La neumonía o inflamación pulmonar es una inflamación aguda o crónica del tejido pulmonar. Las causas incluyen la infección por bacterias, virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology u hongos. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos más raros, la neumonía también puede ser causada por desencadenantes tóxicos a través de la inhalación de sustancias tóxicas, procesos inmunológicos o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el curso de la radioterapia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
| Bacterias gramnegativas multirresistentes y MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus | MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus nosocomial (NAH y NAV) | MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus adquirido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la comunidad |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Los LOS Neisseria patógenos comunes que causan la NAC NAC Acetaminophen Overdose varían en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la gravedad de la misma (i.e., si requiere tratamiento como paciente ambulatorio o como paciente hospitalizado fuera o dentro de la UCI) (véase la Tabla 2):
| Ambulatorio | Hospitalización fuera de cuidados intensivos (UCI) | UCI |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Patógenos recientemente identificados | ||
|
||
Solo se sugiere una etiología anaeróbica cuando hay antecedentes de aspiración días o semanas antes del diagnóstico de neumonía.
Generales
Específicos
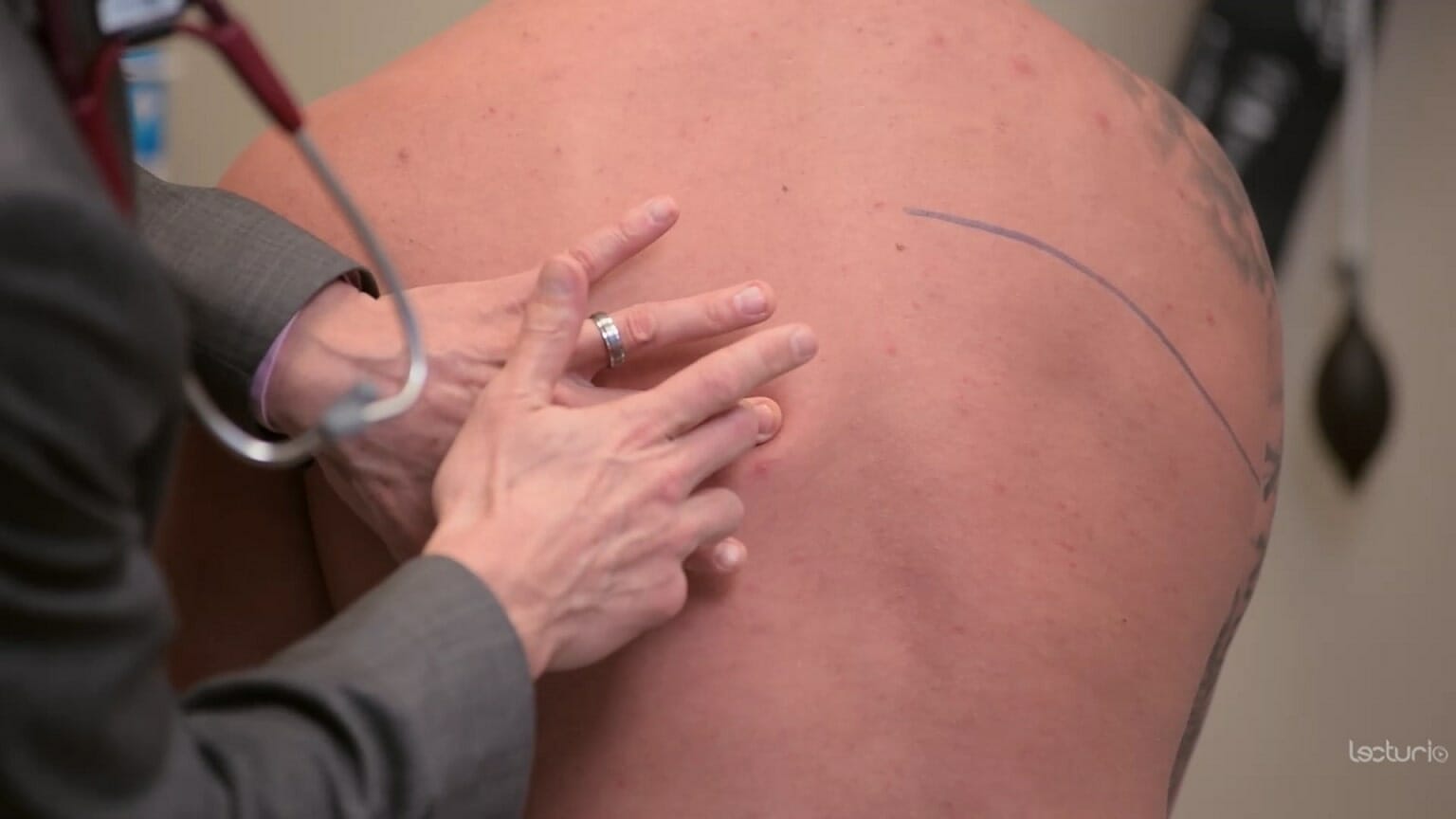
Técnica de percusión:
El dedo corazón del clínico se coloca en la zona de interés. La otra mano golpea el dedo corazón en la articulación interfalángica distal. Una consolidación por neumonía puede sonar mate a la percusión.
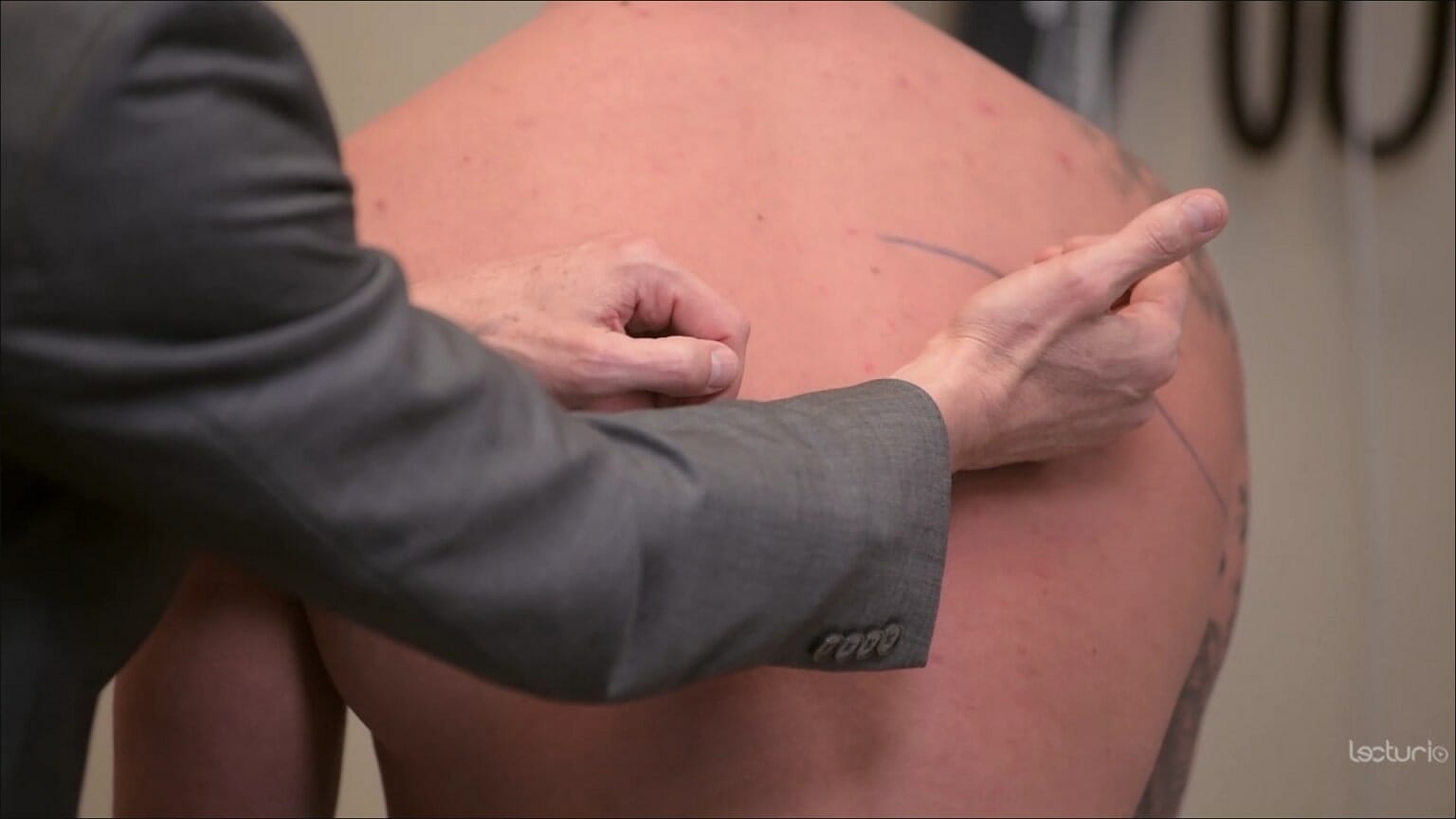
Frémito táctil:
El clínico coloca la superficie cubital de sus manos a ambos lados de la espalda para comparar la transmisión de vibraciones mientras el individuo habla. En la neumonía, el aumento del frémito puede indicar una consolidación (debido al aumento de la densidad del tejido pulmonar). La disminución del frémito puede deberse a un derrame pleural.
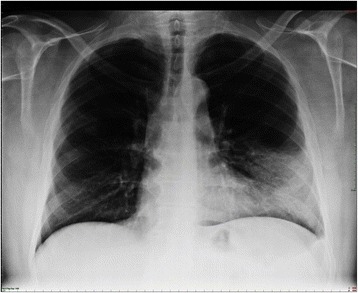
Neumonía lobar. Una infiltración densa en el lóbulo inferior izquierdo ha provocado una silueta del borde cardíaco izquierdo (línea discontinua). El broncograma aéreo es una característica típica de la consolidación.
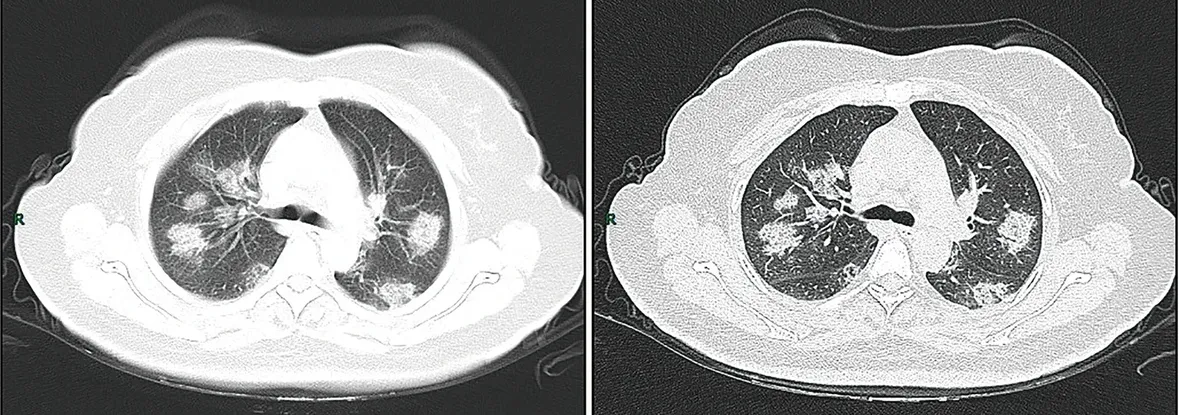
Imágenes de una TC en la etapa de progresión rápida. Mujer de 50 años con anorexia, fatiga, dolor muscular, congestión nasal y goteo nasal durante 1 semana, dolor y prurito en la garganta durante 2 días. Pruebas de laboratorio: aumento de la velocidad de eritrosedimentación (25 mm/h), leucocitos normales (4.08 × 109/L), disminución de los linfocitos (0.96 × 109/ L), aumento de la proteína C reactiva (60.8 mg/L). Evaluación imagenológica: a (TC de cortes finos) y b (TC de alta resolución) mostraron una consolidación ligera y en parches múltiples en ambos pulmones y un grosor cuadriculado de los septos interlobulares.
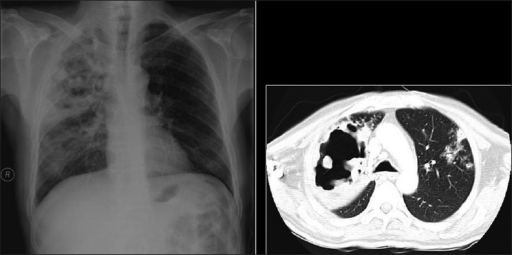
Neumonía cavitante necrosante. Radiografía de tórax y TC que muestran una neumonía cavitante necrosante por Staphylococcus aureus en un hombre de 29 años con síndrome de inmunodeficiencia adquirida.
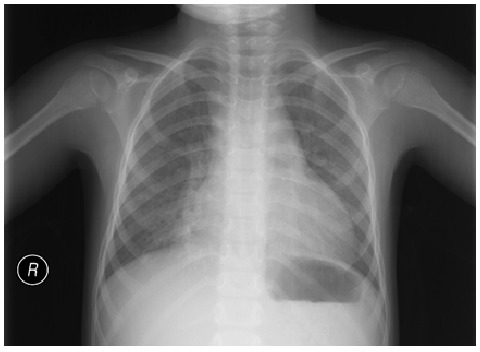
Neumonía atípica: infiltración intersticial leve y difusa. No se observa consolidación lobar, derrame o neumotórax.
Además del juicio clínico, se recomienda una herramienta de predicción validada para determinar la necesidad de hospitalización:
La NAC NAC Acetaminophen Overdose severa o la NAC NAC Acetaminophen Overdose que requiere ingreso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la UCI se define por NAC NAC Acetaminophen Overdose más al AL Amyloidosis menos 1 de los LOS Neisseria siguientes:
Aproximadamente el 10% de los LOS Neisseria pacientes de la UCI tienen neumonía, sobre todo NAV.