La molécula de ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) es el depósito de la información genética heredable. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria humanos, el ADN está contenido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 23 pares de cromosomas dentro del núcleo. La molécula proporciona la plantilla básica para la replicación de la información genética, la transcripción de ácido ribonucleico (ARN) y la biosíntesis de proteínas para promover la función celular y la supervivencia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El ADN es el material hereditario, compuesto de un polímero de nucleótidos de doble cadena:
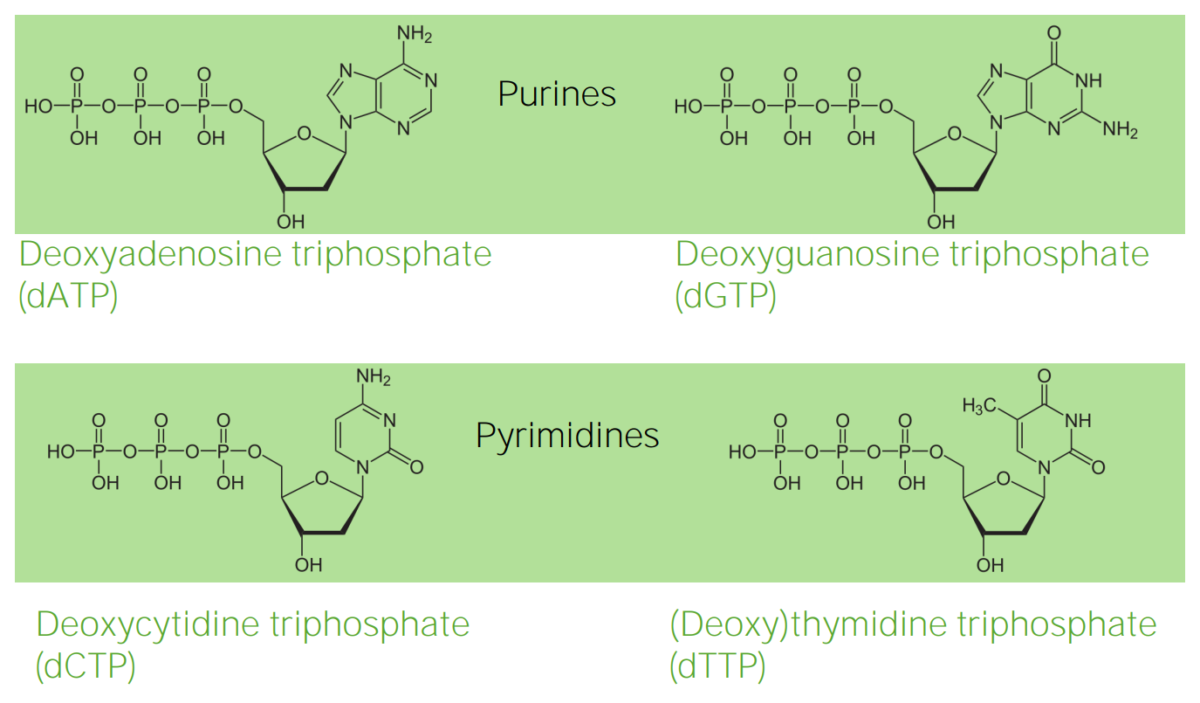
Estructura de los desoxirribonucleótidos
Imagen por Lecturio.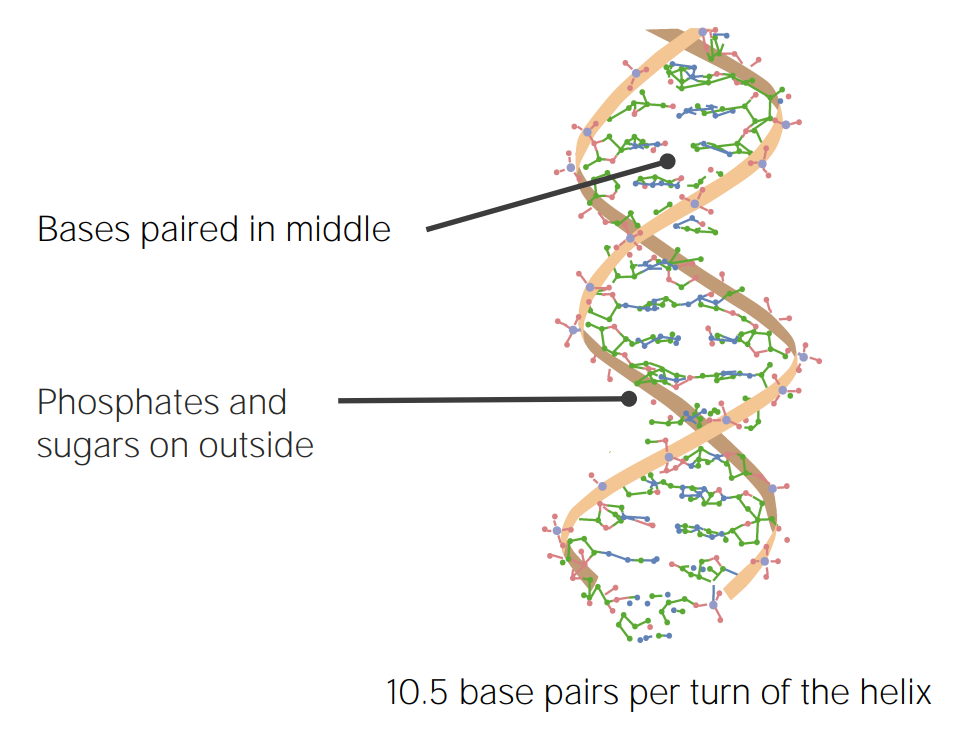
Estructura del ADN descrita por Watson y Crick
Imagen por Lecturio.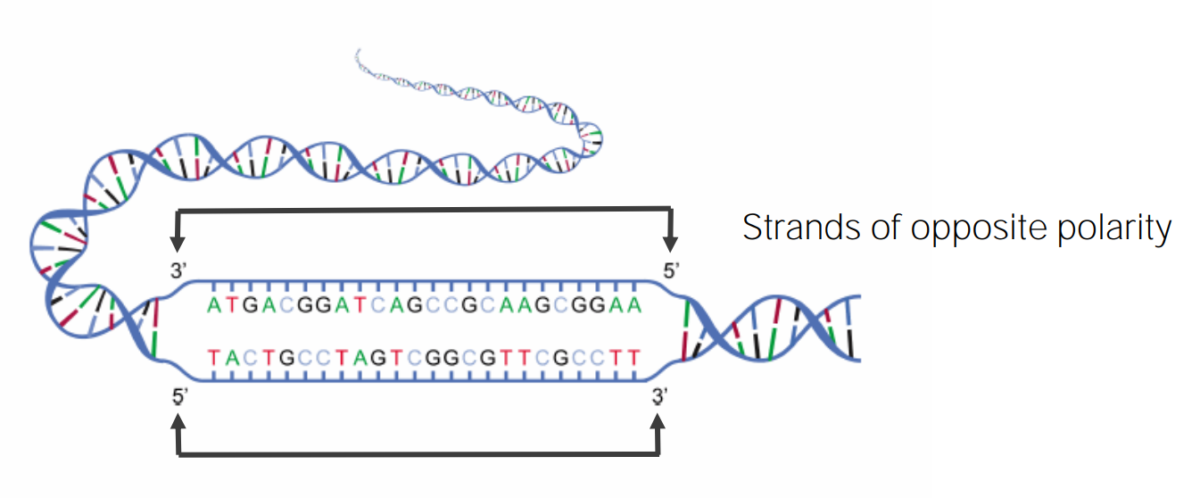
Diagrama de la doble hélice del ADN que muestra la naturaleza antiparalela (polar) de cada hebra complementaria
Imagen por Lecturio.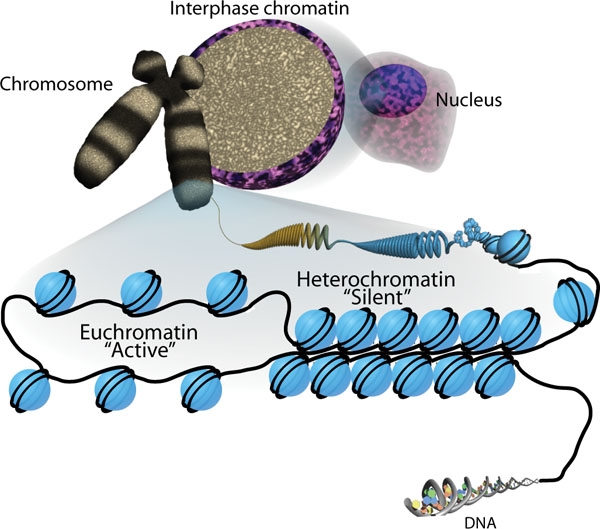
Empaquetamiento del ADN y los 2 estados de la cromatina:
Eucromatina (activa) donde el ADN se replica o transcribe; y heterocromatina (silenciosa), donde el ADN no se replica ni se transcribe.