Las encefalopatías espongiformes transmisibles son enfermedades causadas por priones. Los LOS Neisseria priones se diferencian de los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum que son pequeños patógenos infecciosos que no contienen ácido nucleico. Las encefalopatías espongiformes reconocidas incluyen la enfermedad de Creutzfeldt-Jakob, la variante de la enfermedad de Creutzfeldt-Jakob, Kuru Kuru A prion disease found exclusively among the fore linguistic group natives of the highlands of new guinea. The illness is primarily restricted to adult females and children of both sexes. It is marked by the subacute onset of tremor and ataxia followed by motor weakness and incontinence. Death occurs within 3-6 months of disease onset. The condition is associated with ritual cannibalism, and has become rare since this practice has been discontinued. Pathologic features include a noninflammatory loss of neurons that is most prominent in the cerebellum, glial proliferation, and amyloid plaques. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies, el insomnio familiar fatal y el síndrome de Gerstmann-Straussler. Las características comunes de estas enfermedades incluyen demencia, ataxia Ataxia Impairment of the ability to perform smoothly coordinated voluntary movements. This condition may affect the limbs, trunk, eyes, pharynx, larynx, and other structures. Ataxia may result from impaired sensory or motor function. Sensory ataxia may result from posterior column injury or peripheral nerve diseases. Motor ataxia may be associated with cerebellar diseases; cerebral cortex diseases; thalamic diseases; basal ganglia diseases; injury to the red nucleus; and other conditions. Ataxia-telangiectasia y mioclonías. Desafortunadamente, estas enfermedades están asociadas con largos períodos de incubación (más de 20 años) y una vez que se presentan los LOS Neisseria síntomas, progresan rápidamente hasta la muerte.