Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
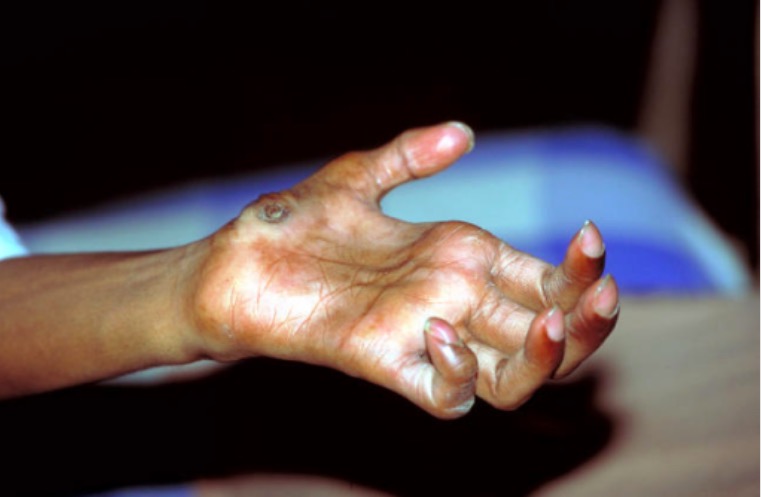
Atypical Mycobacterial Infections
-
Slides Treatment Regimens for Leprosy Non-tuberculous mycobacteria.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
00:01 The Centers for Disease Control Guidelines are shown. 00:04 HIV-negative adults with TB are typically treated with isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for the first two months. 00:15 And with isoniazid and rifampin for the next four months. 00:20 In the case of HIV positive patients, the regime will also include antiretroviral therapy. 00:27 Please note that there are subtleties in this regime. 00:30 It changes if there are active TB lesions in the lung or elsewhere in the body. 00:35 Most physicians will refer patients to an infectious disease specialist, or pulmonologist for treatment and monitoring. 00:44 In the case of pregnant women with TB, we will use a combination of isoniazid, rifampin, and ethambutol for the first two months, and isoniazid and rifampin in the next four months. 00:58 We usually will supplement pyridoxine, Vitamin B6 with the regimen. 01:04 Again, check the CDC website for subtle changes in treatment regimens for breastfeeding women, for pregnant and breastfeeding women with HIV or with active lesions and other conditions. 01:19 For your USMLE exams, you should be familiar with the three regimens listed. 01:26 You will not need to know the regimens of other countries.
About the Lecture
The lecture Atypical Mycobacterial Infections by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Antimicrobial Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the mechanism of action of dapsone?
- Folic acid synthesis inhibition
- Creates pores in the cell wall
- Reverse transcriptase inhibition
- Blocks sodium channels
- Intercalates DNA
Which medications are recommended for treating mild to moderate noncavitary lung disease caused by macrolide-sensitive MAC in immunocompetent patients? Select all that apply.
- Azithromycin
- Doxycycline
- Dapsone
- Rifabutin
- Ethambutol
Which statement is false?
- Rifampin is the most active drug against leprosy.
- Dapsone is associated with hemolysis particularly in patients with G6PD.
- Acedapsone is a depot formulation of dapsone that lasts for months.
- Mycobacterium avium complex is often seen in AIDS patients with low CD4 counts.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
I can't rate five stars to all the classes due to the time, eventually I will. Thank you Dr. Virtual hugs from Mexico.