Los LOS Neisseria 4 pares de senos paranasales incluyen los LOS Neisseria senos maxilares, etmoidales, esfenoidales y frontales. Los LOS Neisseria senos paranasales son un grupo de cavidades llenas de aire situadas dentro del esqueleto facial y craneal; todos están conectados con la cavidad nasal principal y la nasofaringe. Entre sus funciones se incluye el contribuir a la resonancia de la voz, reducir el peso del cráneo para facilitar la posición erguida de la cabeza, acondicionar (calentar y humedecer) el aire inhalado y maximizar la superficie de la mucosa nasal.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
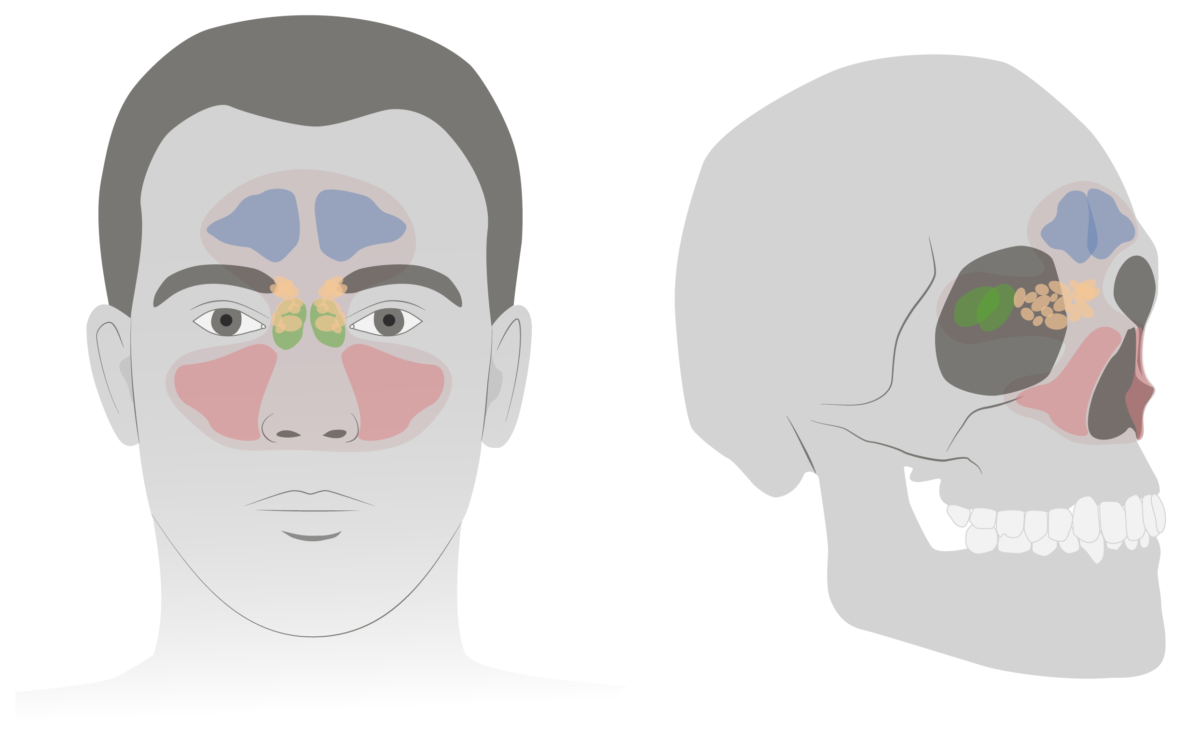
Los senos maxilares (de color rosa) son senos con forma de pirámides situados en las mejillas.
Imagen por Lecturio.
Los senos frontales (azul) son senos de forma irregular que se encuentran sobre las cavidades orbitales.
Imagen por Lecturio.
Los senos etmoidales (amarillos) son senos de paredes finas mediales a las cavidades orbitarias.
Imagen por Lecturio.
Los senos esfenoidales (verde) están situados posterior a los senos etmoidales (amarillo).
Imagen por Lecturio.