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las encefalopatías espongiformes son extremadamente raras.
Enfermedades humanas conocidas:
La encefalopatía espongiforme más común es la enfermedad de Creutzfeldt-Jakob. Las variaciones son:
Los LOS Neisseria factores de alto riesgo son:
Las enfermedades por priones ocurren cuando una proteína ⍺-helicoidal normal conocida como PrPc PrPc Normal cellular isoform of prion proteins encoded by a chromosomal gene and found in normal and scrapie-infected brain tissue, and other normal tissue. PRPC are protease-sensitive proteins whose function is unknown. Posttranslational modification of PRPC into PRPSC leads to infectivity. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies se convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una proteína plegada β anormal conocida como PrPsc PrPsc Abnormal isoform of prion proteins resulting from a posttranslational modification of the cellular prion protein (PRPC proteins). Prpsc are disease-specific proteins seen in certain human and animal neurodegenerative diseases (prion diseases). Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies.
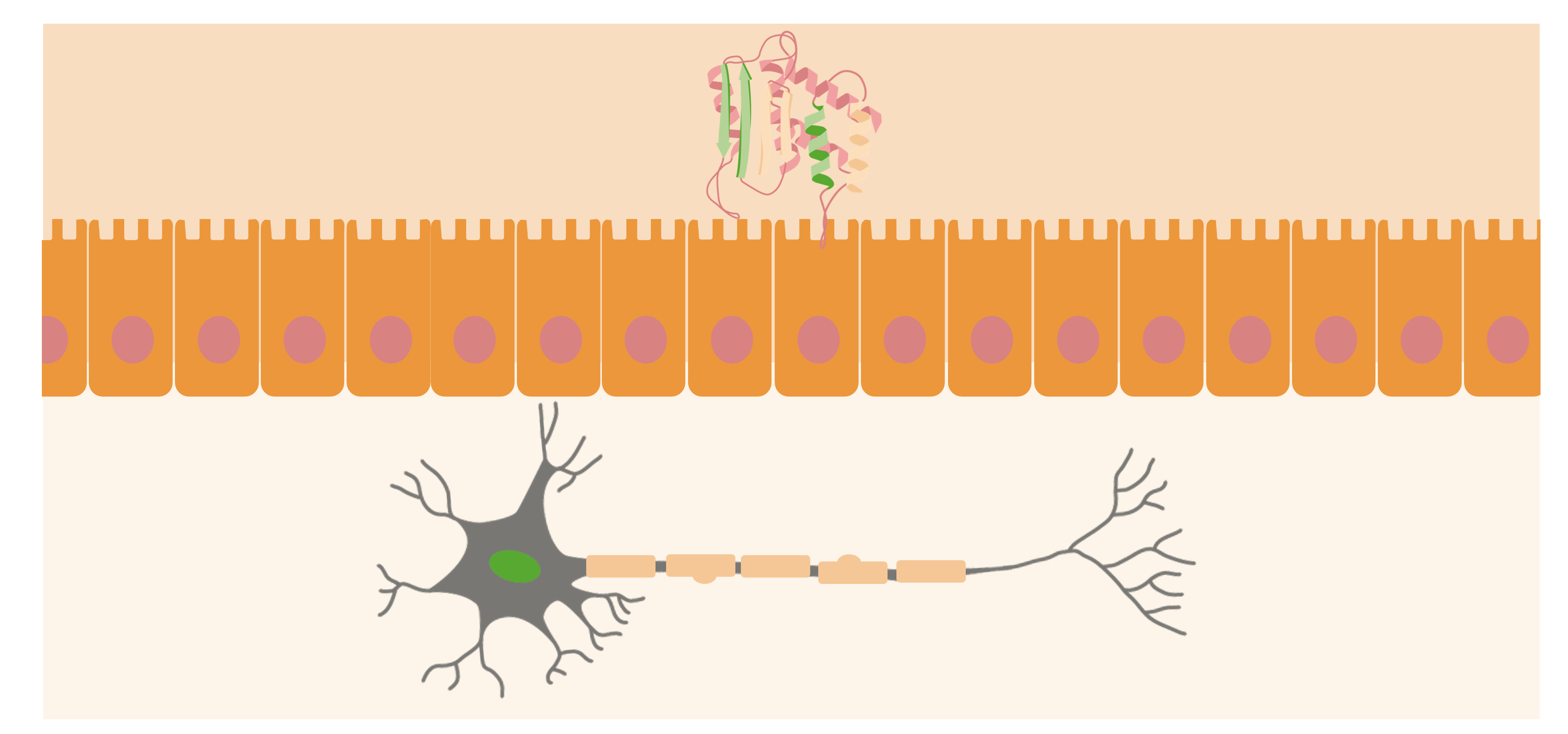
Los priones generalmente se encuentran en las superficies externas de neuronas. Cuando la PrPsc (proteína anormal) se adquiere en el organismo, se acercará a la superficie de la mucosa del intestino y hará que las proteínas priónicas normales se conviertan en formas patógenas.
Imagen por Lecturio.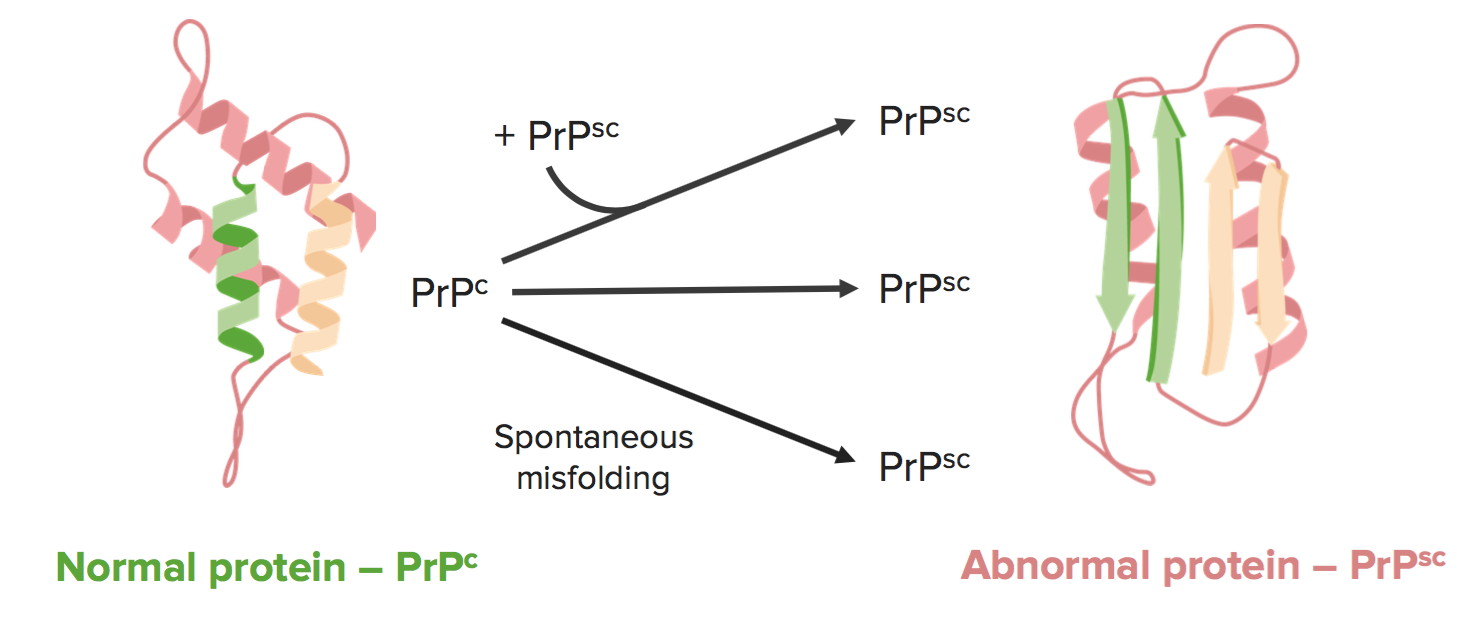
Las encefalopatías espongiformes transmisibles son causadas por el mal plegamiento de los priones. El prión patógeno, PrPsc, es una isoforma de conformación de una proteína huésped normal, PrPc.
Imagen por Lecturio.Hay 3 formas principales de desarrollar encefalopatías espongiformes:
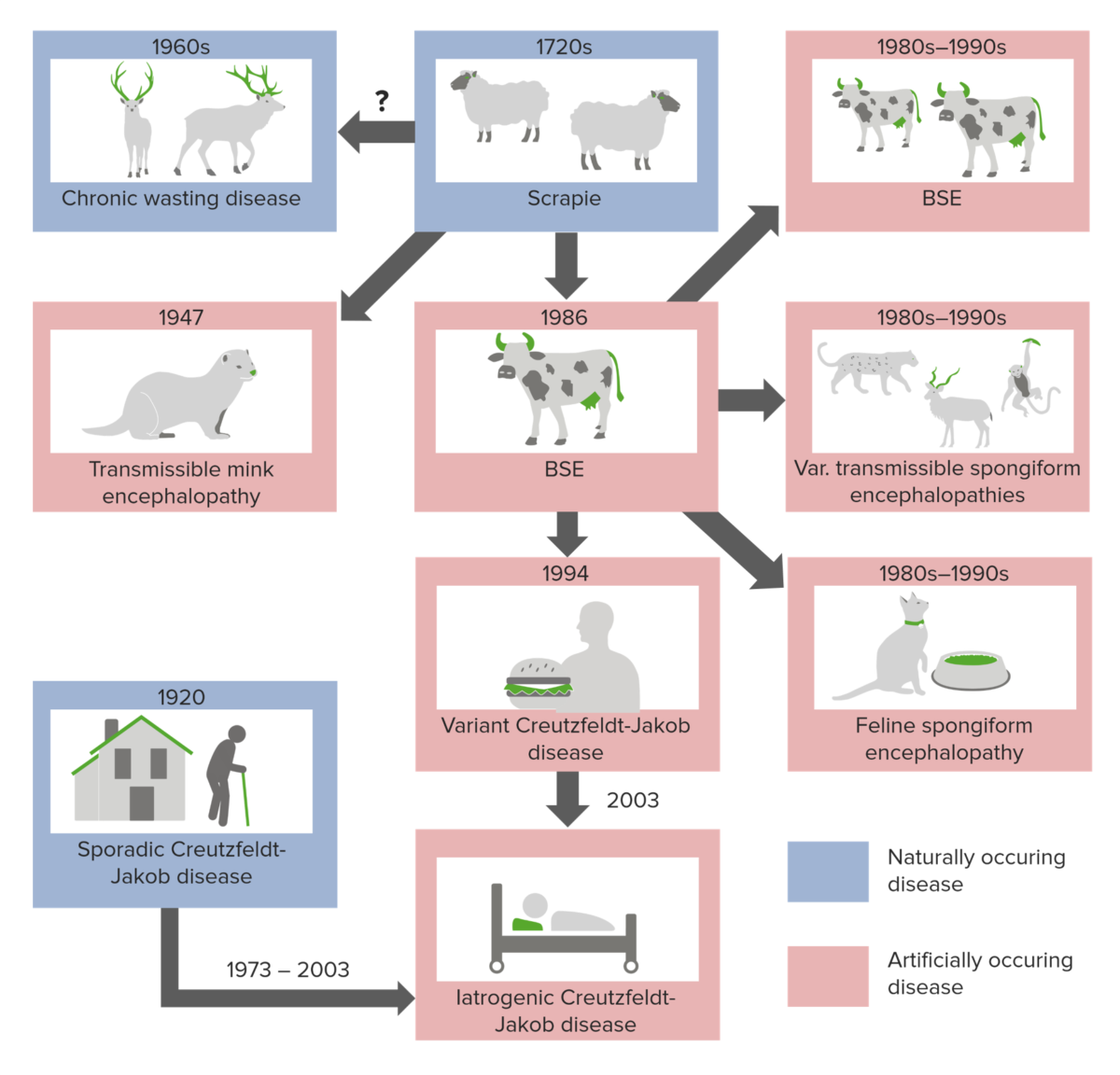
Orígenes de las enfermedades por priones
Imagen por Lecturio.Las encefalopatías espongiformes transmisibles se asocian con tiempos de incubación extremadamente largos (20–50 años) y una vez que aparecen los LOS Neisseria síntomas, la enfermedad progresa rápidamente hasta la muerte.
No existen medidas curativas y las enfermedades son universalmente fatales.
| Síntomas | Diagnóstico | |
|---|---|---|
| Enfermedad de Creutzfeldt-Jakob |
|
|
| Kuru Kuru A prion disease found exclusively among the fore linguistic group natives of the highlands of new guinea. The illness is primarily restricted to adult females and children of both sexes. It is marked by the subacute onset of tremor and ataxia followed by motor weakness and incontinence. Death occurs within 3-6 months of disease onset. The condition is associated with ritual cannibalism, and has become rare since this practice has been discontinued. Pathologic features include a noninflammatory loss of neurons that is most prominent in the cerebellum, glial proliferation, and amyloid plaques. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies |
|
Desconocido; se han realizado pocos estudios debido a casos limitados (principalmente aislados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Papúa Nueva Guinea en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la década de 1950) |
| Insomnio familiar fatal |
En
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum pacientes de 23–73 años:
|
Poco claro; biopsia cerebral post-mortem |
| Síndrome de Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker |
En
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum pacientes de mediados a finales de
los
LOS
Neisseria 40:
|
Biopsia cerebral post-mortem |
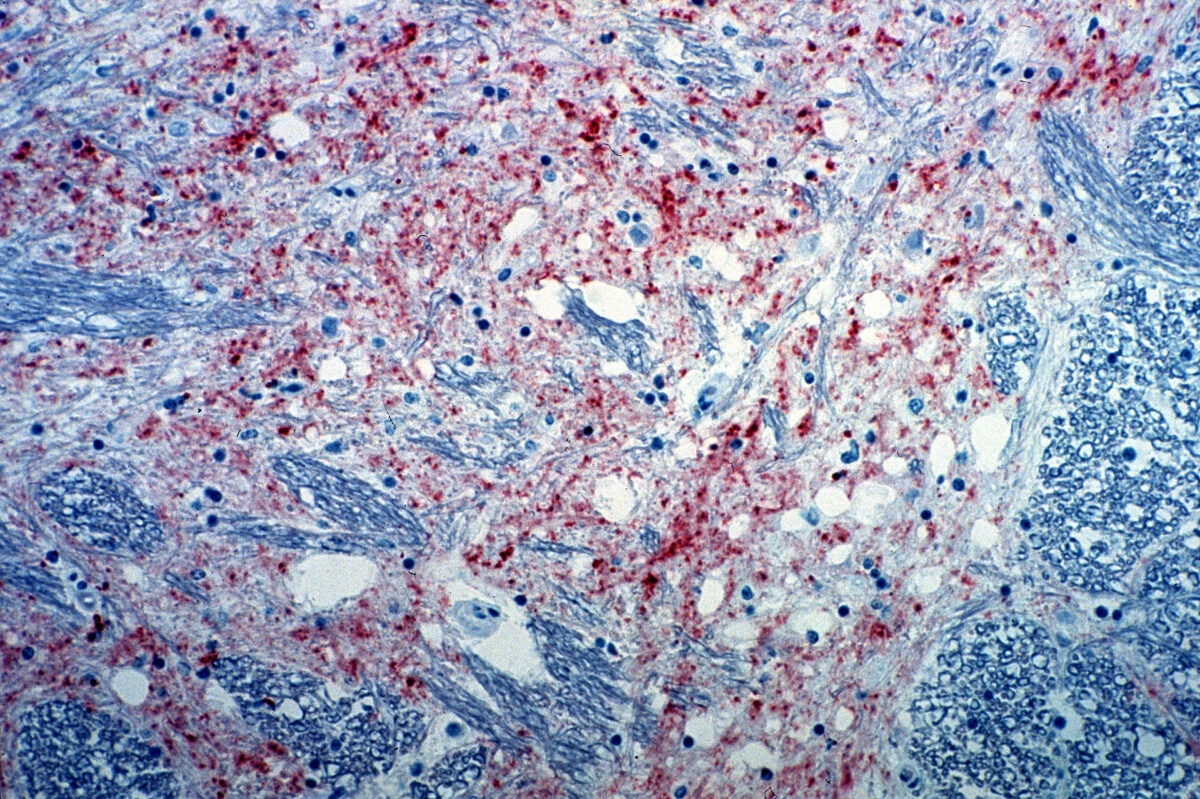
Sección del cerebro de una vaca infectada con encefalopatía espongiforme bovina. La tinción marrón indica la presencia del agente causante de la enfermedad.
Imagen: “Mad_Cow_Disease” por CSIRO. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
Ampliada 100X y teñida con la técnica de tinción H&E (hematoxilina y eosina), esta fotomicrografía de tejido cerebral revela la presencia de cambios espongióticos prominentes en la corteza y la pérdida de neuronas en un caso de ECJv.
Imagen: “Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD)” por Sherif Zaki; MD; PhD; Wun-Ju Shieh; MD; PhD; MPH. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoDiagnóstico diferencial incluye enfermedades que están asociadas con la demencia de progresión rápida, incluidas las siguientes: