Las benzodiacepinas actúan sobre el receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors del ácido gamma-aminobutírico tipo A ( GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNSA) produciendo efectos inhibidores sobre el SNC. Las benzodiacepinas no imitan al AL Amyloidosis GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS, el principal neurotransmisor inhibidor en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos, sino que potencian la actividad del GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS. La clase de medicamentos de las benzodiacepinas tiene propiedades ansiolíticas, relajantes musculares, hipnóticas, sedantes y anticonvulsivantes. Generalmente, estos agentes no se recomiendan para uso a largo plazo, ya que los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden desarrollar dependencia fisiológica y psicológica. Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios pueden incluir deterioro cognitivo, somnolencia y depresión respiratoria.
Last updated: Jul 2, 2022
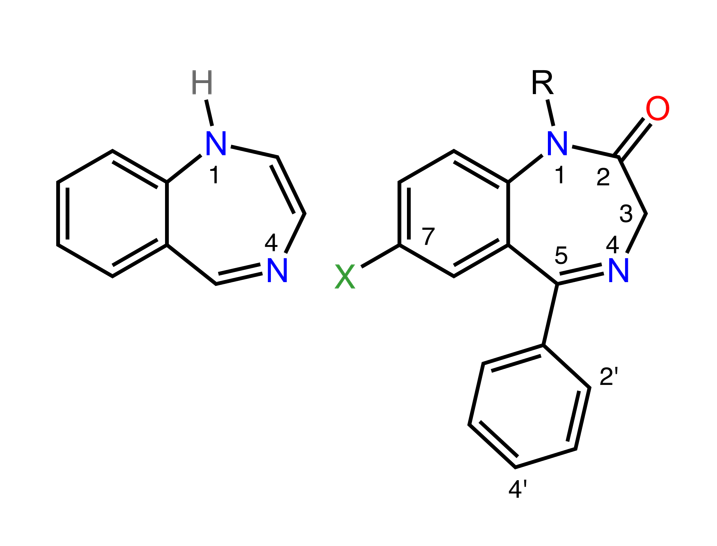
Estructura de las benzodiacepinas:
La imagen de la izquierda muestra el anillo clásico de 1,4-benzodiacepina. La imagen de la derecha muestra el sistema más común de anillos de las benzodiacepinas.
GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS:
Receptores GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS:
Efectos terapéuticos de las benzodiacepinas:
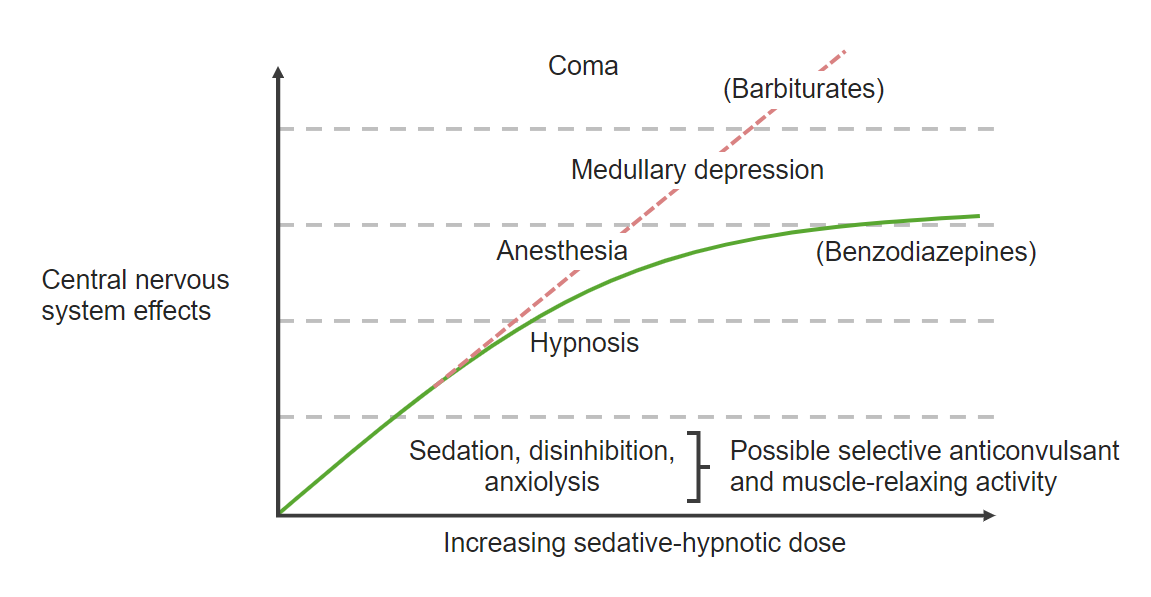
Curva dosis-respuesta de las benzodiacepinas:
La curva dosis-respuesta de las benzodiacepinas se muestra arriba. Las benzodiacepinas ejercen propiedades ansiolíticas a dosis bajas y tienen un efecto de techo, en el cual los incrementos de las dosis alcanzan su punto máximo en los efectos anestésicos.
Las benzodiacepinas lipofílicas tienen una absorción más rápida.
La eliminación se produce a través del riñón ( los LOS Neisseria glucurónidos se excretan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la orina).
La siguiente tabla destaca a las benzodiacepinas y aborda las propiedades de cada una. Con respecto a la farmacocinética, es importante prestar atención al AL Amyloidosis inicio de acción, el metabolismo y la eliminación.
| Medicamento | Inicio de acción | Duración | Metabolismo | Principales metabolitos activos |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alprazolam Alprazolam A triazolobenzodiazepine compound with antianxiety and sedative-hypnotic actions, that is efficacious in the treatment of panic disorders, with or without agoraphobia, and in generalized anxiety disorders. Benzodiazepines | Intermedio | Intermedia | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | No |
| Clordiazepóxido | Intermedio | Larga | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | Sí |
| Clonazepam Clonazepam An anticonvulsant used for several types of seizures, including myotonic or atonic seizures, photosensitive epilepsy, and absence seizures, although tolerance may develop. It is seldom effective in generalized tonic-clonic or partial seizures. The mechanism of action appears to involve the enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor responses. Benzodiazepines | Intermedio | Intermedia | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | No |
| Clorazepato | Rápido | Larga |
|
Sí |
| Diazepam Diazepam A benzodiazepine with anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, sedative, muscle relaxant, and amnesic properties and a long duration of action. Its actions are mediated by enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid activity. Benzodiazepines | Rápido | Larga |
|
Sí |
| Flurazepam Flurazepam A benzodiazepine derivative used mainly as a hypnotic. Benzodiazepines | Rápido | Larga | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | Sí |
| Lorazepam Lorazepam A benzodiazepine used as an anti-anxiety agent with few side effects. It also has hypnotic, anticonvulsant, and considerable sedative properties and has been proposed as a preanesthetic agent. Benzodiazepines | Intermedio | Intermedia | Glucuronidación | No |
| Midazolam Midazolam A short-acting hypnotic-sedative drug with anxiolytic and amnestic properties. It is used in dentistry, cardiac surgery, endoscopic procedures, as preanesthetic medication, and as an adjunct to local anesthesia. The short duration and cardiorespiratory stability makes it useful in poor-risk, elderly, and cardiac patients. It is water-soluble at ph less than 4 and lipid-soluble at physiological pH. Benzodiazepines | Rápido | Corta | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | Sí |
| Oxazepam Oxazepam A benzodiazepine used in the treatment of anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and insomnia. Benzodiazepines | Lento | Corta | Glucuronidación | No |
| Temazepam Temazepam A benzodiazepine that acts as a gamma-aminobutyric acid modulator and anti-anxiety agent. Benzodiazepines | Lento | Intermedia | Glucuronidación | No |
| Triazolam Triazolam A short-acting benzodiazepine used in the treatment of insomnia. Its use at lower doses with appropriate care and labeling has been reaffirmed by the fda and most other countries. Benzodiazepines | Rápido | Corta | CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) | No |
Las benzodiacepinas son depresores del SNC. Por lo tanto, son clínicamente útiles para situaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las que puede ser necesario un agente sedante. La siguiente tabla aborda los LOS Neisseria agentes individuales y sus indicaciones. Estas son las indicaciones generales de las benzodiacepinas:
| Medicamento | Vías de administración | Indicaciones |
|---|---|---|
| Alprazolam Alprazolam A triazolobenzodiazepine compound with antianxiety and sedative-hypnotic actions, that is efficacious in the treatment of panic disorders, with or without agoraphobia, and in generalized anxiety disorders. Benzodiazepines | Oral |
|
| Clordiazepóxido | Oral |
|
| Clonazepam Clonazepam An anticonvulsant used for several types of seizures, including myotonic or atonic seizures, photosensitive epilepsy, and absence seizures, although tolerance may develop. It is seldom effective in generalized tonic-clonic or partial seizures. The mechanism of action appears to involve the enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor responses. Benzodiazepines | Oral |
|
| Clorazepato | Oral |
|
| Diazepam Diazepam A benzodiazepine with anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, sedative, muscle relaxant, and amnesic properties and a long duration of action. Its actions are mediated by enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid activity. Benzodiazepines |
|
|
| Flurazepam Flurazepam A benzodiazepine derivative used mainly as a hypnotic. Benzodiazepines | Oral | Insomnio |
| Lorazepam Lorazepam A benzodiazepine used as an anti-anxiety agent with few side effects. It also has hypnotic, anticonvulsant, and considerable sedative properties and has been proposed as a preanesthetic agent. Benzodiazepines (Ativan®) |
|
|
| Midazolam Midazolam A short-acting hypnotic-sedative drug with anxiolytic and amnestic properties. It is used in dentistry, cardiac surgery, endoscopic procedures, as preanesthetic medication, and as an adjunct to local anesthesia. The short duration and cardiorespiratory stability makes it useful in poor-risk, elderly, and cardiac patients. It is water-soluble at ph less than 4 and lipid-soluble at physiological pH. Benzodiazepines (Versed®) |
|
|
| Oxazepam Oxazepam A benzodiazepine used in the treatment of anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and insomnia. Benzodiazepines | Oral |
|
| Temazepam Temazepam A benzodiazepine that acts as a gamma-aminobutyric acid modulator and anti-anxiety agent. Benzodiazepines (Restoril®) | Oral | Insomnio |
| Triazolam Triazolam A short-acting benzodiazepine used in the treatment of insomnia. Its use at lower doses with appropriate care and labeling has been reaffirmed by the fda and most other countries. Benzodiazepines (Halcion®) | Oral | Insomnio |
Hay algunos puntos de alta importancia a los LOS Neisseria que se debe prestar atención al AL Amyloidosis considerar las benzodiacepinas:
Estos medicamentos rara vez provocan una sobredosis de forma aislada. Cuando se combinan con otras clases de medicamentos, como el alcohol y los LOS Neisseria opiáceos, existe un riesgo mucho mayor de toxicidad.
Los LOS Neisseria siguientes son usos terapéuticos de las benzodiacepinas: