieve”.
Imagen: “Transvaginal ultrasonography showing a molar pregnancy” por Mikael Häggström. Licencia: CC0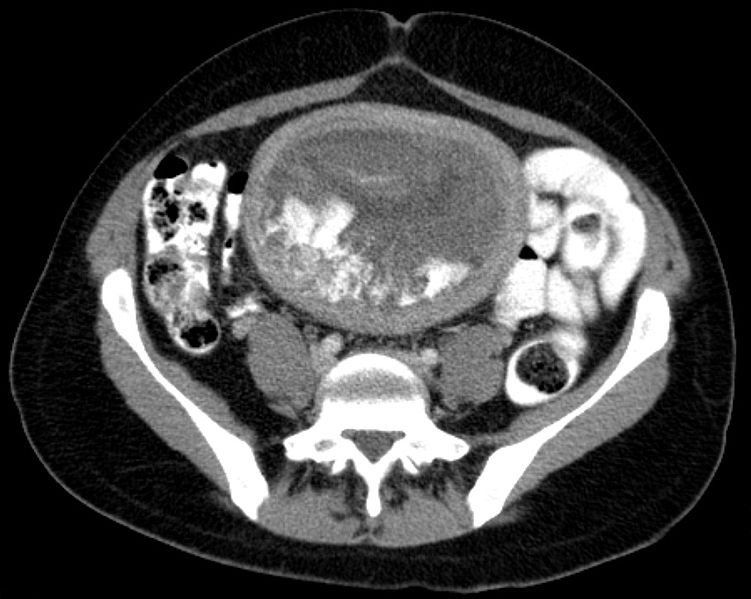
Hidatide en imagen de tomografía computarizada (TC) axial
Imagen: “Blasenmole Computertomographie axial” por Hellerhoff. Licencia: CC BY-SA 3.0El coriocarcinoma es una neoplasia maligna muy agresiva de células trofoblásticas que puede desarrollarse durante o después del embarazo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la madre o el bebé.
Puede ser precedido por:
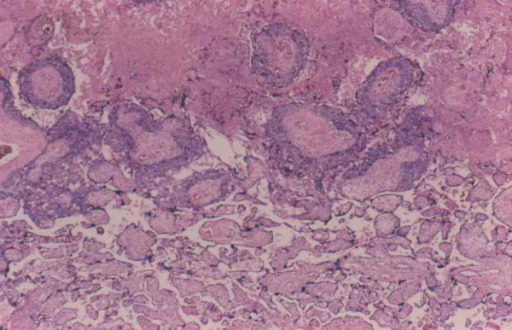
Coriocarcinoma con necrosis central
Imagen: “Interface between choriocarcinoma with central necrosis and normal placenta” por Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, St. Louis University, Missouri, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Las siguientes afecciones son diagnósticos diferenciales de la enfermedad trofoblástica gestacional: