El cráneo es la estructura esquelética de la cabeza que sostiene la cara y forma una cavidad protectora para el cerebro. El cráneo consta de 22 huesos divididos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el viscerocráneo (esqueleto facial) y el neurocráneo. El neurocráneo se subdivide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la calota (bóveda craneal) y la base del cráneo (fosa craneal).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El viscerocráneo es responsable de mantener la estructura de los LOS Neisseria músculos de la cara. Los LOS Neisseria músculos están dispuestos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un patrón anatómico complejo para permitir una variedad de funciones faciales, como la masticación, la sonrisa, el ceño fruncido, el movimiento de los LOS Neisseria ojos y la permeabilidad de las fosas nasales.
| Hueso viscerocráneo | Número de huesos | Rasgos faciales |
|---|---|---|
| Cigomático | Par PAR The PAR is the attributable risk for an entire population. It represents the fraction of cases that would not occur in a population if the exposure was eliminated. Measures of Risk | Pómulo |
| Lagrimal | Par PAR The PAR is the attributable risk for an entire population. It represents the fraction of cases that would not occur in a population if the exposure was eliminated. Measures of Risk | Pared anteromedial de la órbita |
| Nasal | Par PAR The PAR is the attributable risk for an entire population. It represents the fraction of cases that would not occur in a population if the exposure was eliminated. Measures of Risk | Puente de la nariz |
| Palatino | Par PAR The PAR is the attributable risk for an entire population. It represents the fraction of cases that would not occur in a population if the exposure was eliminated. Measures of Risk | Cuarto posterior del paladar duro |
| Maxilar superior | Par PAR The PAR is the attributable risk for an entire population. It represents the fraction of cases that would not occur in a population if the exposure was eliminated. Measures of Risk | Mandíbula superior y tres-cuartos del paladar duro (el proceso palatino del maxilar) |
| Vómer | Único | Porción posterior del tabique nasal |
| Mandíbula | Único | Mandíbula inferior y mentón |
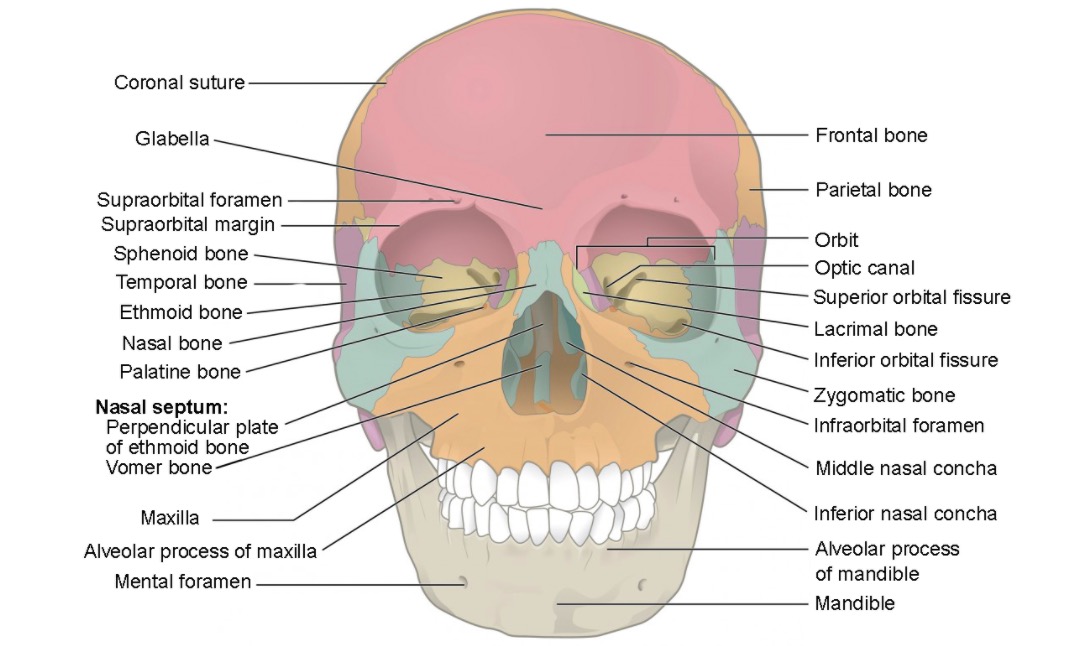
Vista anterior del cráneo mostrando los huesos del viscerocráneo:
Cigomático (azul), lagrimal (verde), nasal (azul/línea media), cornetes nasales inferiores (azul dentro de la cavidad nasal), palatino (naranja oscuro), maxilar (naranja claro), vómer (azul/línea media), mandíbula (beige), y etmoides (gris dentro de la cavidad nasal)
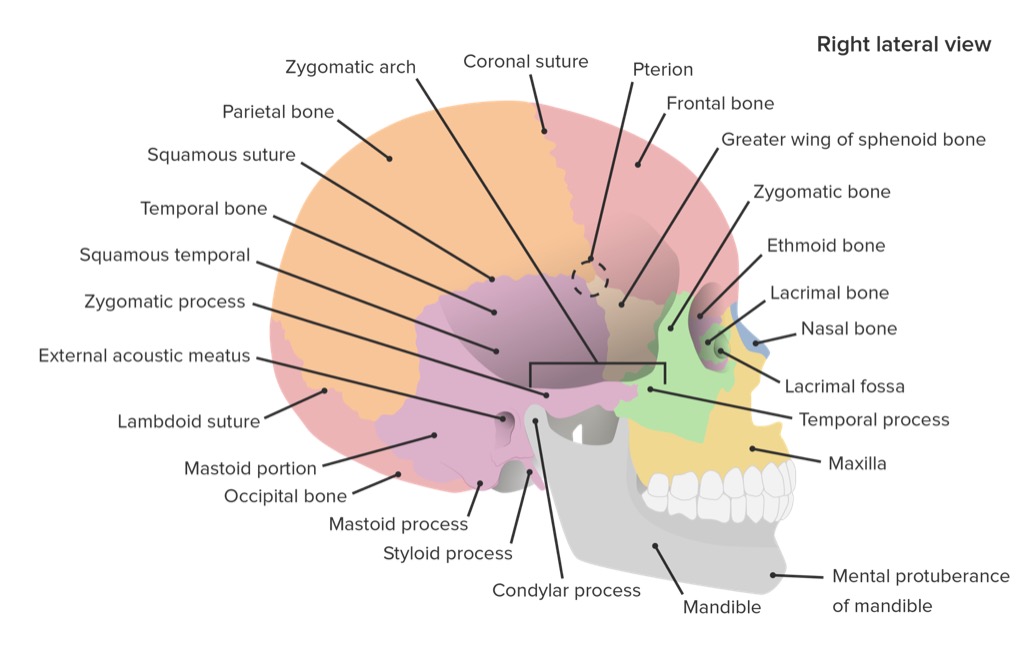
Vista lateral del cráneo mostrando los huesos y las suturas.
Imagen por Lecturio.El neurocráneo es el complejo de huesos que recubre el cerebro. La calota es la parte superior del neurocráneo y está formado por el hueso frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy no apareado, el hueso occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy no apareado, los LOS Neisseria huesos parietales bilaterales y los LOS Neisseria huesos temporales bilaterales. Los LOS Neisseria huesos están inicialmente separados (las fontanelas al AL Amyloidosis nacer) y se fusionan durante la infancia. A continuación, los LOS Neisseria huesos se unen mediante suturas específicas: coronal Coronal Computed Tomography (CT), escamosa, lambdoidea y sagital.
Huesos del neurocráneo:
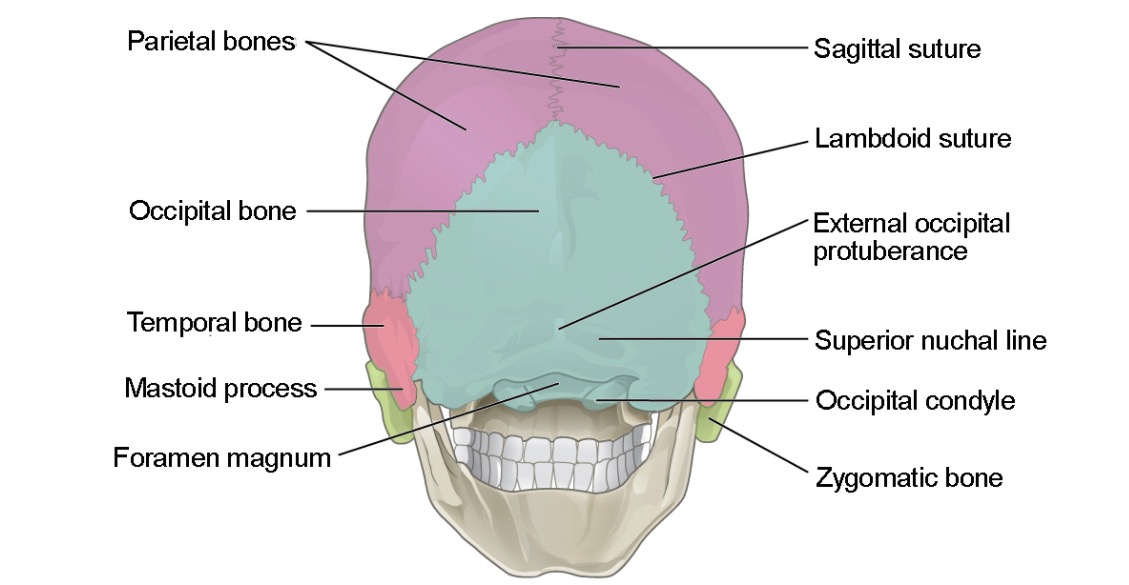
Vista posterior (ligeramente inferior) del cráneo mostrando los huesos de la calota:
el hueso frontal (no se muestra), el hueso occipital (azul) y el hueso parietal (púrpura)

Vista lateral del cráneo mostrando los huesos y las suturas del cráneo.
Imagen por Lecturio.Las suturas principales son articulaciones inmóviles entre huesos adyacentes del cráneo:

Vista lateral del cráneo mostrando las suturas coronal, lambdoidea y escamosa
Imagen: “Skull sutures” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Las fontanelas principales son áreas de tejido conectivo dentro de los LOS Neisseria espacios/entre las placas óseas, que están abiertas durante la infancia:
| Fontanela | Forma | Localización | Cierre |
|---|---|---|---|
| Posterior, occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy o lambdoidea | Triángulo | Unión de las suturas sagital y lambdoidea | 3 meses |
| Anterior, bregmática o frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy | Diamante | Unión de las suturas sagital y coronal Coronal Computed Tomography (CT) | 18–24 meses |
| Esfenoidal o anterolateral | Irregulares y bilaterales | Entre los LOS Neisseria huesos frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy, parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy y esfenoides | 6 meses |
| Mastoidea o posterolateral | Irregulares y bilaterales | Entre los LOS Neisseria huesos parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy, temporal y occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy | 24 meses |
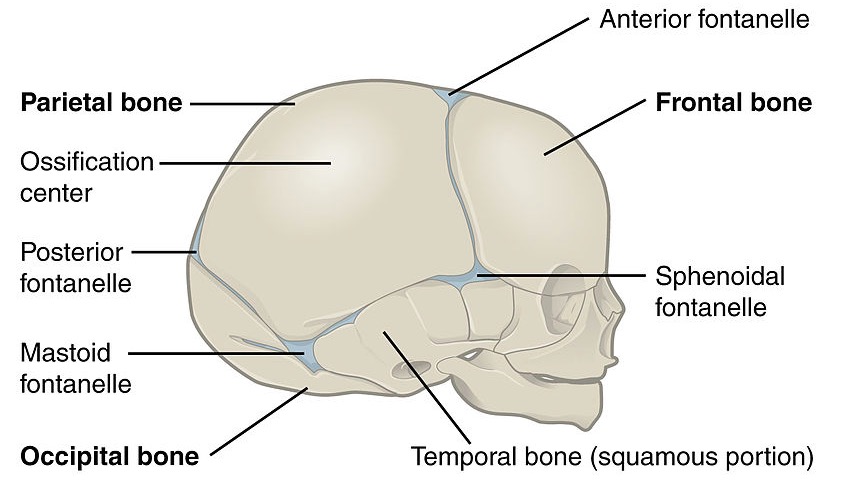
Vista lateral del cráneo de un recién nacido mostrando las fontanelas posterior, anterior, esfenoidal y mastoidea
Imagen: “Lateral view of a newborn’s skull” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0La base del cráneo es una región altamente compleja del cráneo con muchos puntos de referencia anatómicos importantes y forámenes para que los LOS Neisseria nervios craneales y la irrigación entren y salgan del cráneo. El conocimiento profundo de la ubicación de los LOS Neisseria forámenes y las estructuras que los LOS Neisseria atraviesan son de vital importancia.
| Región | Límites | Huesos | Estructuras que penetran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria forámenes | Contenido |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fosa craneal anterior |
|
Frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy (placas orbitales) | Foramen ciego: venas emisarias nasales que conducen al AL Amyloidosis seno sagital superior |
|
| Etmoides (placa cribiforme y crista galli) |
|
|||
| Fosa craneal media |
|
Esfenoides ( alas ALAS An enzyme of the transferase class that catalyzes condensation of the succinyl group from succinyl coenzyme a with glycine to form delta-aminolevulinate. It is a pyridoxal phosphate protein and the reaction occurs in mitochondria as the first step of the heme biosynthetic pathway. The enzyme is a key regulatory enzyme in heme biosynthesis. In liver feedback is inhibited by heme. Heme Metabolism menores y mayores) |
|
|
| Esfenoides ( alas ALAS An enzyme of the transferase class that catalyzes condensation of the succinyl group from succinyl coenzyme a with glycine to form delta-aminolevulinate. It is a pyridoxal phosphate protein and the reaction occurs in mitochondria as the first step of the heme biosynthetic pathway. The enzyme is a key regulatory enzyme in heme biosynthesis. In liver feedback is inhibited by heme. Heme Metabolism mayores) |
|
|||
| Temporal |
|
|||
| Fosa craneal posterior | Anterior: dorso de la silla turca del esfenoides/borde superior de la porción petrosa de los LOS Neisseria huesos temporales | Temporal |
|
|
| Occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy |
|
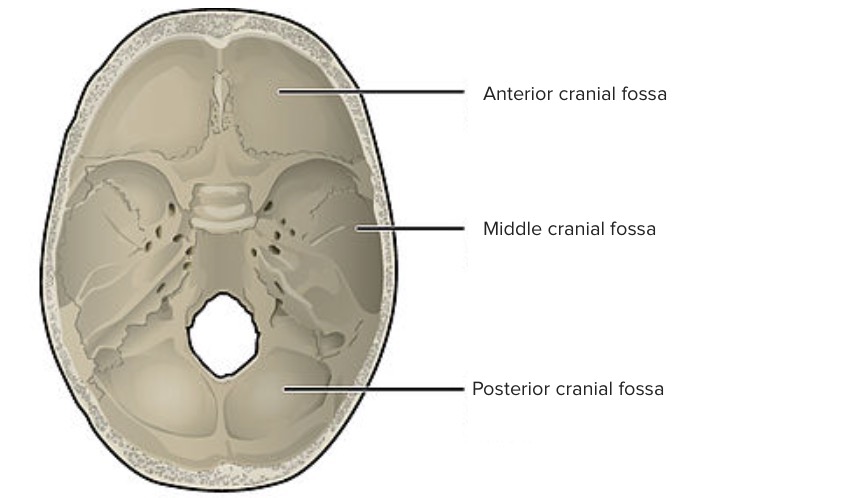
Vista superior de la base del cráneo:
La superficie interna de la base del cráneo se divide en fosa craneal anterior, media y posterior. Las fosas contienen los lóbulos frontal y temporal de los hemisferios cerebrales, el cerebelo, la protuberancia y el bulbo raquídeo.
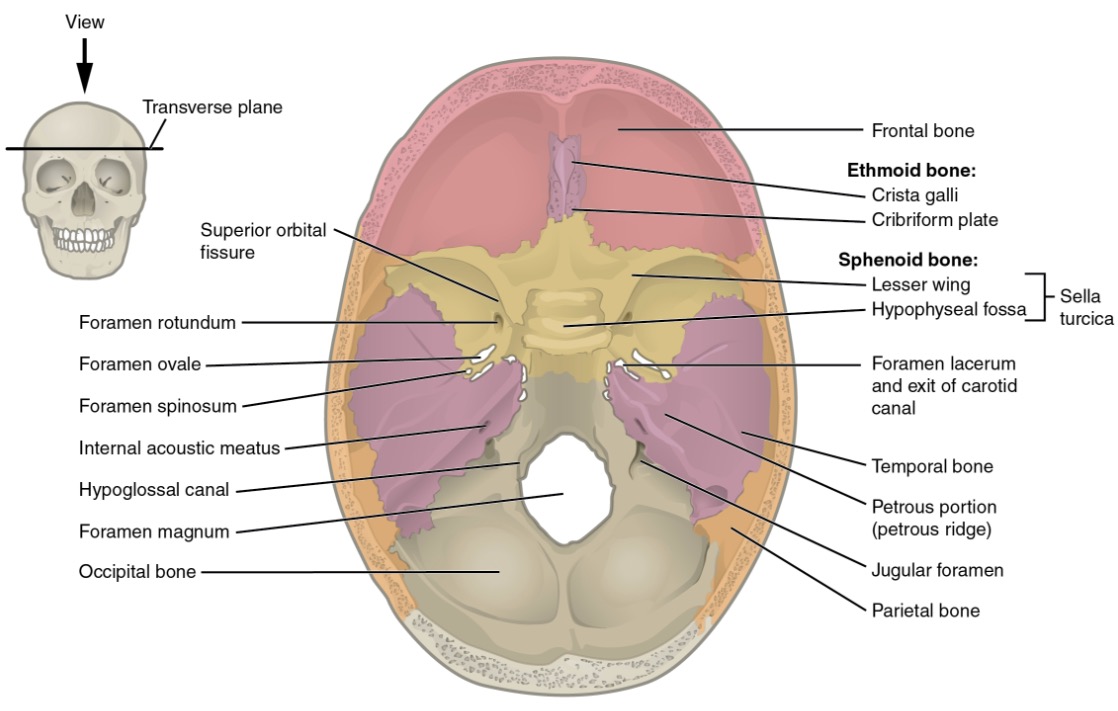
Vista superior de la base del cráneo mostrando los límites de la fosa craneal
Imagen: “Superior view of skull base” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0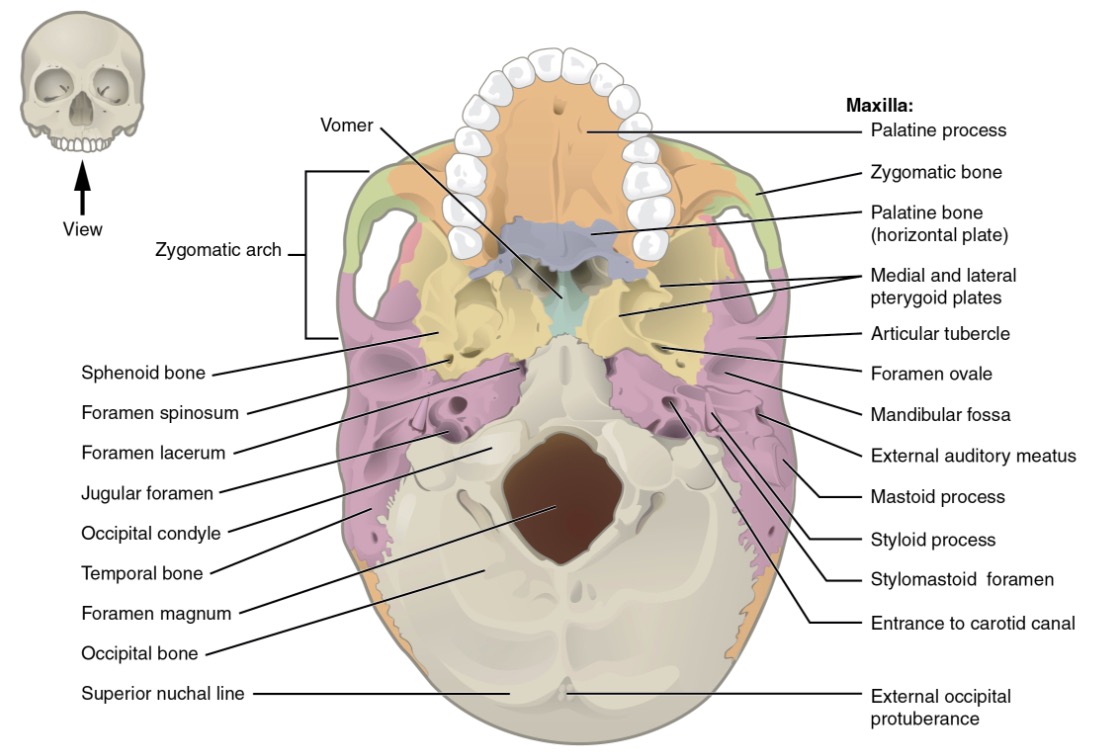
Vista inferior del cráneo mostrando los diversos forámenes
Imagen: “Inferior view of skull base” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0| Fosa temporal* | Fosa infratemporal | Fosa pterigopalatina | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Localización | Por encima del arco cigomático del hueso temporal |
|
|
| Límites |
|
|
|
| Contenido |
|
|
|
| Forámenes (y la estructura de conexión) | Fisura orbitaria inferior: órbita |
|
|
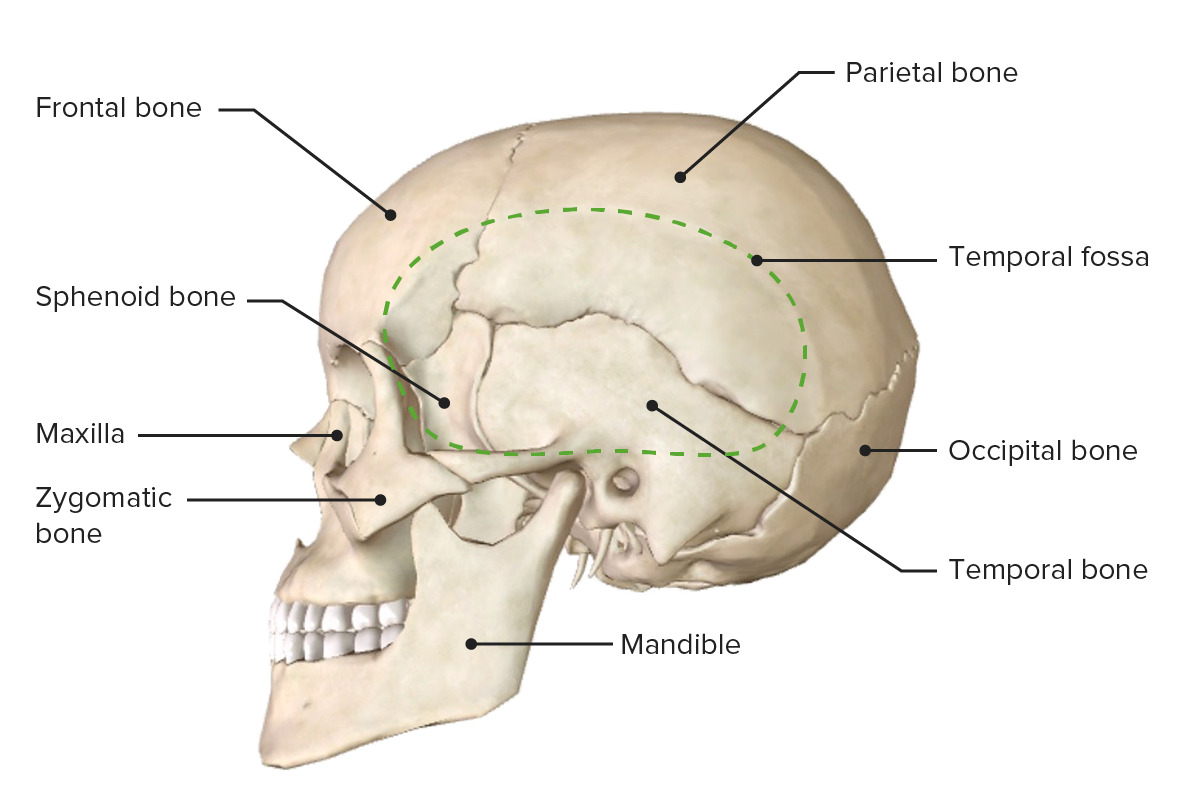
Vista lateral del cráneo mostrando la fosa temporal
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio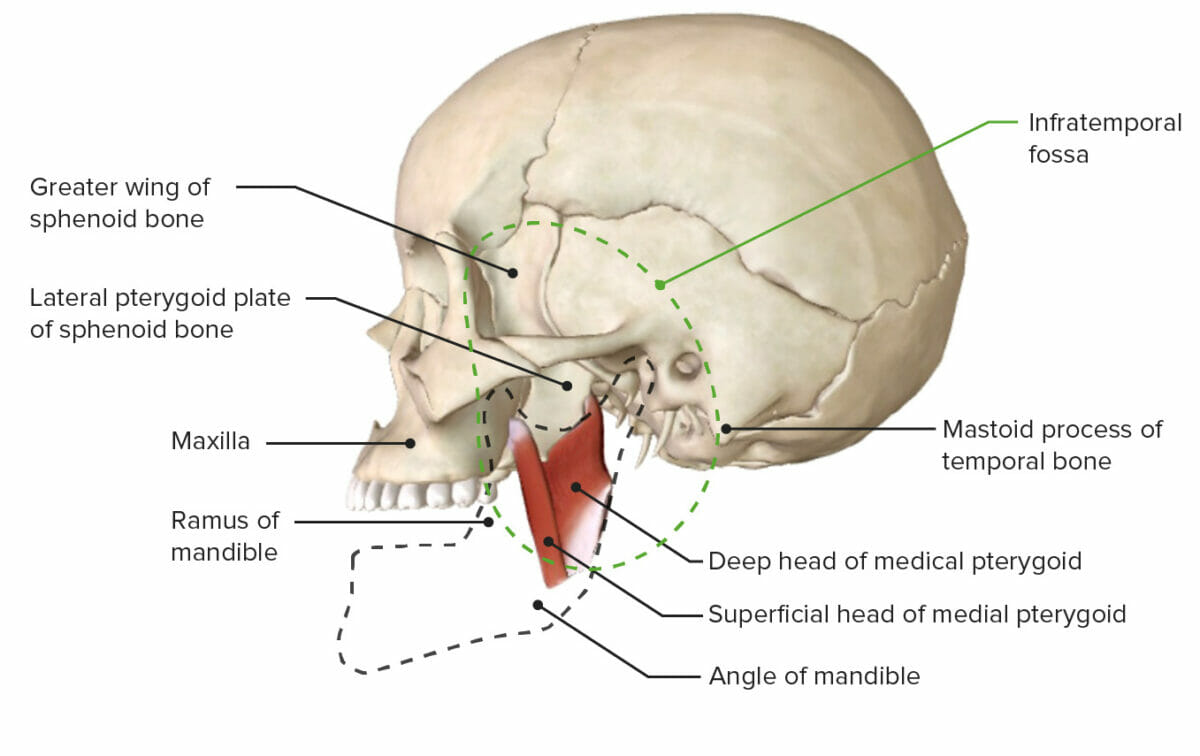
Vista lateral de la base del cráneo mostrando la fosa infratemporal
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio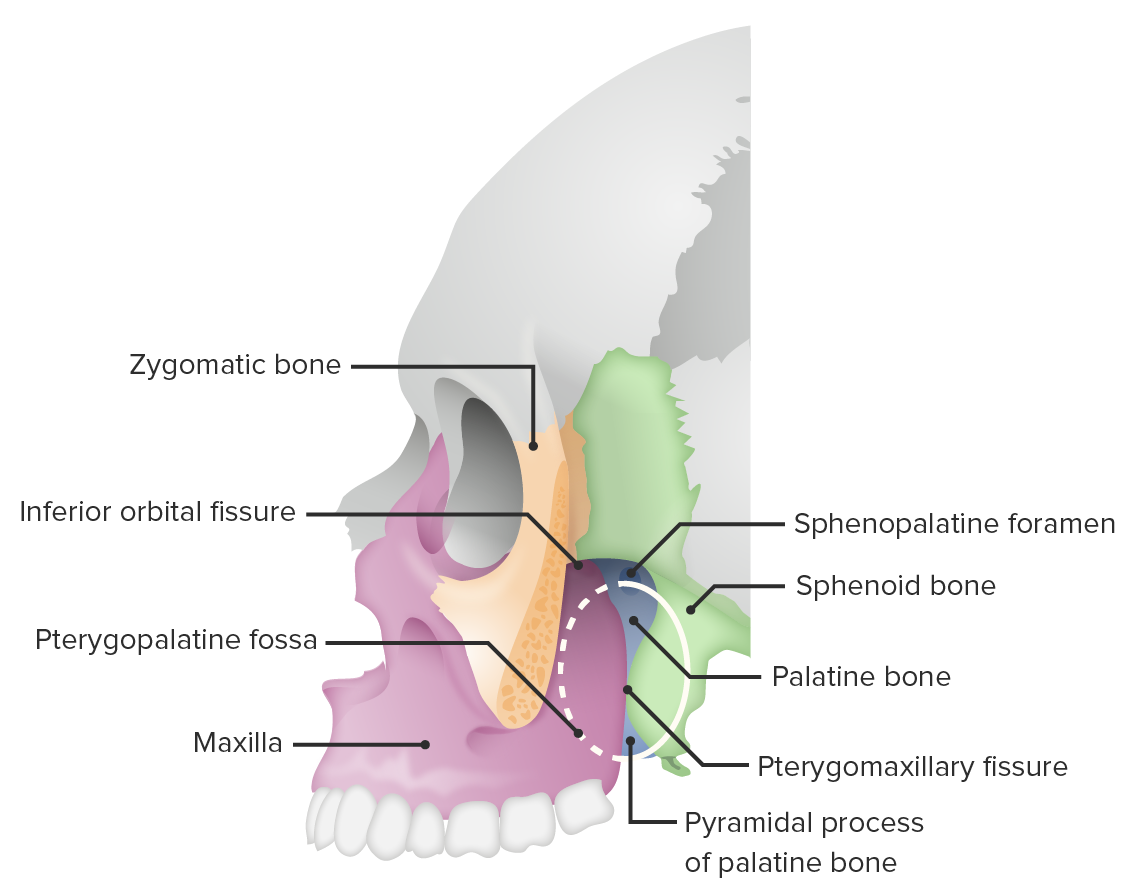
Vista lateral del cráneo (corte del hueso cigomático) mostrando la fosa pterigopalatina
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio