Las lesiones agudas de hombro son un motivo de consulta común a los LOS Neisseria médicos de atención primaria y la sala de emergencias. Las lesiones más comunes son las fracturas de clavícula, los LOS Neisseria esguinces y dislocaciones esternoclaviculares, los LOS Neisseria desgarros del manguito de los LOS Neisseria rotadores, las fracturas del húmero proximal, las fracturas escapulares, las dislocaciones glenohumerales y las lesiones de la articulación acromioclavicular. La evaluación del dolor Dolor Inflammation agudo de hombro requiere una comprensión del mecanismo de la lesión, así como una exploración física adecuada y estudios radiológicos necesarios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el contexto agudo. Es esencial realizar un interrogatorio y una exploración física dirigidos que incluyan la inspección, la palpación y un examen neurovascular exhaustivo. La imagenología comienza con radiografías simples y, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ocasiones, se complementa con imágenes de RM o TC. El tratamiento incluye el control del dolor Dolor Inflammation y varía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función del diagnóstico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Recuerda los LOS Neisseria músculos del manguito rotador con SITS:
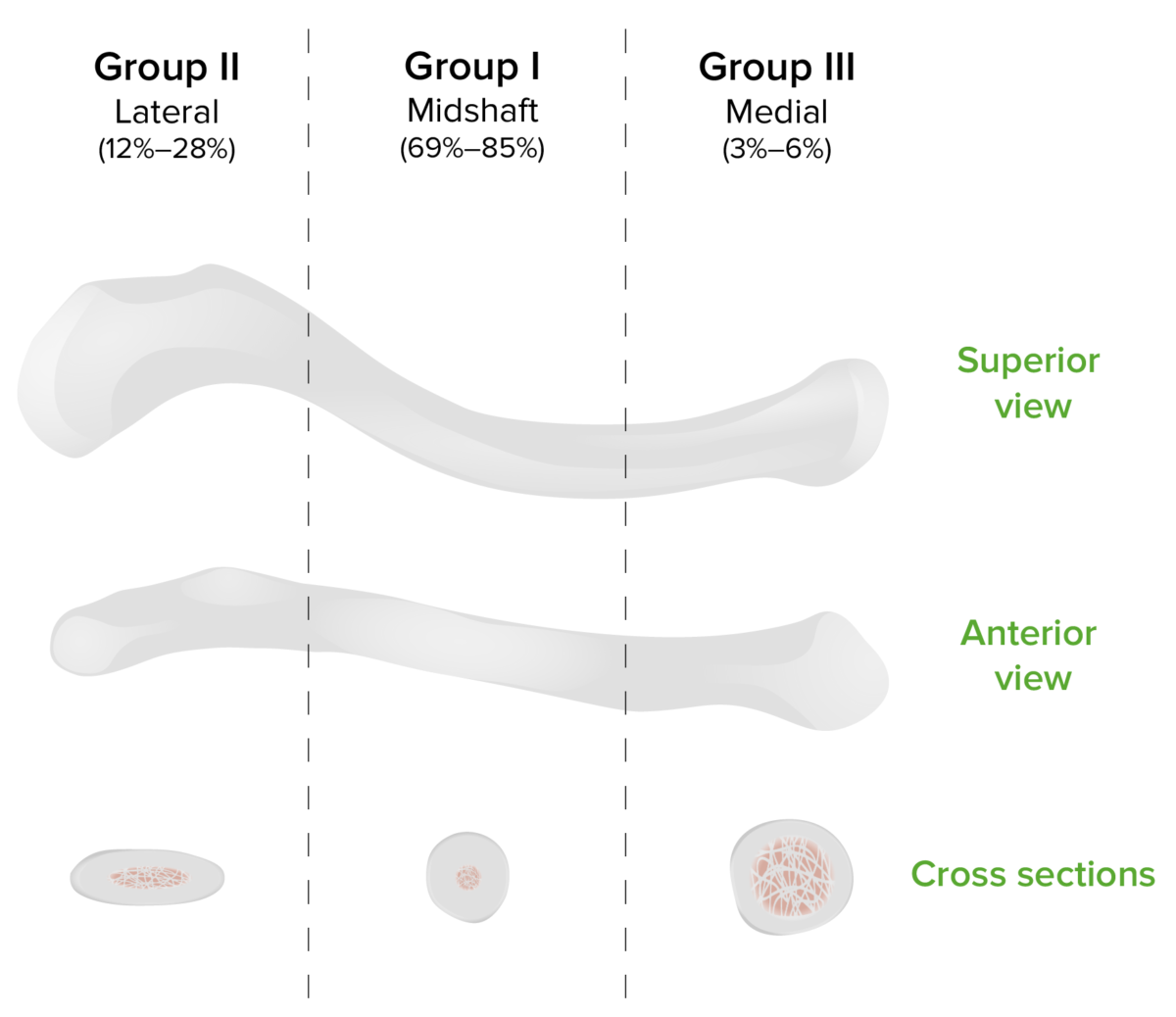
Clasificación de Allman de la fractura clavicular
Imagen por Lecturio.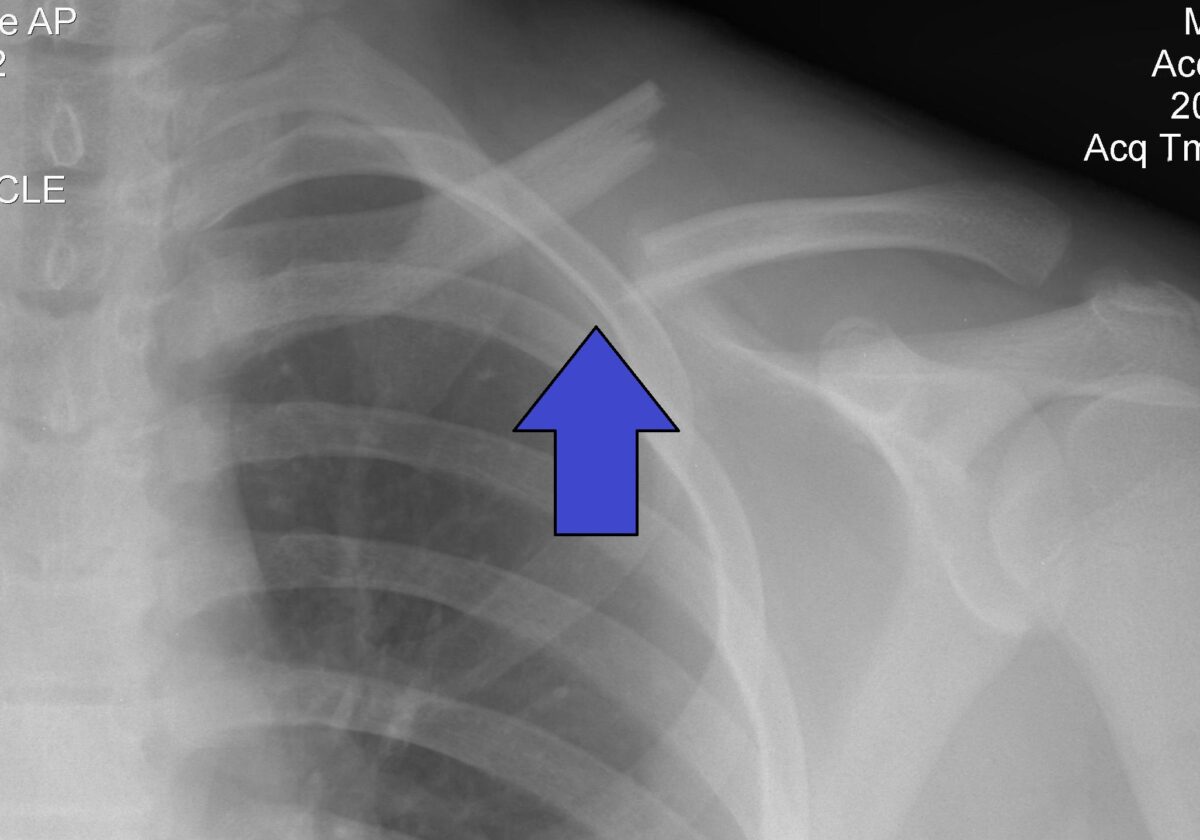
Fractura de clavícula del grupo 1 indicada por la flecha
Imagen: “Fractura de clavícula izquierda” por Majorkev. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
Clasificación de Rockwood de las lesiones de la articulación acromioclavicular
Imagen por Lecturio.
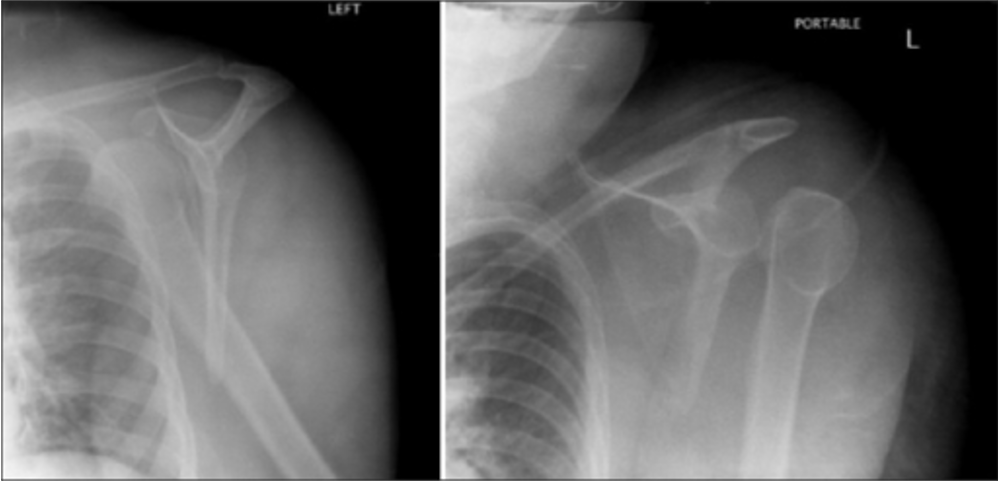
Lesión de la articulación acromioclavicular de tipo III en la radiografía:
La flecha muestra la clavícula por encima del nivel del acromion, pero no más del doble de la distancia normal.
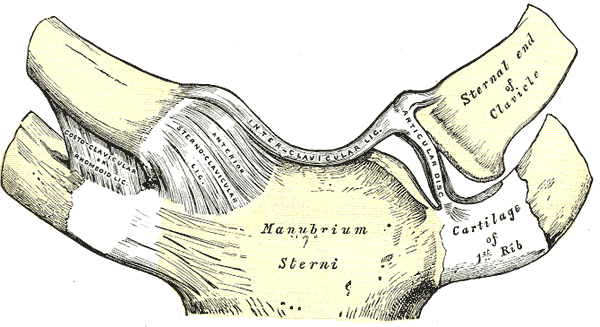
Vista anterior normal de la articulación esternoclavicular
Imagen: “Gray325” por Henry Gray, Warren H. Lewis. Licencia: Dominio Público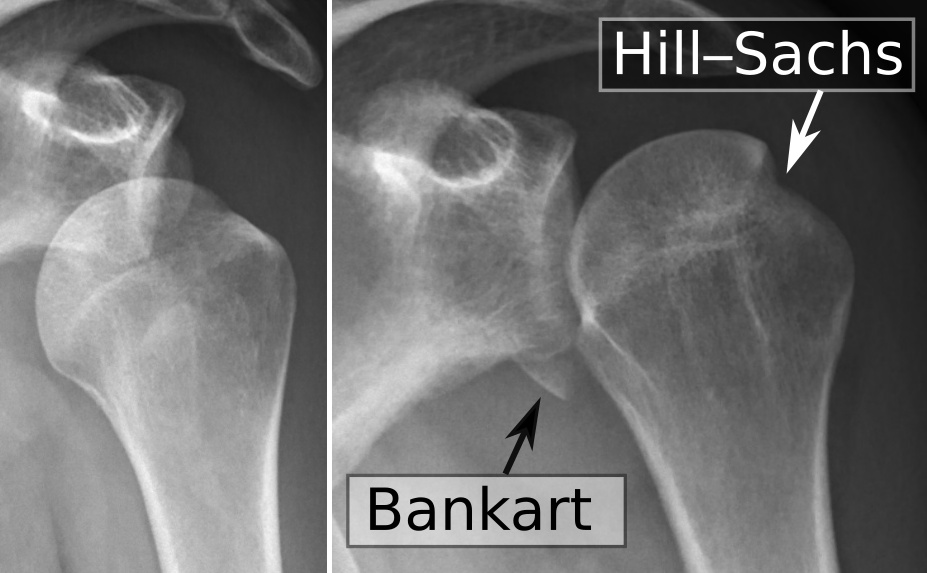
Proyección en Y de la escápula de la luxación anterior (izquierda) y posterior (derecha) del hombro izquierdo
Imagen: “Scapular Y views of (a) anterior and (b) posterior dislocation of the left shoulder” por Day MS, Epstein DM, Young BH, Jazrawi LM. Licencia: CC BY 2.0
Radiografía normal en Y
Imagen: “Y-projection X-ray of a normal shoulder” por Mikael Häggström. Licencia: CC0 1.0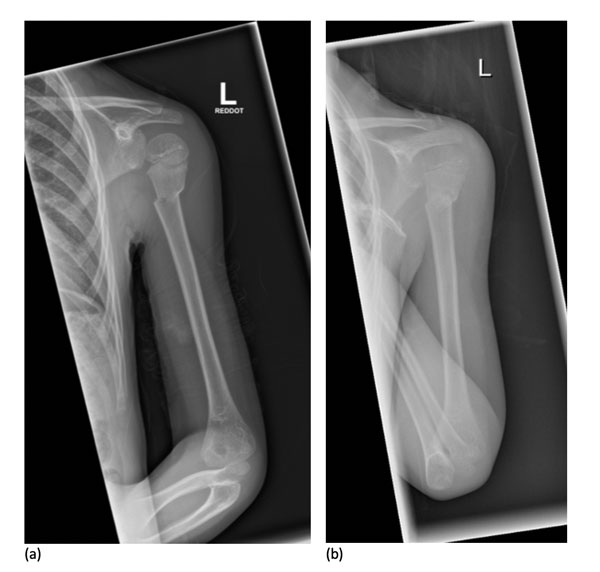
Radiografía de una fractura de húmero proximal
Imagen: “X-Ray images showing the progression from injury (a) to 7 days after (b) a non-operative approach” por Woojin Chae, Akib Khan, Sarah Abbott, Angelos Assiotis. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Desgarro completo del manguito rotador (flecha) mostrado en una RM coronal-oblicua ponderada en T2: La alta intensidad de señal del líquido que sustituye a la inserción del tendón del supraespinoso en la tuberosidad mayor indica un desgarro.
Imagen: “F0003: Coronal-oblique T2-weighted magnetic resonance image showing full-thickness rotator cuff tear (arrow), indicated by high signal intensity fluid replacing the insertion of the supraspinatus tendon at the greater tuberosity” por Gohar Abbas Naqvi, Mutaz Jadaan, and Paul Harrington. Licencia: CC BY 2.0