Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Allergy: Diagnosis, Therapy and Treatment of Asthma
-
Slides Hypersensitivity.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
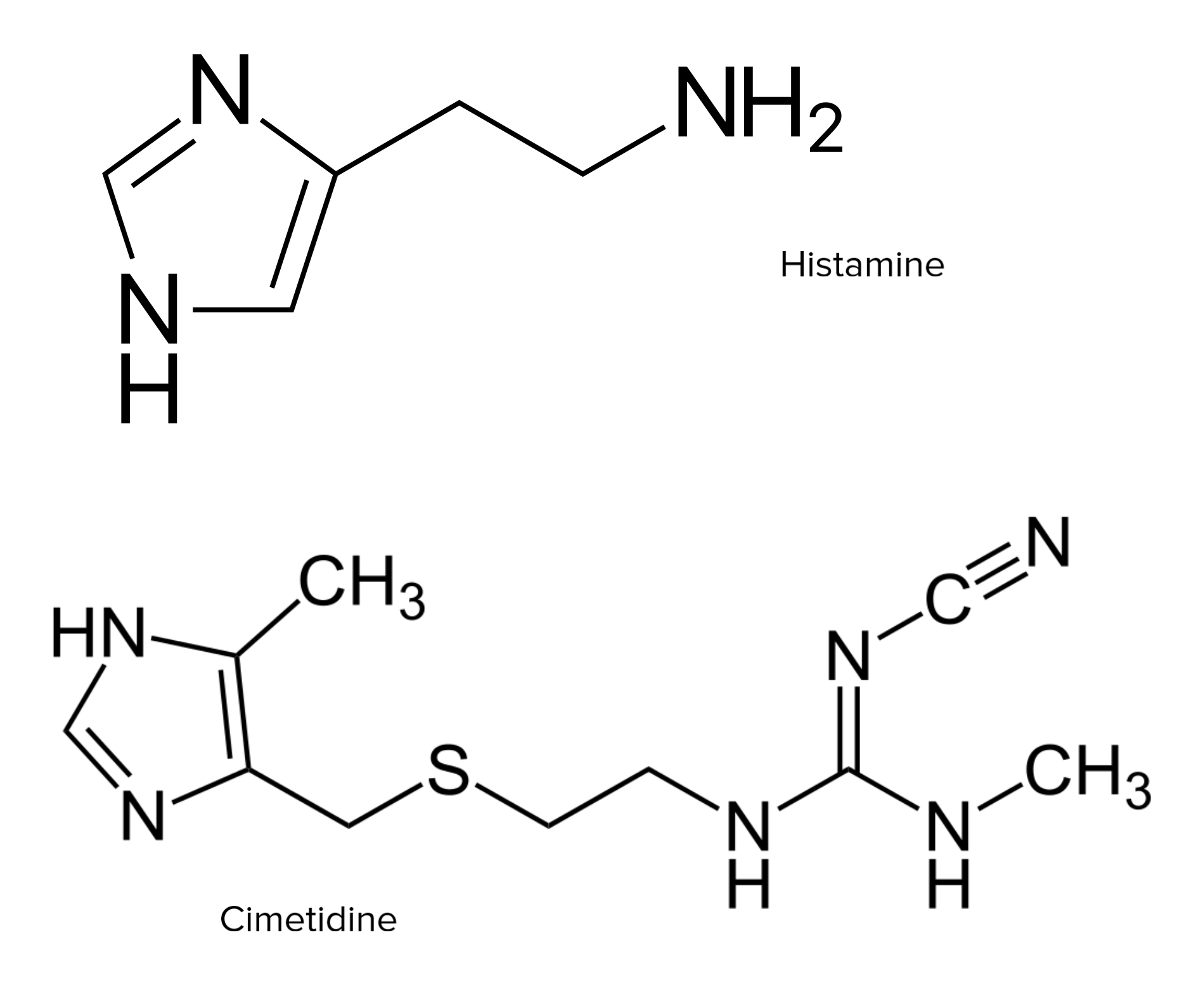
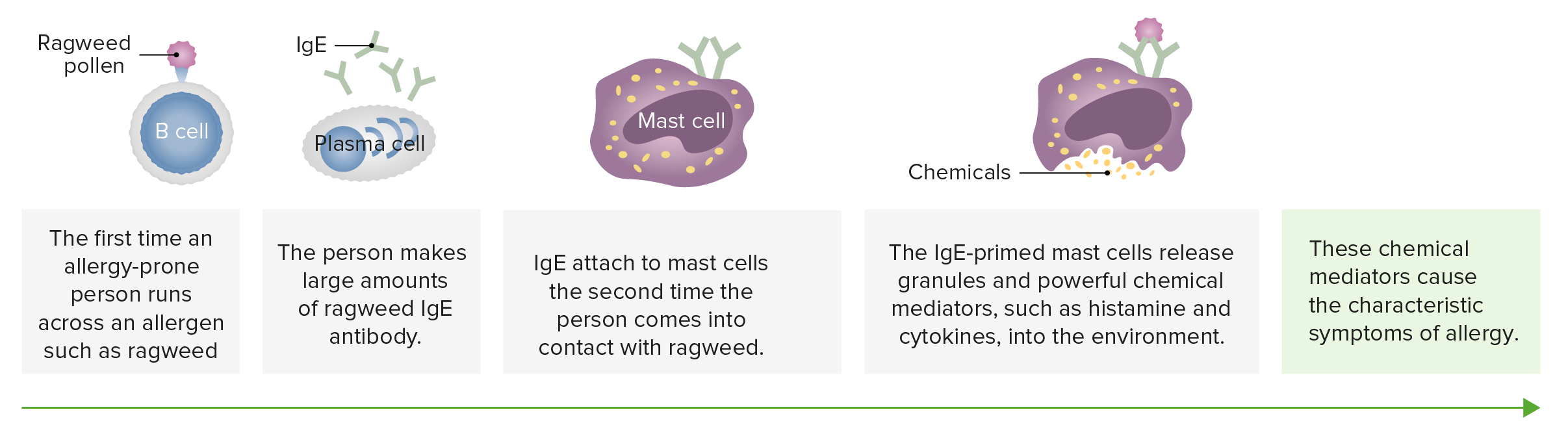
00:01 Atopic allergy can be diagnosed using the skin prick test, where small amounts of the suspected allergen are injected under the skin. 00:10 This leads to the release of inflammatory mediators from any mast cells that have been pre-sensitized with IgE antibody against the suspected allergen. 00:23 This will lead to vasodilation and edema causing the characteristic wheal and flare response that is detected as a response to the suspected allergen, if that proves to be the allergen that is responsible for the patient’s symptoms. The amount of IgE specific for a particular allergen that is present in a patient can be measured using the allergen specific IgE test or RAST. In this test, the allergen is immobilized on a disc or some other surface, and then patient’s serum is added. If the patient has antibodies that are specific for the allergen, then those antibodies will bind to the allergen. If the antibody is IgE antibody, it can be detected using a labeled anti-IgE antibody. In the past, the label most commonly employed was a radioactive isotope. Hence, the name of this test, RAST which stands for radioallergosorbent test. However nowadays, most commonly instead of using a radiolabel, some other type of detectable label is used. For example, an enzyme that causes a colour change in a substrate. What are the therapeutic options for allergy? Well of course the easiest approach is to remove or avoid the allergic trigger. If you are allergic to the cat, then it would be a good idea maybe to give your cat away to a friend. If you’re allergic to pollen, don’t go out in the spring time. Of course this is very easy to say, it’s much harder to achieve in practice. But where possible, avoidance of the allergen is the best. And if you’re allergic to a particular food, it may not be too difficult to avoid exposure to that food as long as you know what it is. 02:28 If removal or avoidance of the allergen is not practical, then one can use H1 blockers, mast cell stabilizers, anti-inflammatory corticosteroids and leukotriene inhibitors or immunotherapy. 02:48 Another approach is to use a monoclonal antibody that is specific for the IgE class of antibody. 02:56 This particular antibody, omalizumab, is specific for IgE. 03:02 And when injected into the patient, the antibody binds to IgE and removes it from the patient’s circulation. 03:12 And therefore mast cells do not get sensitized. 03:16 It also has a secondary effect of reducing the number of FcεR1 receptors on the surface of mast cells, because it turns out there’s a feedback mechanism where the less IgE there is, the less FcεR1 there is. 03:32 So it has a doubly beneficial effect. 03:35 And we can see here, the antigen activated mast cell, or basophils in the circulation can also release these inflammatory mediators. 03:44 And by using this monoclonal antibody against IgE, you can block this activity. 03:52 Cromolyn is a mast cell stabilizer that prevents mast cell degranulation. 04:00 And here you can see the cromolyn is blocking the release of mast cell mediators. 04:07 Leukotriene antagonists such as montelukast, can block bronchial constriction caused by leukotrienes, here shown on this diagram. 04:19 β-adrenergic agonists such as albuterol can stimulate bronchial relaxation. 04:27 And finally, corticosteroids can suppress transcription of pro-inflammatory genes. 04:35 Histamine does not play a significant role in bronchial constriction, and therefore antihistamines such as H1 receptor antagonists are not used to treat asthma. 04:56 One potentially very beneficial approach to the treatment of allergy is to use immunotherapy. 05:04 And this is used for allergens that are hard to avoid such as pollens, house dust mites, molds, insect venoms and so on. 05:13 It involves the subcutaneous injection of small amounts of allergen in gradually increasing doses. 05:22 These are increased weekly or biweekly by two or less times until the maximum tolerated dose is reached. 05:31 That is the dose at which symptoms begin to be seen in response to the injections. 05:38 The patients are observed for 30 minutes post injection during dose escalation due to the risk of anaphylaxis. 05:46 Alternative routes of administration include sublingual and oral rather than subcutaneous. 05:53 And the way in which these allergen immunotherapies work is by shifting the immune response away from the Th2 IgE mediated type of response and by increasing the activity of regulatory T-cells.
About the Lecture
The lecture Allergy: Diagnosis, Therapy and Treatment of Asthma by Peter Delves, PhD is from the course Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune Disease. It contains the following chapters:
- Diagnosis of Atopic Allergy
- Therapeutic Options for Allergy
- Treatment of Asthma
- Allergy Immunotherapy
Included Quiz Questions
Albuterol belongs to which of the following drug classes?
- β-adrenergic agonists
- H₁ receptor antagonists
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Leukotriene antagonists
- Corticosteroids
Which of the following tests is used to measure the amount of specific IgE antibodies in the blood, indicating a 'true' allergic reaction?
- Radioallergosorbent test (RAST)
- Skin prick test
- Skin scratch test
- Skin scrape test
- Intradermic test
Which of the following is NOT a therapeutic option for the treatment of allergies?
- Cytotoxic chemotherapy
- H1 blockers
- Corticosteroids
- Leukotriene inhibitors
- Immunotherapy
Which of the following drugs is a recombinant monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to free human immunoglobulin E (IgE) in the blood and interstitial fluid and removes it from the patient’s circulation so that mast cells do not get sensitized?
- Omalizumab
- Zafirlukast
- Epinephrine
- Alemtuzumab
- Bevacizumab
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |