El botulismo es un síndrome neuroparalítico poco frecuente causado por el Clostridium botulinum Clostridium botulinum A species of anaerobic, gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria in the family clostridiaceae that produces proteins with characteristic neurotoxicity. It is the etiologic agent of botulism in humans, wild fowl, horses; and cattle. Seven subtypes (sometimes called antigenic types, or strains) exist, each producing a different botulinum toxin (botulinum toxins). The organism and its spores are widely distributed in nature. Clostridia ( C. botulinum C. botulinum A species of anaerobic, gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria in the family clostridiaceae that produces proteins with characteristic neurotoxicity. It is the etiologic agent of botulism in humans, wild fowl, horses; and cattle. Seven subtypes (sometimes called antigenic types, or strains) exist, each producing a different botulinum toxin (botulinum toxins). The organism and its spores are widely distributed in nature. Clostridia). Libera una neurotoxina mortal (toxina botulínica) que provoca diversos grados de parálisis muscular y distintos síndromes clínicos. Los LOS Neisseria tipos más comunes de botulismo son los LOS Neisseria transmitidos por alimentos y el infantil. El botulismo se presenta con visión borrosa, insuficiencia respiratoria y una parálisis flácida simétrica y descendente. La caracterización incluye el sensorio intacto, frecuencia cardíaca y presión arterial normales, ausencia de fiebre y ausencia de déficits sensoriales. El diagnóstico se realiza por motivos clínicos y puede confirmarse mediante el aislamiento de las bacterias o toxinas a partir de heces, muestras de las heridas o fuentes de alimentos. El enfoque del tratamiento de un caso de botulismo debe incluir el manejo rápido de la insuficiencia respiratoria, la administración de la antitoxina y los LOS Neisseria cuidados de soporte para la parálisis.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El botulismo es un síndrome neuroparalítico poco frecuente causado por la bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology Clostridium botulinum Clostridium botulinum A species of anaerobic, gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria in the family clostridiaceae that produces proteins with characteristic neurotoxicity. It is the etiologic agent of botulism in humans, wild fowl, horses; and cattle. Seven subtypes (sometimes called antigenic types, or strains) exist, each producing a different botulinum toxin (botulinum toxins). The organism and its spores are widely distributed in nature. Clostridia ( C. botulinum C. botulinum A species of anaerobic, gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria in the family clostridiaceae that produces proteins with characteristic neurotoxicity. It is the etiologic agent of botulism in humans, wild fowl, horses; and cattle. Seven subtypes (sometimes called antigenic types, or strains) exist, each producing a different botulinum toxin (botulinum toxins). The organism and its spores are widely distributed in nature. Clostridia), que libera una neurotoxina mortal (toxina botulínica), que provoca diversos grados de parálisis muscular y distintos síndromes clínicos.
Una fotomicrografía de la bacteria C. botulinum
Imagen: “Clostridium botulinum” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl medio de exposición a la toxina determinará el tipo de botulismo; la toxina no se absorbe a través de la piel intacta.
La exposición puede producirse a través de los LOS Neisseria siguientes mecanismos:
Mecanismo de patogénesis:
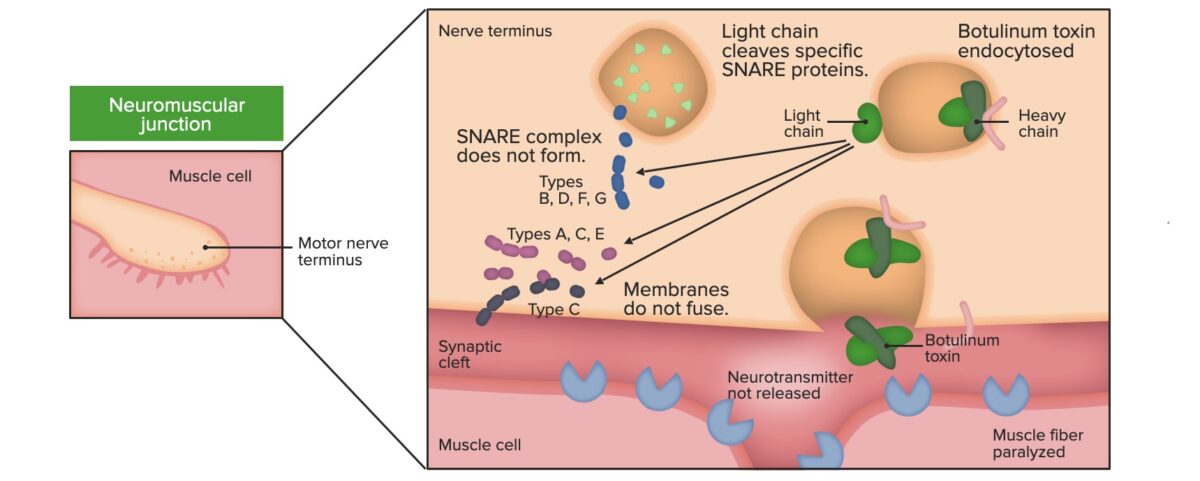
Efecto de la toxina botulínica a nivel de la unión neuromuscular: inhibición de la liberación de ACh
Imagen por Lecturio.La presentación clásica del botulismo incluye parálisis simétricas de los LOS Neisseria nervios craneales y parálisis descendente. Las 5 características clave del botulismo son:
Las neuropatías craneales son comunes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todos los LOS Neisseria tipos de botulismo. La presentación clásica incluye las “4 D” (síntomas bulbares):
El botulismo se presenta con hallazgos autonómicos:
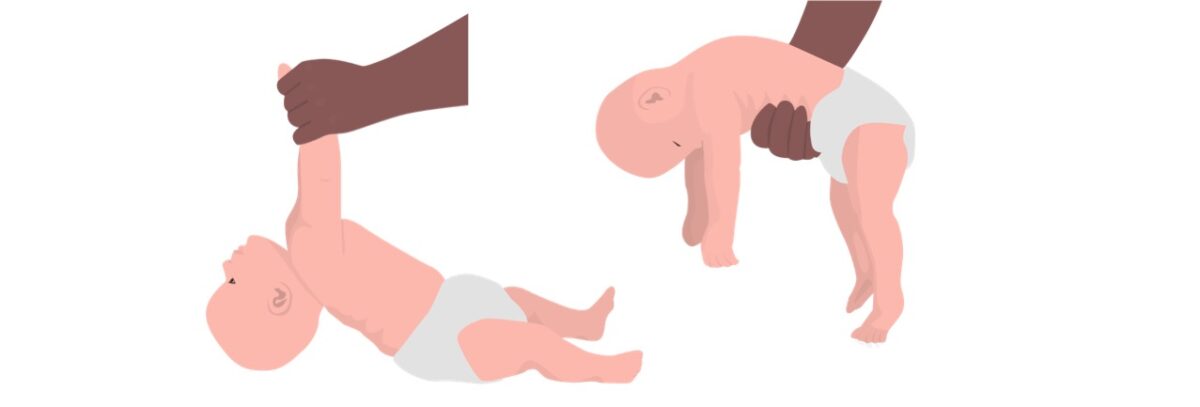
Una presentación importante en el botulismo infantil: el síndrome del bebé flácido
Imagen por Lecturio.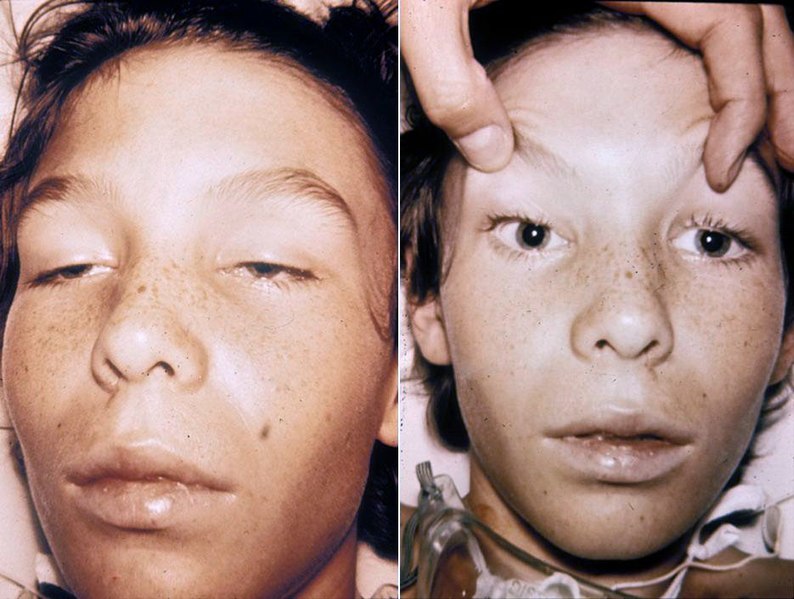
Ptosis en un niño con botulismo: El paciente está alerta y orientado.
Imagen: “Botulism1and2” por Herbert L. Fred, MD and Hendrik A. van Dijk. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Una historia clínica y un diagnóstico detallado son importantes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el botulismo, ya que las pruebas tardan mucho tiempo. Si los LOS Neisseria antecedentes del caso son altamente sugestivos de botulismo, el tratamiento no debe retrasarse.
La antitoxina es la piedra angular del tratamiento del botulismo. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos existen dos presentaciones principales:
Antitoxina botulínica heptavalente:
Inmunoglobulina botulínica humana intravenosa (BIG-IV):