El síndrome de muerte súbita infantil describe la muerte súbita de un lactante por lo demás sano (< 1 año de edad) sin causa identificable. El síndrome de muerte súbita infantil es la principal causa de fallecimiento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños entre 1 y 12 meses de edad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos. El síndrome de muerte súbita infantil es un diagnóstico de exclusión y solo puede confirmarse después de que se hayan descartado otras causas de fallecimiento con una toma completa de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y una autopsia. Brindar a los LOS Neisseria padres educación preventiva es clave para reducir el riesgo de síndrome de muerte súbita infantil. Las medidas preventivas incluyen que los LOS Neisseria lactantes duerman en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum decúbito supino, sobre superficies firmes, sin desorden en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cuna.
Last updated: Dec 8, 2024
El síndrome de muerte súbita infantil es la muerte súbita e inexplicable de un niño en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la infancia (< 1 año de edad) sin una causa identificable después del examen físico, la revisión del caso clínico y la autopsia.
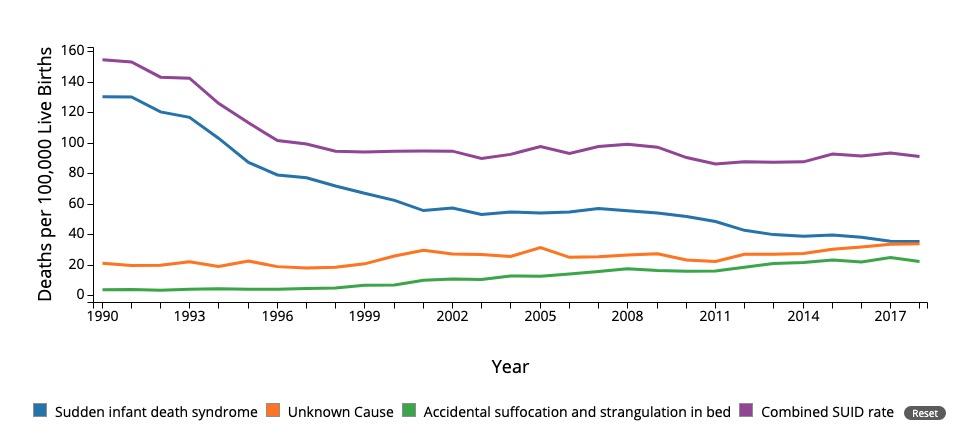
Mortalidad por síndrome de muerte súbita infantil y otras causas. Nótese la disminución desde 1994 debido a las intervenciones públicas, incluida la campaña de “dormir boca arriba”.
SUID: muerte súbita e inesperada (en inglés)
La causa más probable de síndrome de muerte súbita infantil implica una génesis multifactorial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum bebés particularmente vulnerables, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que los LOS Neisseria factores internos y externos trabajan juntos.
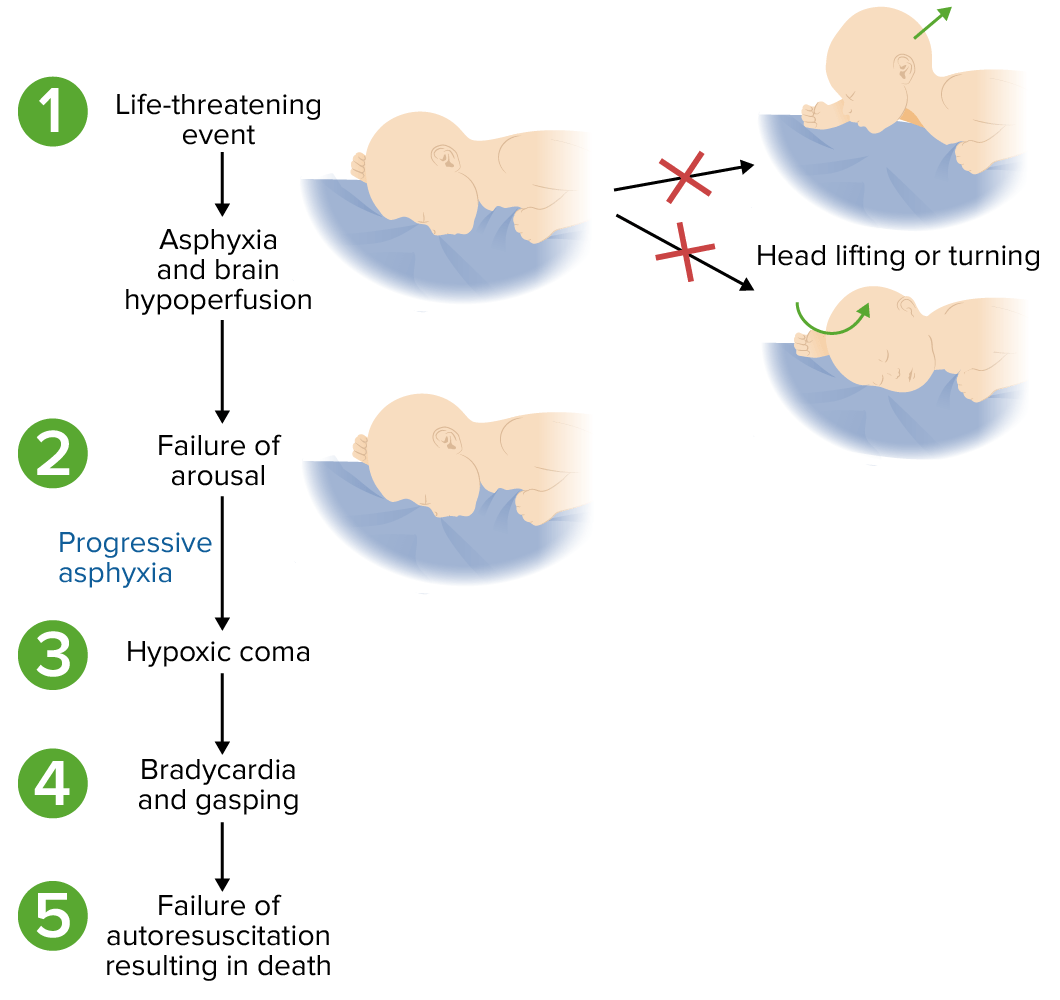
Posible fisiopatología del síndrome de muerte súbita del lactante:
En algunos lactantes vulnerables, un evento puede provocar hipoxia y/o hipercapnia. La incapacidad de detectar o responder conduce a consecuencias fisiológicas progresivas y a la muerte.
| Categoría | Mecanismos | Ejemplos de efectos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lactante |
|---|---|---|
| Sistema nervioso central | Reducción de la detección y respuesta al AL Amyloidosis aumento de CO2 y la caída de O2, lo que aumenta la vulnerabilidad a la apnea y la hipoxia | |
| Genética y factores autonómicos | Disminución de la capacidad para iniciar esfuerzos respiratorios protectores o ajustar la frecuencia cardíaca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum respuesta a un bajo nivel de oxígeno | |
| Anomalías cardíacas | Predisposición a alteraciones fatales del ritmo cardíaco, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum condiciones de estrés o hipóxicas | |
| Factores metabólicos | Dificultad para mantener un suministro adecuado de energía, lo que exacerba el impacto del estrés respiratorio o cardíaco | |
| Infecciones y respuesta inmunitaria | Mayor riesgo de insuficiencia respiratoria e incapacidad para recuperarse de la hipoxia debido a una inflamación excesiva o desregulada |
El síndrome de muerte súbita infantil es un diagnóstico de exclusión que se puede asignar solo después de:
El enfoque principal del tratamiento es proporcionar un diagnóstico post mortem preciso, así como apoyo emocional y psicológico a los LOS Neisseria padres. Para los LOS Neisseria padres y miembros de la familia también se debe:
La educación de los LOS Neisseria padres es clave para prevenir el síndrome de muerte súbita infantil. Como se señaló anteriormente, muchos de los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo son modificables y se pueden prevenir. La educación de los LOS Neisseria padres incluye:
Las siguientes afecciones son causas naturales de fallecimiento que se distinguen del síndrome de muerte súbita infantil: