Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Overview of Antiviral Activity – Antiviral Drugs
-
Slides Overview Antiviral Activity Antiviral Drugs.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
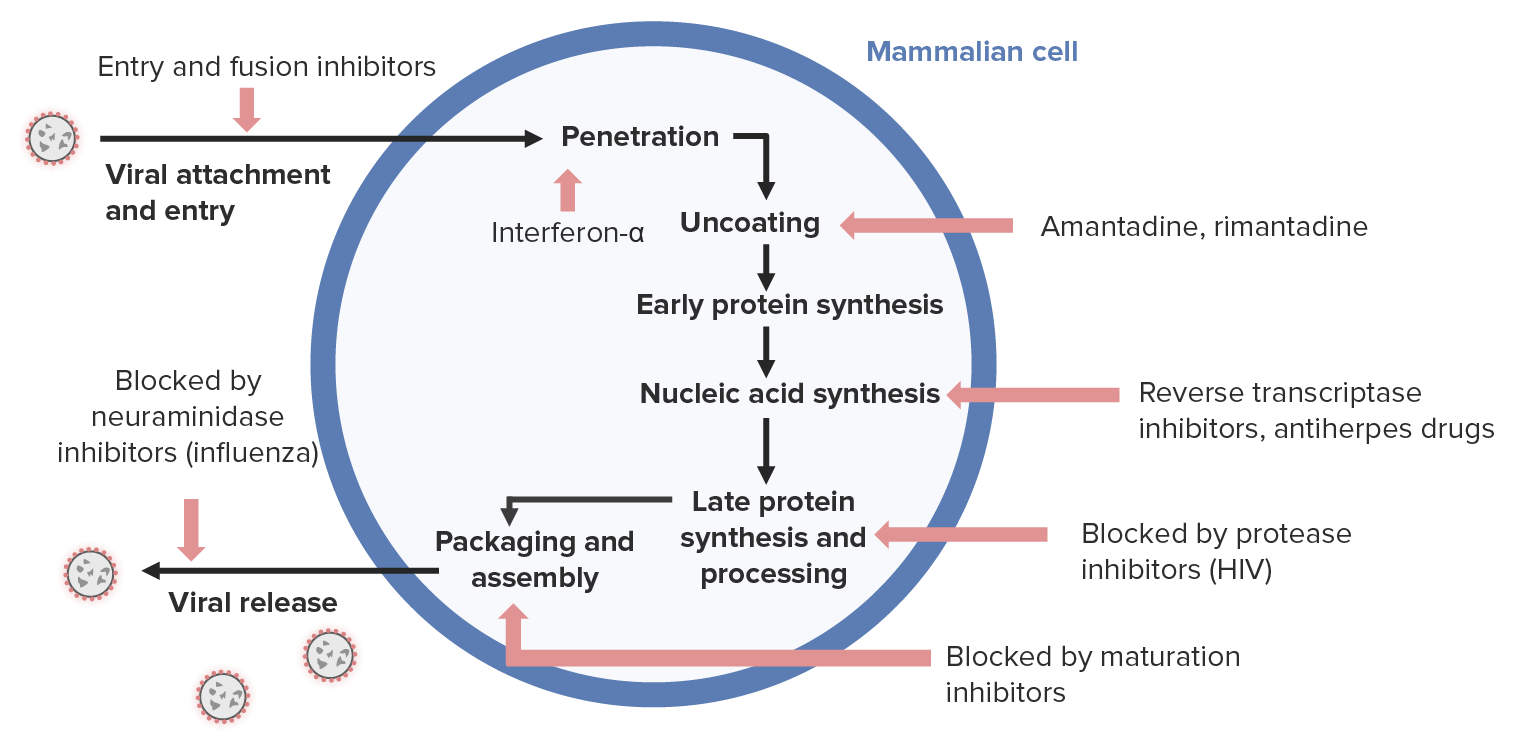
00:01 Welcome to Pharmacology by Lecturio. My name is Dr. 00:05 Shukle and we're going to talk today about antiviral agents. 00:09 The pharmacology of antiviral agents is complex, so what we're going to do is we're going to take a look at how viruses get into a mammalian cell first so that we can understand where each of these drugs work. 00:22 The first part of a viral entry is the attachment of the virus to the cell, to the membrane of the cell. 00:29 This is where entry and fusion inhibitors act. By inhibiting viral attachment and entry, these drugs work very, very well in reducing the effectiveness of the virus to replicate. 00:43 The second stage of viral penetration is viral penetration. This is where the interferon, especially interferon alpha, is quite effective. 00:52 However, it's important to note that interference are not used much today because they have limited efficacy with significant side effects, and there are more effective and better tolerated treatments. 01:02 The third stage is the uncoating of the virus particle. Now, drugs like amantadine and rimantadine are very effective at preventing uncoating and therefore replication within the cell. 01:14 However, due to widespread resistance, these drugs are no longer recommended for treating or preventing influenza. 01:21 Now, speaking of replication, one of the first stages of replication is early protein synthesis and then nucleic acid synthesis. 01:29 In terms of nucleic acid synthesis, we can inhibit a reverse transcriptase. I'll explain what that means in a minute. 01:35 The next stage or the last stage of protein synthesis is called late protein synthesis. 01:42 This is also processing of these proteins and this process is blocked by protease inhibitors. 01:50 We package up the virus and send it off into the interstitium through packaging and assembly steps. 01:58 This is blocked by maturation inhibitors. 02:01 However, maturation inhibitors are still in the early stages of development, and only a few drugs in this class are being explored, so they are not yet available for use. 02:10 And finally, we have viral release. 02:13 Some of the neuraminidase inhibitors, like those that we use in influenza, act at this stage to prevent the viral release. 02:21 So there's an overview of all of the viral drugs. Now let's deal specifically with certain disease states. 02:28 So we have, in general, anti-HIV drugs, anti-herpes drugs, drugs that we use in the treatment and prevention of influenza, and drugs that we use in other types of viral infections. We're going to focus first on the anti-HIV agents.
About the Lecture
The lecture Overview of Antiviral Activity – Antiviral Drugs by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Antimicrobial Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
At what stage do neuraminidase inhibitors act to prevent influenza viral release?
- Viral Release
- Viral Attachment
- Viral Penetration
- Viral Uncoating
- Viral Assembly
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
high yield info, the overview is excellent and helped me towards the exams.