El síndrome de Swyer es un trastorno del desarrollo sexual causado por un defecto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen SRY del cromosoma Y. El síndrome se caracteriza por una disgenesia testicular completa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un individuo que tiene un cariotipo 46,XY y es fenotípicamente femenino. La presentación del síndrome de Swyer es la de una mujer alta con una infancia y un desarrollo normales hasta la pubertad, que se caracteriza por amenorrea primaria y el no desarrollo de los LOS Neisseria caracteres sexuales secundarios. El tratamiento incluye la terapia de sustitución hormonal y la gonadectomía.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El cariotipo de un individuo con síndrome de Swyer es 46 XY.
El síndrome de Swyer puede estar causado por diversas anomalías genéticas:
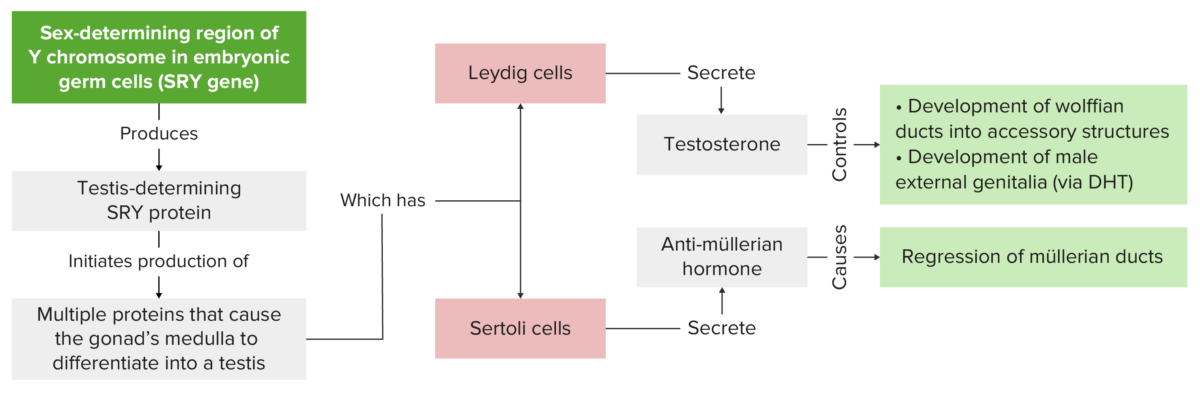
Imagen que muestra la importancia del SRY en el desarrollo genital masculino normal
DHT: dihidrotestosterona
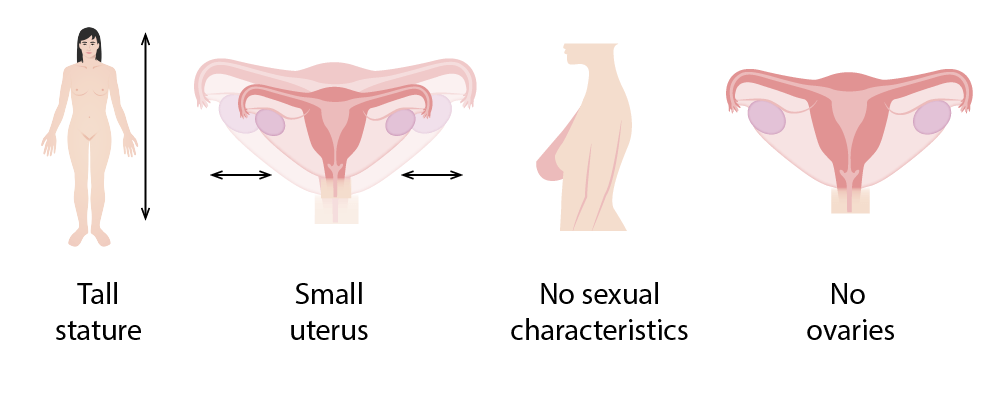
Manifestaciones clínicas del síndrome de Swyer:
Estatura alta, útero pequeño, ausencia de caracteres sexuales secundarios y ausencia de ovarios (en su lugar tendrá gónadas en forma de estrías)
Las siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales para el síndrome de Swyer: