A ataxia Ataxia Impairment of the ability to perform smoothly coordinated voluntary movements. This condition may affect the limbs, trunk, eyes, pharynx, larynx, and other structures. Ataxia may result from impaired sensory or motor function. Sensory ataxia may result from posterior column injury or peripheral nerve diseases. Motor ataxia may be associated with cerebellar diseases; cerebral cortex diseases; thalamic diseases; basal ganglia diseases; injury to the red nucleus; and other conditions. Ataxia-telangiectasia de Friedreich é uma doença autossómica recessiva caracterizada por degeneração espinocerebelar progressiva. Apresenta-se na 1ª a 2ª décadas de vida com ataxia Ataxia Impairment of the ability to perform smoothly coordinated voluntary movements. This condition may affect the limbs, trunk, eyes, pharynx, larynx, and other structures. Ataxia may result from impaired sensory or motor function. Sensory ataxia may result from posterior column injury or peripheral nerve diseases. Motor ataxia may be associated with cerebellar diseases; cerebral cortex diseases; thalamic diseases; basal ganglia diseases; injury to the red nucleus; and other conditions. Ataxia-telangiectasia progressiva da marcha, fraqueza, tremor Tremor Cyclical movement of a body part that can represent either a physiologic process or a manifestation of disease. Intention or action tremor, a common manifestation of cerebellar diseases, is aggravated by movement. In contrast, resting tremor is maximal when there is no attempt at voluntary movement, and occurs as a relatively frequent manifestation of parkinson disease. Myotonic Dystrophies, disartria, disfagia, cardiomiopatia hipertrófica e/ou diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus. Os doentes acabam por ficar acamados. O diagnóstico é confirmado por testes Testes Gonadal Hormones genéticos que mostram expansão repetida de trinucleotídeos no gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics FXN. O tratamento é de suporte e a maioria dos doentes morre de doença cardíaca na 4ª ou 5ª década de vida.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Exemplo de cifoescoliose grave, um achado comum na ataxia de Friedreich
Imagem : “Lateral curvature of the spine and round shoulders ” por Lovett, Robert W. Licença: Public Domain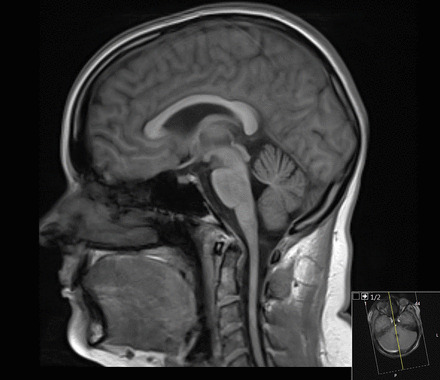
RM de um doente com ataxia de Friedreich: observar a diminuição de espessura da medula espinhal cervical
Imagem : “Figure 6” por Rajith Nilantha de Silva et al. Licença: CC BY 4.0O diagnóstico diferencial para FA FA Inhaled Anesthetics inclui as seguintes condições: