Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Azoles – Antifungals
-
Slides Azoles Antifungals.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
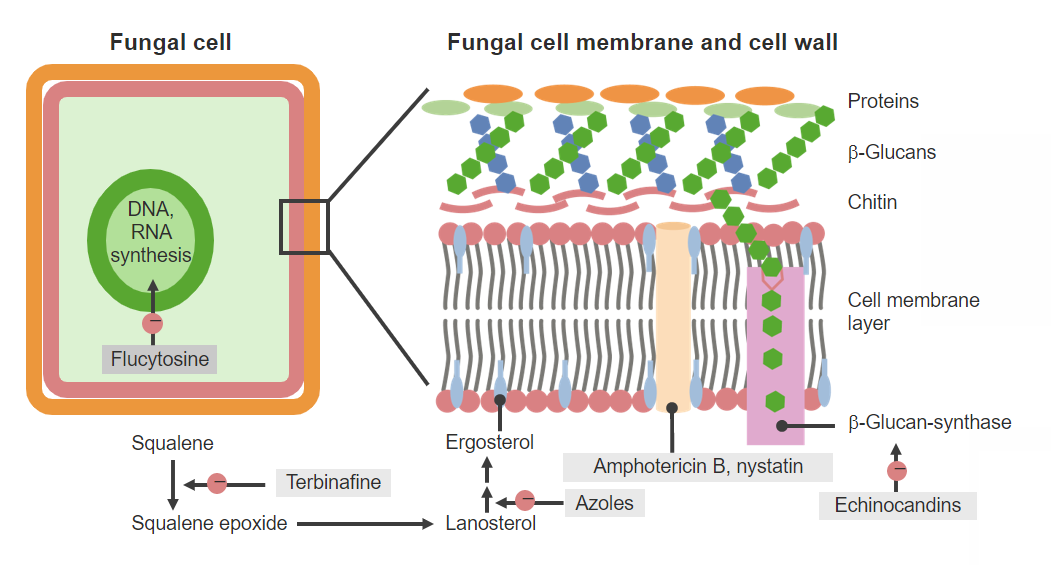
00:01 Take a look at this particular diagram. 00:03 We're going to start of with the azole antifungals. 00:06 The right down at the bottom here. 00:08 Now azole antifungals are often used in systemic infections. 00:12 And they have a variable oral bioavailability. 00:15 Some of them are actually intravenous only. 00:17 Now inducers of cytochrome P450 such as rifampin may actually decrease the bioavailability of some these agents. 00:28 So it is important to be aware that ketoconazole and other azole antifungals can be effected by inducers of cytochrome. 00:36 In terms of toxicity, common toxic reactions include vomiting, diarrhea, rash and heptatotoxicity. 00:45 Ketoconazole is a particularly bad drug for drug interaction and steroid blocking effects because it has lots of systemic effects as well as it's antifungal effect. 00:58 In terms of how these agents work, they inhibit ergosterol formation. 01:03 So ergosterol is going to be very important for the development of the cell wall within the fungal organisms. 01:10 It increases the membrane permeability and it allows leakage of cations and nutrients out of the fungal cell. 01:16 Resistance is due to widespread use. 01:19 And we're starting to see it more and more. 01:21 It's usually because the susceptible enzymes that azoles act on, are either becoming reduced or changed. 01:29 Ketoconazole is considered a broad spectrum antifungal. 01:33 However, its spectrum is limited compared to the newer azoles. 01:36 More adverse events than other azoles. 01:39 So it's falling out of favor. 01:41 The patients that we use it on are usually patients who have chronic oral candidiasis. 01:47 And sometimes patients who have dermatological fungal infections. 01:51 I've mentioned to you before that it is a strong inhibitor of cytochrome P450. 01:57 And may increase the level of other drugs. 02:00 And inducers like rifampin may actually reduce ketoconazole levels. 02:05 Now a newer agent is fluconazole. 02:08 It's the drug of choice in most esophageal infections and oropharyngeal candidiasis. 02:13 A single oral dose often eliminates completely vaginal candidiasis. Cryptococcal meningitis can also be treated with fluconazole, though it's typically reserved for consolidation and maintenance therapy after the initial combination of amphotericin and flucytosine. 02:29 In terms of other agents you can see them here, clotrimazole is the most well known azole antifungal. 02:35 It's a topical antifungal agent that works quite well topically or vaginally but it doesn't have a lot of use systemically. 02:42 It's often combined with a steroid like betamethasone used to treat Tinea corporis or Tinea cruris or Tinea pedis. 02:53 Itraconazole is a wide spectrum azole antifungal. 02:58 And it's often the drug of choice for infections like Blastomyces and Sporothrix schenckii. 03:05 It's the drug of choice for other types of infections as well. 03:09 Now it's an alternate drug of choice for aspergillosis, for coccidiomycoses, Cryptococcus and Histoplasma. 03:18 Voriconazole is a relatively new azole antifungal. 03:23 It has a slightly wider spectrum than the Itroconazole does. 03:26 And it may actually be better than amphotericin B. 03:29 I'm going to cover amphotericin B later. 03:33 Up to 30% of patients will develop visual blurring of unknown cause with this agent. 03:38 This is an important question, issued for you to know for questions because we often ask this particular question on exams. 03:48 Posaconazole is the broadest spectrum triazole out there. 03:53 It works against most species including Candida and Aspergillus. 03:59 It's the only azole with activity against Rhizopus and mucormycosis which may not be that commonly seen but it's something important to remember if you see a patient with mucor.
About the Lecture
The lecture Azoles – Antifungals by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Antimicrobial Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which antifungal drug is associated with visual blurring of an unknown cause in up to 30% of patients?
- Voriconazole
- Posaconazole
- Clotrimazole
- Fluconazole
- Ketoconazole
What is a side effect associated with ketoconazole?
- Gynecomastia
- Chronic kidney disease
- Rhinorrhea
- Pneumonitis
- Thyrotoxicosis
What is the only azole with activity against Rhizopus infections (e.g., mucormycosis)?
- Posaconazole
- Variconazole
- Itraconazole
- Clotrimazole
- Fluconazole
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |