La enfermedad de Tay-Sachs es un trastorno autosómico recesivo del almacenamiento lisosómico, causado por mutaciones genéticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen de la hexosaminidasa A (HEXA), que conduce a una neurodegeneración progresiva. Esta enfermedad es muy frecuente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la población judía asquenazí. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas clásicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria lactantes incluyen una rápida degeneración de las capacidades cognitivas y neuromusculares, ceguera progresiva y una mancha macular de color rojo cereza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el examen físico. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante la medición de la actividad de las enzimas hexosaminidasa A y beta-hexosaminidasa. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la actualidad, no hay cura para esta enfermedad, y el tratamiento está dirigido a mejorar la calidad de vida del paciente.
Last updated: Apr 23, 2025
La enfermedad de Tay-Sachs, es un trastorno de almacenamiento lisosómico causado por una deficiencia de la enzima hexosaminidasa A (Hex-A).
La enfermedad de Tay-Sachs se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 variantes según la edad de inicio y la actividad enzimática.
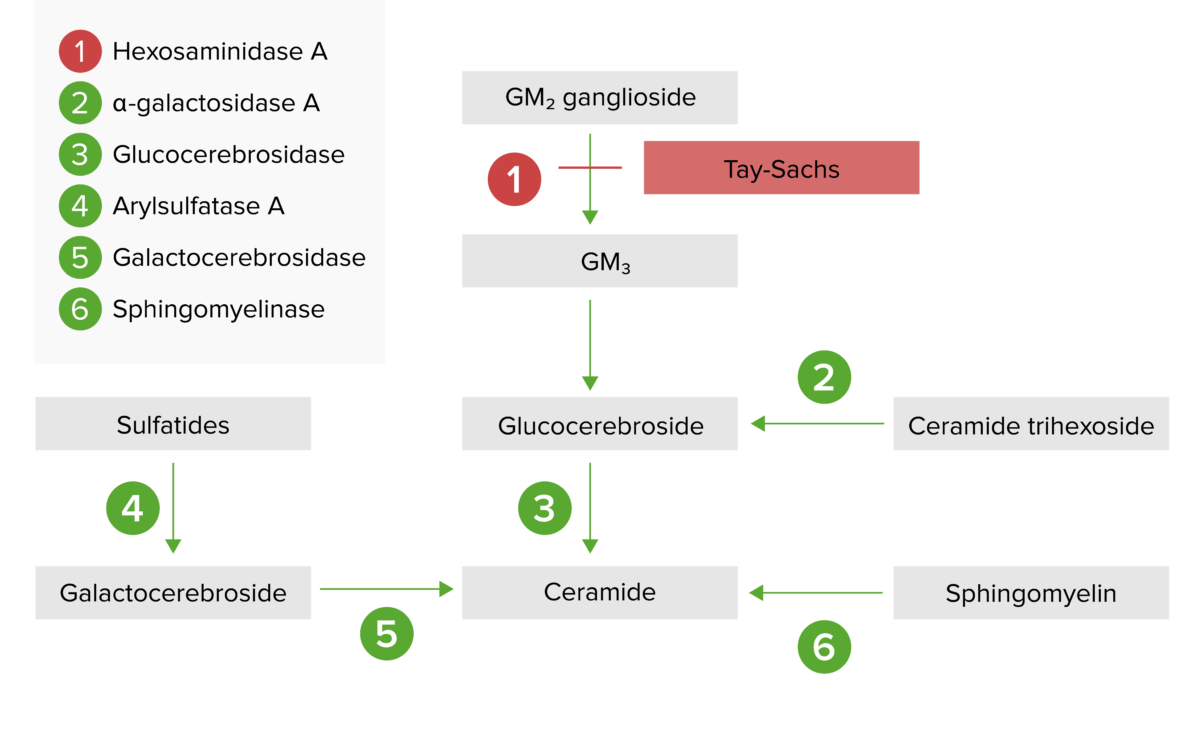
La vía de almacenamiento lisosómico:
La enfermedad de Tay-Sachs resulta de una deficiencia de hexosaminidasa A, provocando una acumulación de gangliósidos GM2.
La enfermedad de Tay-Sachs, es un trastorno neurodegenerativo con una presentación clínica variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables según el tipo.
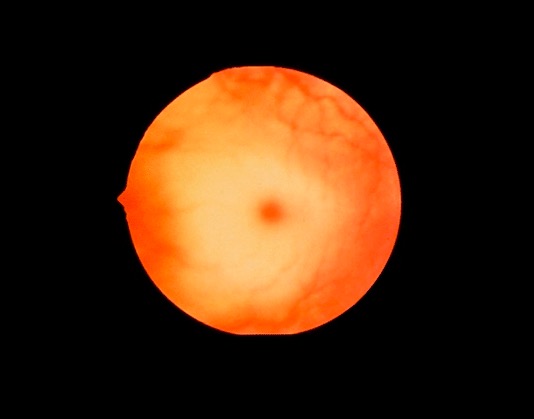
Mancha de color rojo cereza:
La mácula es normalmente roja. La palidez se desarrolla alrededor de la mácula roja debido a la acumulación de glicolípidos, dando la apariencia de una mancha de color rojo cereza. La mancha suele desarrollarse a la edad de 1 año en la enfermedad de Tay-Sachs, y también puede encontrarse en otros trastornos por almacenamiento lisosómico.
Las pruebas se llevan a cabo tras la sospecha clínica. El tamizaje prenatal también es posible mediante la toma de muestras de vellosidades coriónicas o la amniocentesis Amniocentesis Percutaneous transabdominal puncture of the uterus during pregnancy to obtain amniotic fluid. It is commonly used for fetal karyotype determination in order to diagnose abnormal fetal conditions. Polyhydramnios.
La deficiencia de hexosaminidasa A no tiene cura. El tratamiento es de soporte, centrado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el control de los LOS Neisseria síntomas y la mejora de la calidad de vida.