El metabolismo de la fructosa es una cascada compleja en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que intervienen varias enzimas. Las enzimas pueden ser deficientes o causar un procesamiento anormal y enfermedades. La fructosuria esencial, la intolerancia hereditaria a la fructosa y la intolerancia intestinal a la fructosa son 3 de los LOS Neisseria distintos trastornos. La presentación puede variar desde asintomática hasta quejas de vómitos, distensión abdominal, flatulencia y diarrea. El tratamiento es variado y, a menudo, se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la modificación de la dieta. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la intolerancia hereditaria a la fructosa pueden ocurrir complicaciones graves como insuficiencia renal e incluso la muerte.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
El metabolismo de la fructosa es una cascada enzimática que provoca la descomposición de la fructosa, un monosacárido, para la producción de energía. El proceso complejo se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una serie de enzimas (ausentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunas personas) y puede causar 3 trastornos distintos: fructosuria esencial, intolerancia hereditaria a la fructosa e intolerancia intestinal a la fructosa.
La fructólisis es la 1ra porción del metabolismo de la fructosa:
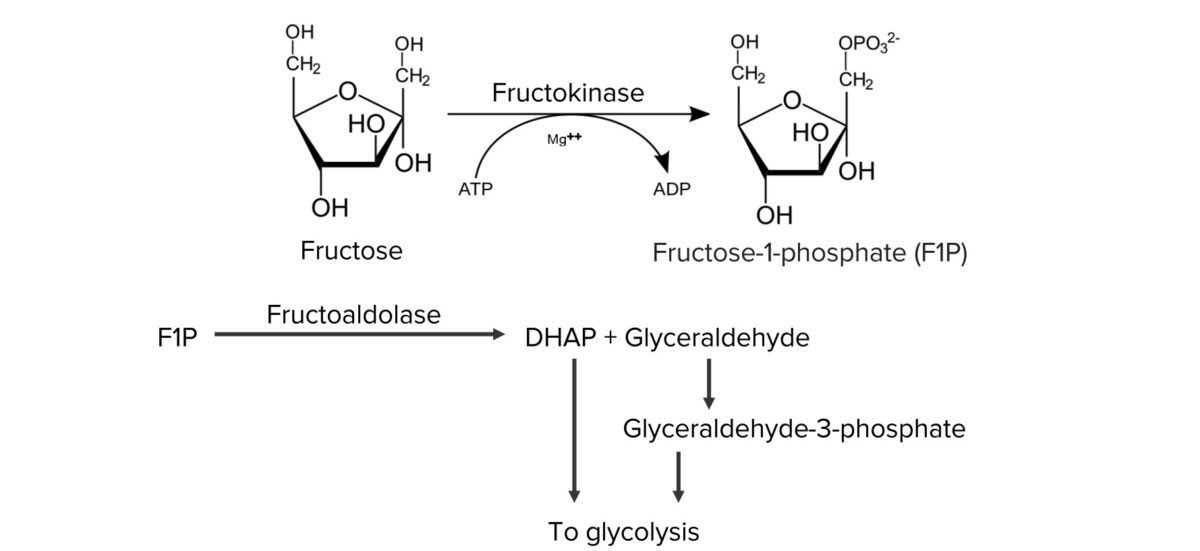
Metabolismo normal de la fructosa:
La fructosa se metaboliza en los hepatocitos para producir fosfato de dihidroxiacetona (DHAP) y gliceraldehído, que se canalizan hacia la glucólisis.
Fructosuria esencial (deficiencia de fructoquinasa):
Intolerancia hereditaria a la fructosa (deficiencia de aldolasa B/fructoaldolasa):
Intolerancia intestinal a la fructosa (deficiencia/actividad reducida de los LOS Neisseria transportadores de fructosa del intestino delgado ( GLUT5 GLUT5 A hexose transporter that mediates fructose transport in skeletal muscle and adipocytes and is responsible for luminal uptake of dietary fructose in the small intestine. Digestion and Absorption)):
La fructosuria esencial es asintomática.
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas aparecen cuando se introduce fructosa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dieta.
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas son más evidentes después de la ingestión de una carga de fructosa (e.g., jugo, fruta).
La prueba de hidrógeno en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el aliento detecta el hidrógeno producido por las bacterias gastrointestinales.
Solo los LOS Neisseria pacientes con intolerancia hereditaria a la fructosa tienen complicaciones clínicamente significativas: