Todo el ADN de una célula se replica durante la fase S (de síntesis) del ciclo celular. El principio de la replicación se basa en el emparejamiento de bases de nucleótidos complementarios: la adenina forma enlaces de hidrógeno con la timina (o uracilo en el ARN) y la guanina forma enlaces de hidrógeno con la citosina. La replicación se produce antes de la división celular en la fase S del ciclo celular para permitir la presencia de 2 conjuntos de cromosomas durante la metafase de la mitosis, tras lo cual se dividen por igual en 2 nuevas células durante la separación (anafase).
Last updated: Apr 23, 2025
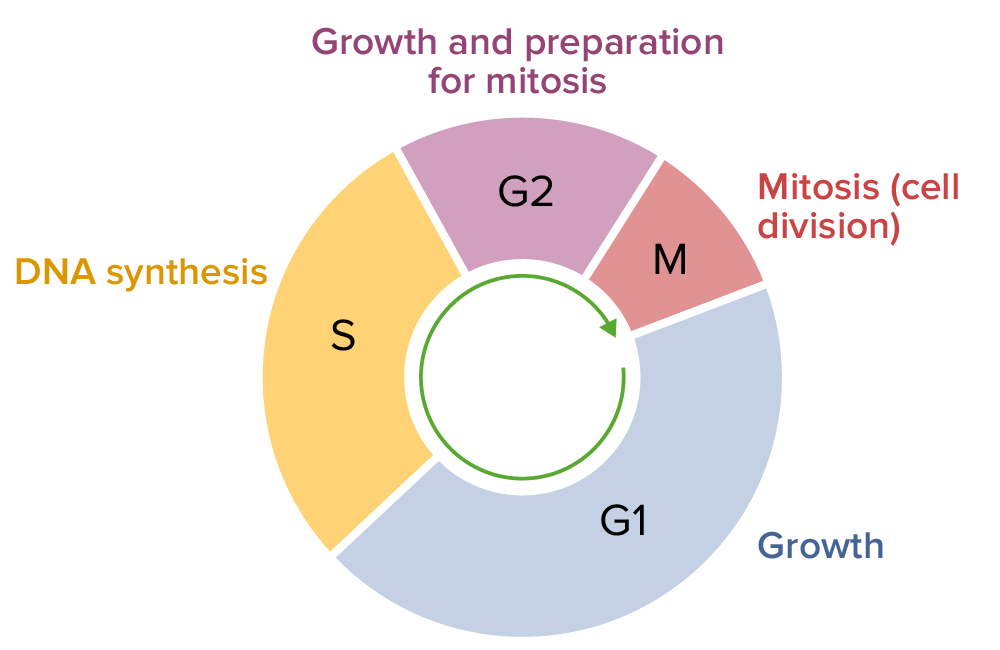
Ciclo celular, compuesto por las fases G1, S, G2 y M
Imagen pro Lecturio.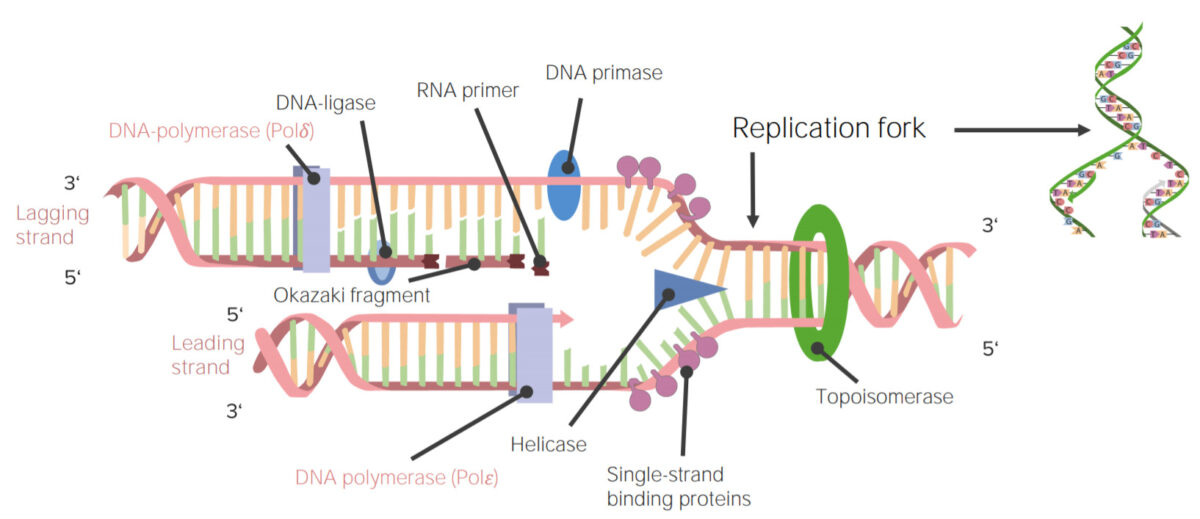
La replicación del ADN o síntesis del ADN es el proceso de copia de una molécula de ADN de doble cadena. Este proceso es primordial para toda la vida tal y como la conocemos.
Imagen: “DNA Replication” por Mariana Ruiz. Licencia: Dominio Público| Polimerasa | Función | Actividad exonucleasa |
|---|---|---|
| α | Sintetiza el cebador de ARN e inicia la síntesis de ADN a lo largo de la hebra rezagada | 3′ → 5′ |
| β | Repara el ADN | Ninguno |
| γ | Replica el ADN mitocondrial | 3′ → 5′ |
| δ | Sintetiza la hebra rezagada, rellenando los LOS Neisseria huecos de ADN tras la retirada del cebador | 3′ → 5′ |
| ε | Sintetiza el hilo conductor | 3′ → 5′ y 5′ → 3′ |