Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus – Hyperglycemia
-
Slides HyperglycemiaDiabetesMellitus EndocrinePathology.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
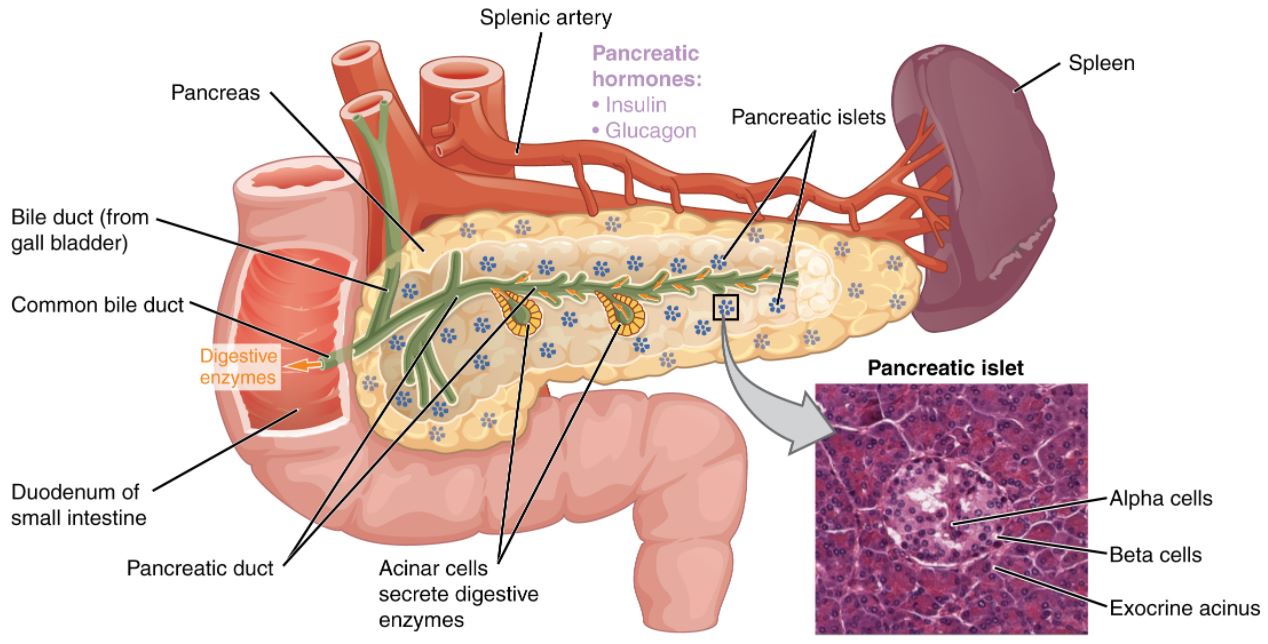
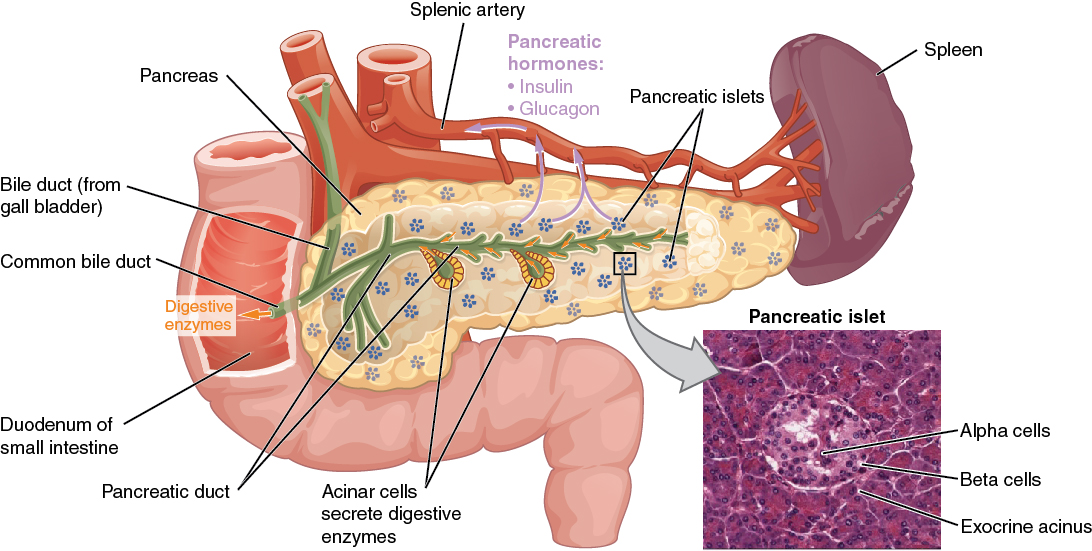
00:01 Let’s talk about type I, epidemiology: early age. 00:05 Remember when I say early, we’re not talking just infants, huh? It has a bimodal distribution, with peaks at 4 to 6 years of age and between 10 and 14 years of age. 00:16 The incidence in the United States is 22 per 100,000 annually. 00:20 With type I, insulin or non-insulin dependent? Good, insulin dependent. 00:27 Weight usually normal, they won’t be obese; genetic predisposition, 50 percent amongst twins. 00:36 HLA, definitely know about DQ, also know about DR3 and 4, those links you definitely want to know; pathophysiology, ah, autoimmunity. 00:49 So, apart from genetic, which could be a component, autoimmune disease. 00:53 What if you have autoimmune disease of the thyroid, what’s that called? I’m sorry, I can’t hear you. 01:01 Good, Hashimoto. 01:02 Autoimmune disease of the adrenals, what’s that called? Addison’s. 01:07 Autoimmune disease of the pancreas, what’s this called? Type I diabetes. 01:11 Put those together, give me diagnosis… polyglandular endocrinopathies… do not forget that. 01:19 Polyglandular? poly - many glands, these three… thyroid, pancreas, adrenal pathology… endocrinopathy. 01:30 Carbohydrate intolerance with hyperglycemia. 01:34 Clinical PPP… polyphagia, polyuria, polydipsia; acute complication… DKA. 01:43 Now, with the autoimmune disease, I told you that for the most part, your patient walking through that door with type I diabetes doesn’t have insulin. 01:54 Theoretically, if there was a time in which you can actually measure your autoimmunity, you’d find the phenomenon in type I diabetes called insulitis. 02:07 Some immunologists will call type I diabetic a type II hypersensitivity. 02:14 Many immunologists will call type I diabetic a type IV hypersensitivity. 02:21 Destruction of pancreatic beta cells resulting in complete lack of insulin… insulitis. 02:25 It’s a reaction that’s occurring early on, an autoimmune destruction of your beta islet cells. 02:32 Immune-mediated process, type II, type IV, they will not have you choose between the two, but usually, you-you’ll be referring to type IV. 02:41 Often detectable antibodies directed against pancreatic islet cells. 02:44 You tell me what kind of hypersensitivity that is. 02:46 That’s a type II. 02:49 And here, the anti-islet cell antibody here, you must know the exact detail, a glutamic acid decarboxylase 65… auto antibodies. 03:02 Patient require insulin at all times to prevent hyperglycemia and therefore, not present with DKA. 03:09 That’s your patient, the bottom line, coming through that door. 03:13 Theoretically, what happened prior… an autoimmune destruction of a beta islet cell, what do we call this? Insulitis, either type IV or type II hypersensitivity. 03:23 In pathology, I will refer to type II hypersensitivity against glutamic acid decarboxylase. 03:34 Which one of these is diabetic, which one of these is not and what are we looking at? On our slide, we have two photomicrographs placed side by side for comparison. 03:45 On the left, we observe a pancreas from a non-diabetic individual, featuring pancreatic islets of normal size and appearance. 03:53 These islets are rich in all types of islet cells, including alpha, beta, delta, and PP cells, each playing a crucial role in the endocrine function of the pancreas. 04:04 On the right, the photomicrograph presents a starkly different scene—a pancreas from a Type 1 diabetic patient. 04:11 Here, we notice a significant reduction in the size of the pancreatic islet, and there is also a decrease in their number, not shown here. 04:20 This change is primarily due to the autoimmune destruction of beta cells, which are responsible for insulin production.
About the Lecture
The lecture Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus – Hyperglycemia by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Pancreatic Disease and Diabetes.
Included Quiz Questions
What is associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus?
- HLA-DR3 and 4
- HLA-D6
- HLA-B27
- HLA-B17
- HLA-Q19
What is the result of the autoimmune process in type I diabetes mellitus?
- Destruction of β islet cells of the pancreas
- Hyperplasia of β islet cells of the pancreas
- Ectopic production of β islet cells of the pancreas
- Genetic mutation of β islet cells of the pancreas
- Differentiation of β islet cells of the pancreas
What is targeted by autoantibodies in type I diabetes mellitus?
- GAD65
- TPO
- dsDNA
- sp100
- Histones
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |