La fiebre Q es una zoonosis bacteriana causada por Coxiella burnetii Coxiella burnetii A species of gram-negative bacteria that grows preferentially in the vacuoles of the host cell. It is the etiological agent of q fever. Coxiella/Q Fever. La transmisión ocurre principalmente a través de la inhalación de aerosoles contaminados y la exposición a productos animales infectados. La presentación clínica puede variar y a menudo resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una enfermedad leve con síntomas similares a los LOS Neisseria de la gripe. Otras manifestaciones incluyen neumonía, hepatitis, endocarditis Endocarditis Endocarditis is an inflammatory disease involving the inner lining (endometrium) of the heart, most commonly affecting the cardiac valves. Both infectious and noninfectious etiologies lead to vegetations on the valve leaflets. Patients may present with nonspecific symptoms such as fever and fatigue. Endocarditis y meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis aséptica. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un pequeño porcentaje de pacientes, la enfermedad puede volverse crónica. Para el diagnóstico se requiere un alto grado de sospecha, que se apoya en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la serología y reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). Los LOS Neisseria antibióticos son el tratamiento de elección.
Last updated: Jan 29, 2026
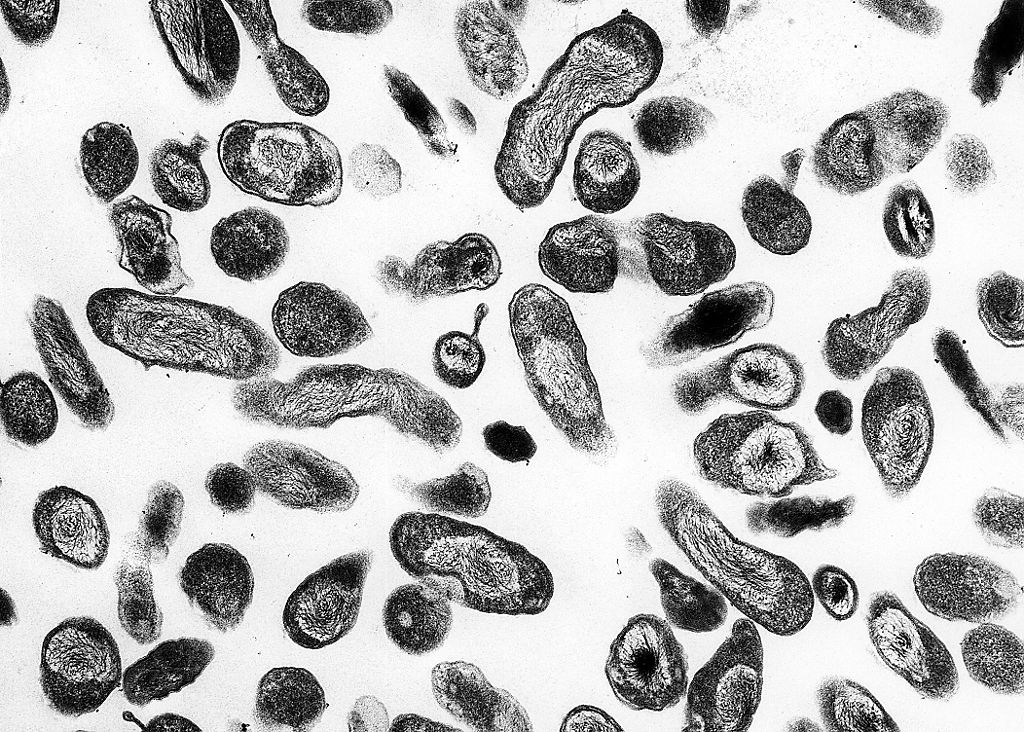
Coxiella bajo microscopio de luz
Imagen: “Coxiella burnetii” por NIAID. Licencia: Dominio Público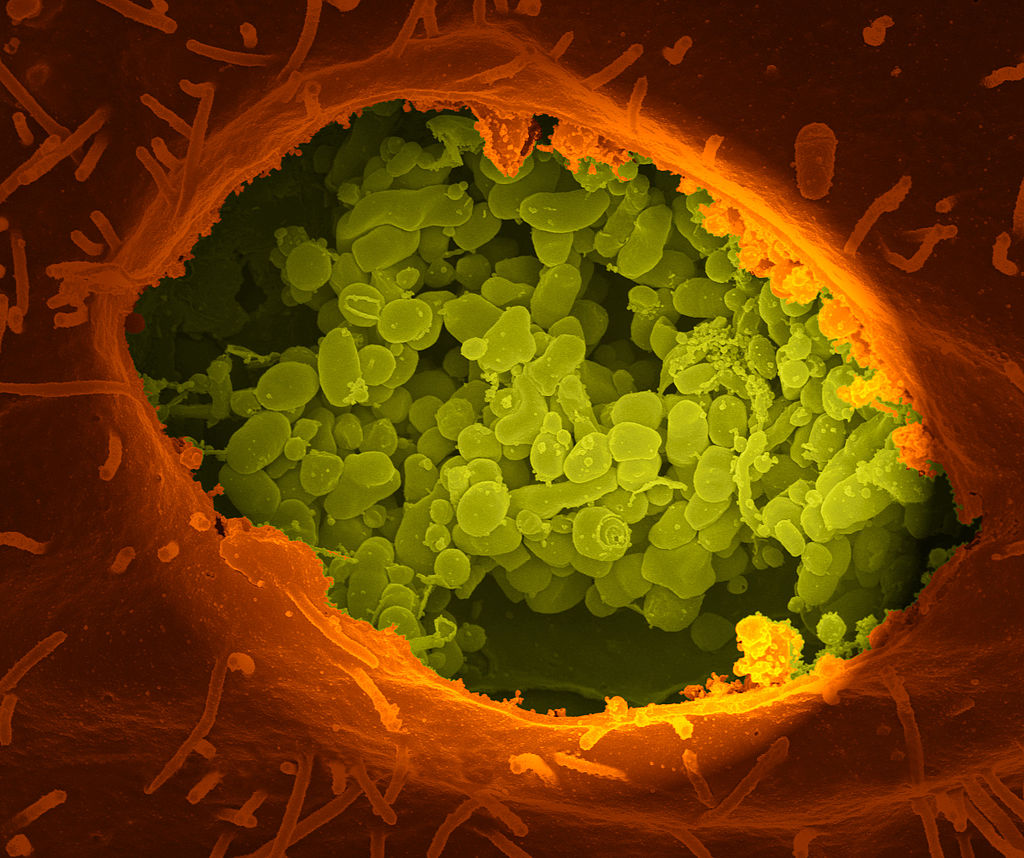
Una fractura seca de una celda que expone el contenido de una vacuola donde crece Coxiella burnetii (color verde)
Imagen: “A dry fracture of a Vero cell” por National Institutes of Health (NIH). Licencia: Dominio PúblicoCoxiella burnetii Coxiella burnetii A species of gram-negative bacteria that grows preferentially in the vacuoles of the host cell. It is the etiological agent of q fever. Coxiella/Q Fever causa la fiebre Q.
Variación de fase antigénica:
Variantes morfológicas:
Escape de muerte intracelular:
Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden presentar una amplia gama de síntomas que varían en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gravedad, desde asintomáticos hasta enfermedad severa.
El período de incubación de la infección aguda es de aproximadamente 20 días. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden presentar cualquiera de las siguientes afecciones:
La infección crónica puede manifestarse meses o años después de una infección aguda.
La fiebre Q en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el embarazo se asocia con:
La fiebre Q carece de una presentación clínica distintiva; por lo tanto, el diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un alto índice de sospecha basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo del paciente.
Pruebas de diagnóstico:
Evaluación de soporte:
La terapia con antibióticos incluye:
| Organismo | Coxiella burnetii Coxiella burnetii A species of gram-negative bacteria that grows preferentially in the vacuoles of the host cell. It is the etiological agent of q fever. Coxiella/Q Fever | Legionella pneumophila Legionella pneumophila A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria that is the causative agent of legionnaires’ disease. It has been isolated from numerous environmental sites as well as from human lung tissue, respiratory secretions, and blood. Legionella/Legionellosis | Francisella tularensis Francisella Tularensis Aminoglycosides |
|---|---|---|---|
| Características |
|
|
|
| Reservorio |
|
Acuático |
|
| Transmisión |
|
|
|
| Presentación clínica | Fiebre Q |
|
Tularemia |
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
| Tratamiento | Doxiciclina |
|
Estreptomicina |
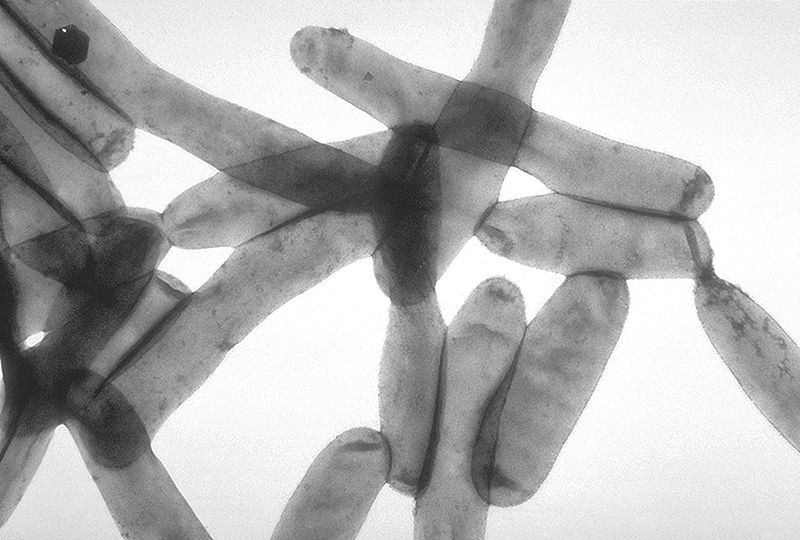
Vista microscópica de Legionella pneumophila
Imagen: “Legionella pneumophila” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público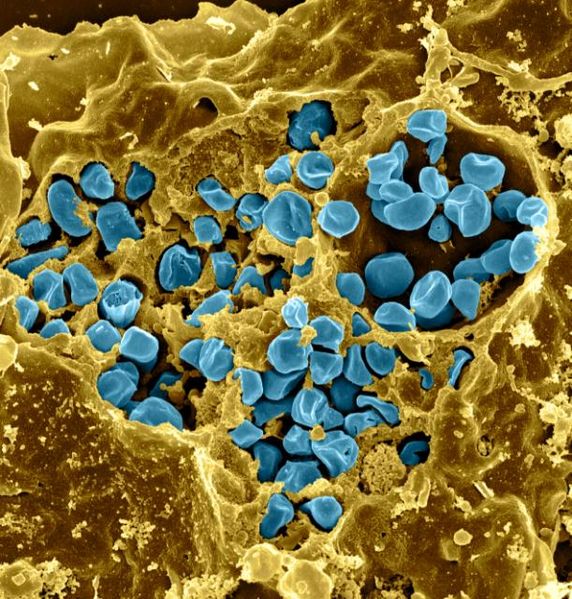
Fractura seca de un macrófago infectado con Francisella tularensis (color azul)
Imagen: “Macrophage Infected with Francisella tularensis Bacteria” por NIAID. Licencia: CC BY 2.0