La fosa poplítea o “fosa de la rodilla” es una depresión poco profunda en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de diamante y llena de tejido adiposo, situada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara posterior de la articulación de la rodilla. La fosa poplítea está situada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara posterior de la rodilla y contiene un mayor número de ganglios linfáticos, así como estructuras vasculares y nerviosas que se desplazan desde el muslo hasta la parte inferior de la pierna. Los LOS Neisseria límites están formados por varios músculos del muslo y la pierna.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Múltiples músculos de la parte dorsal del muslo y de la parte inferior de la pierna forman la mayor parte de los LOS Neisseria límites de la fosa poplítea.
| Límites | Estructuras |
|---|---|
| Superolateralmente |
|
| Superomedialmente |
|
| Inferolateralmente |
|
| Inferomedialmente |
|
| Techo |
|
| Piso |
|
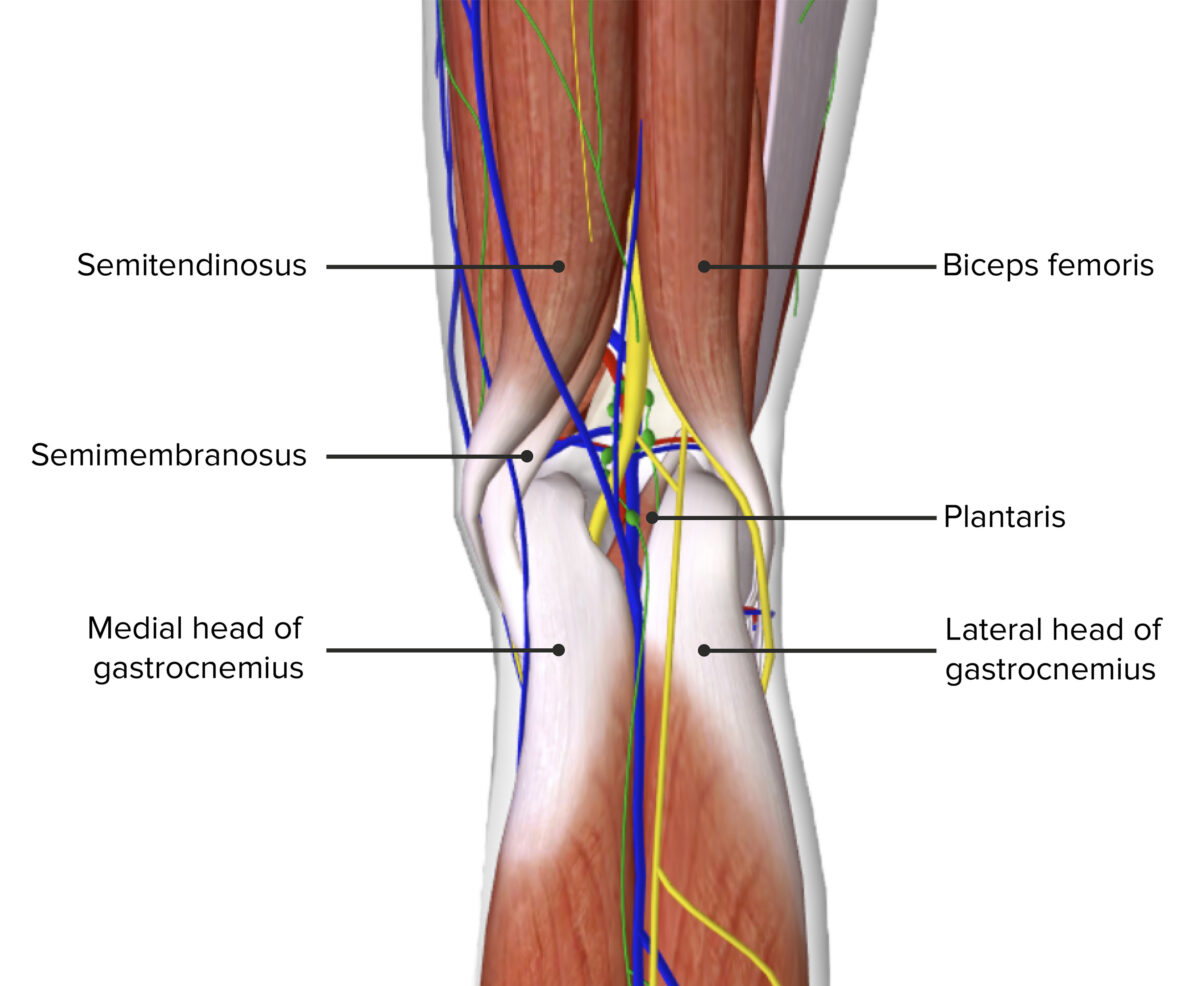
Los límites de la fosa poplítea
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio.| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Inervación | Función |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semimembranoso |
|
Cóndilo medial de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy | Nervio tibial |
|
| Semitendinoso | Superficie superomedial de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy | |||
| Bíceps femoral |
|
La cabeza del peroné y el cóndilo lateral de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy |
|
|
| Gastrocnemio |
|
Ayuda a formar el tendón calcáneo o de Aquiles, insertado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara posterior del hueso calcáneo |
|
|
| Poplíteo |
|
Tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy, por debajo del cóndilo tibial medial |
|
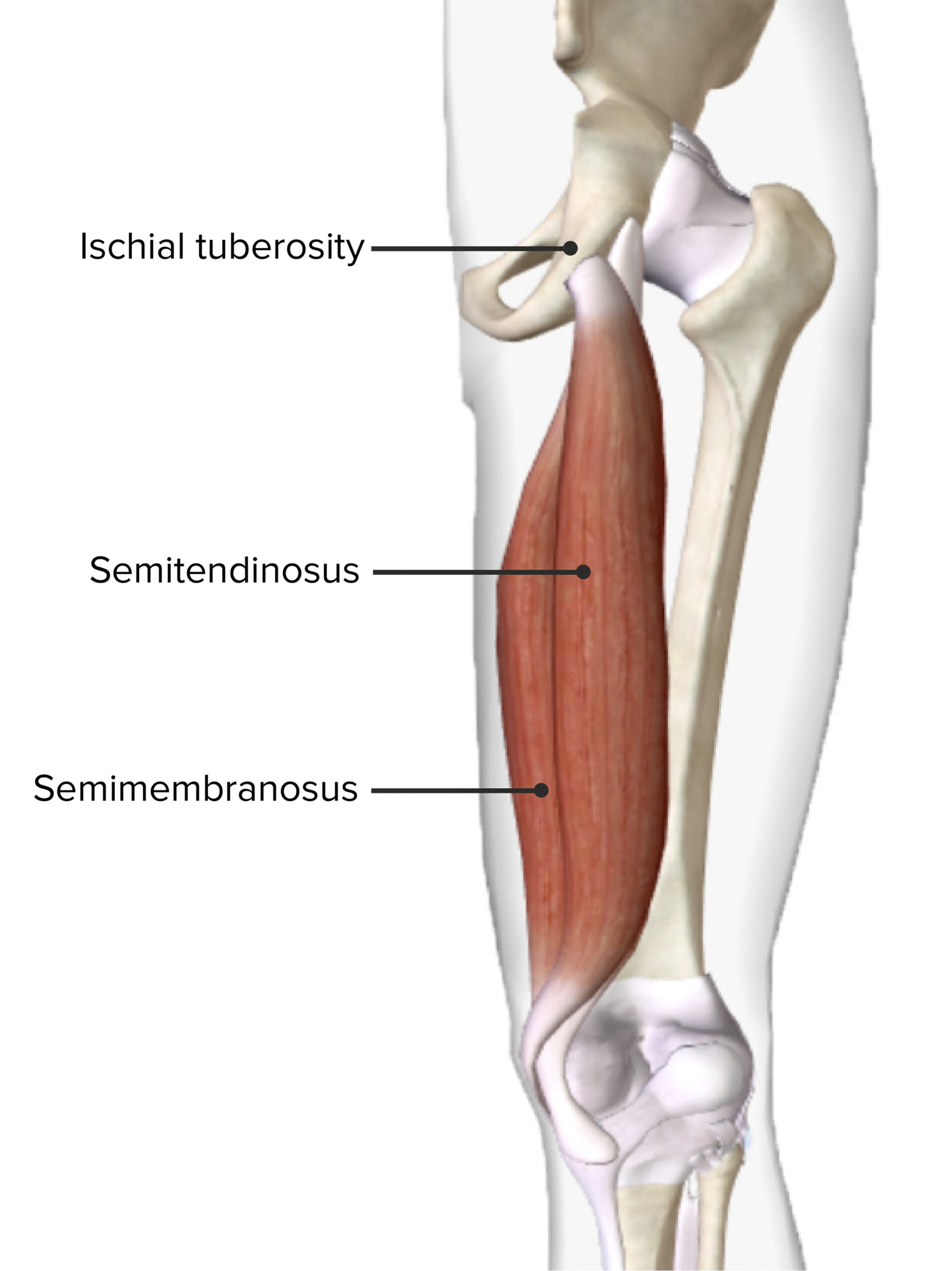
Vista posterior del muslo derecho mostrando el origen y la inserción de los músculos semitendinoso y semimembranoso
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio.En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fosa poplítea se encuentran muchos nervios y vasos importantes de la extremidad inferior y es el canal principal del sistema neurovascular entre el muslo y la parte inferior de la pierna.
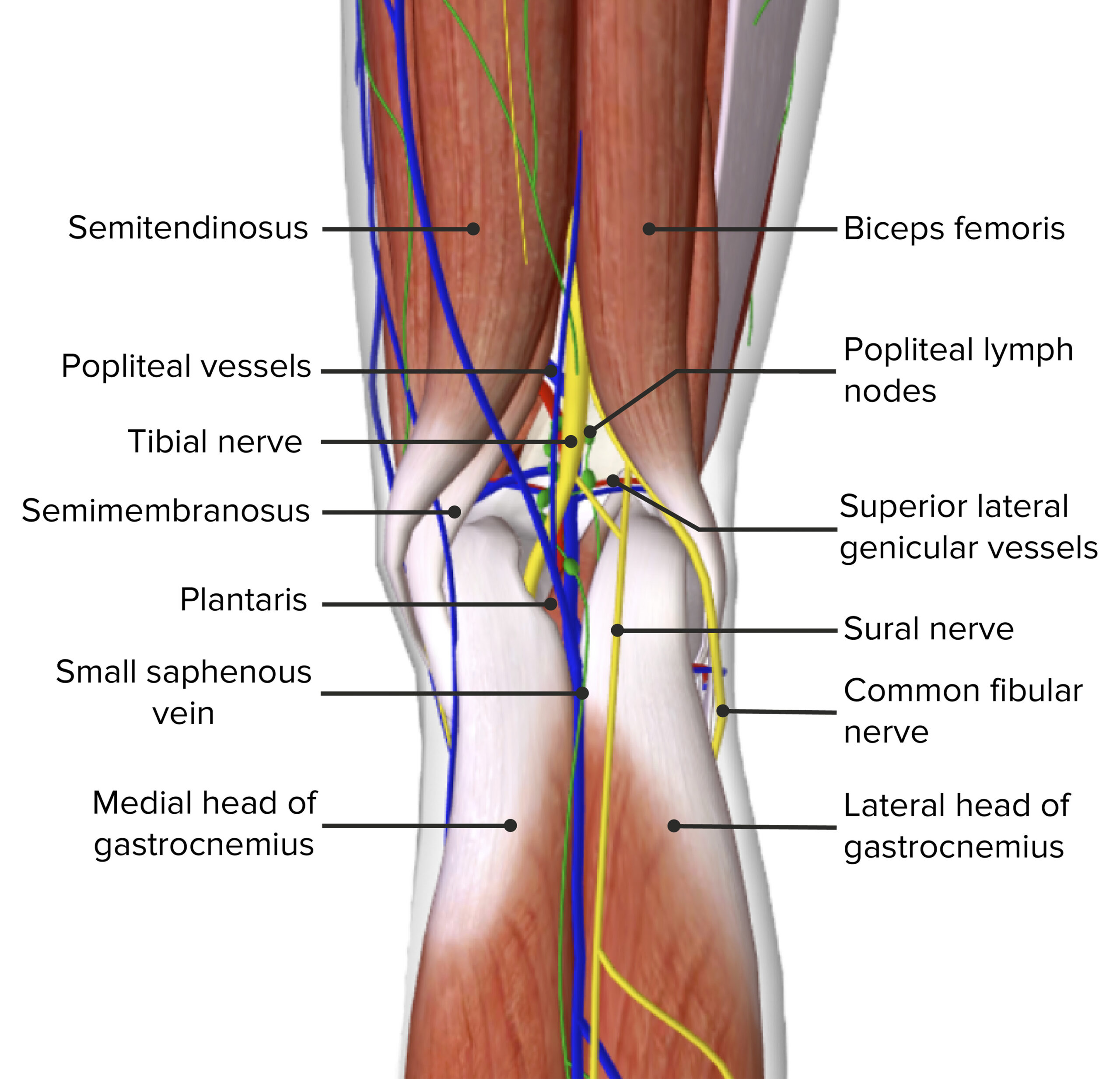
Contenido de la fosa poplítea
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio.Mnemotecnia
Para recordar el contenido de la fosa poplítea de medial a lateral, recuerde Serve and Volley Next Ball ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
Arteria poplítea:
Vena poplítea:
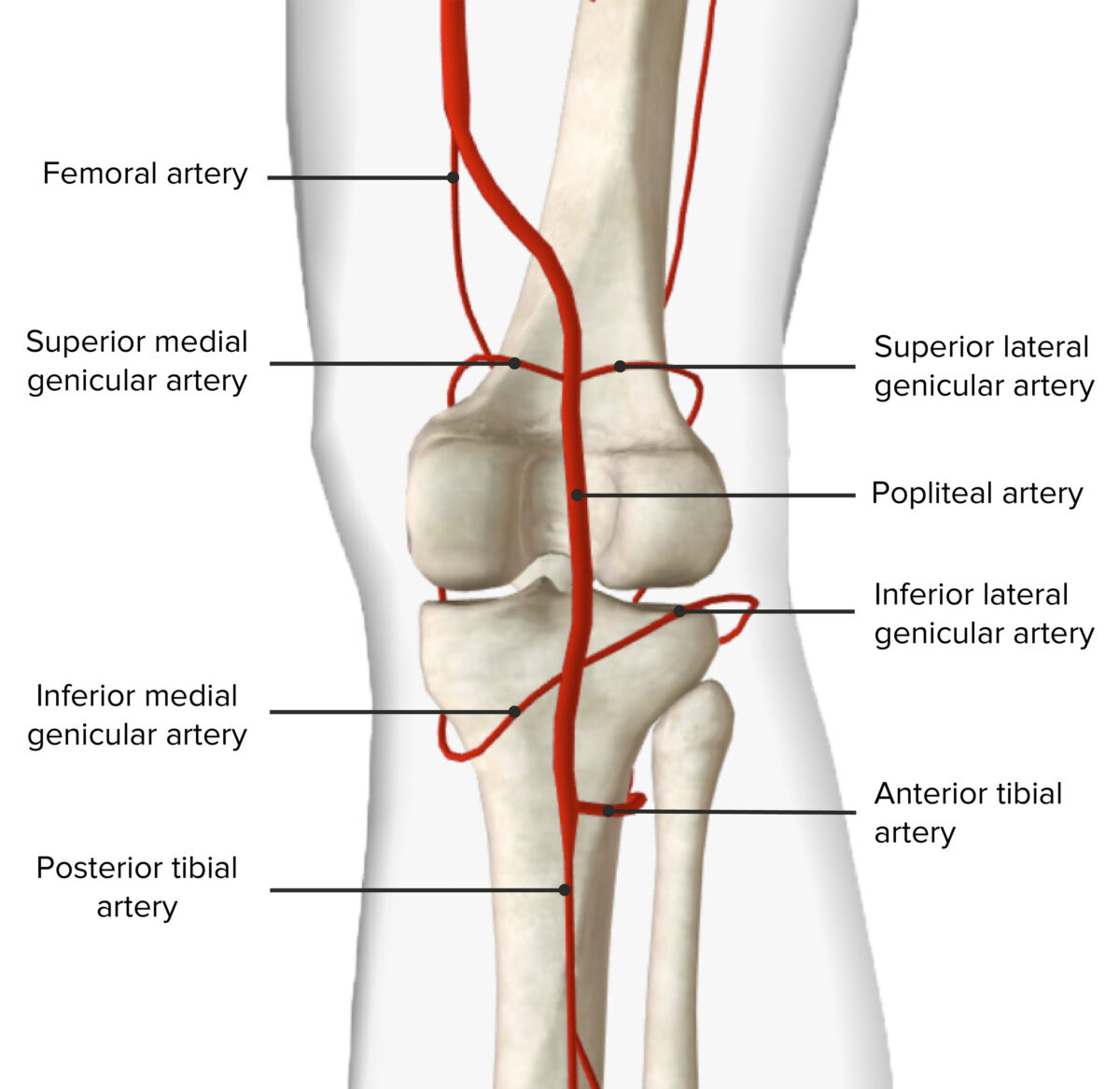
Irrigación arterial de la fosa poplítea
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio.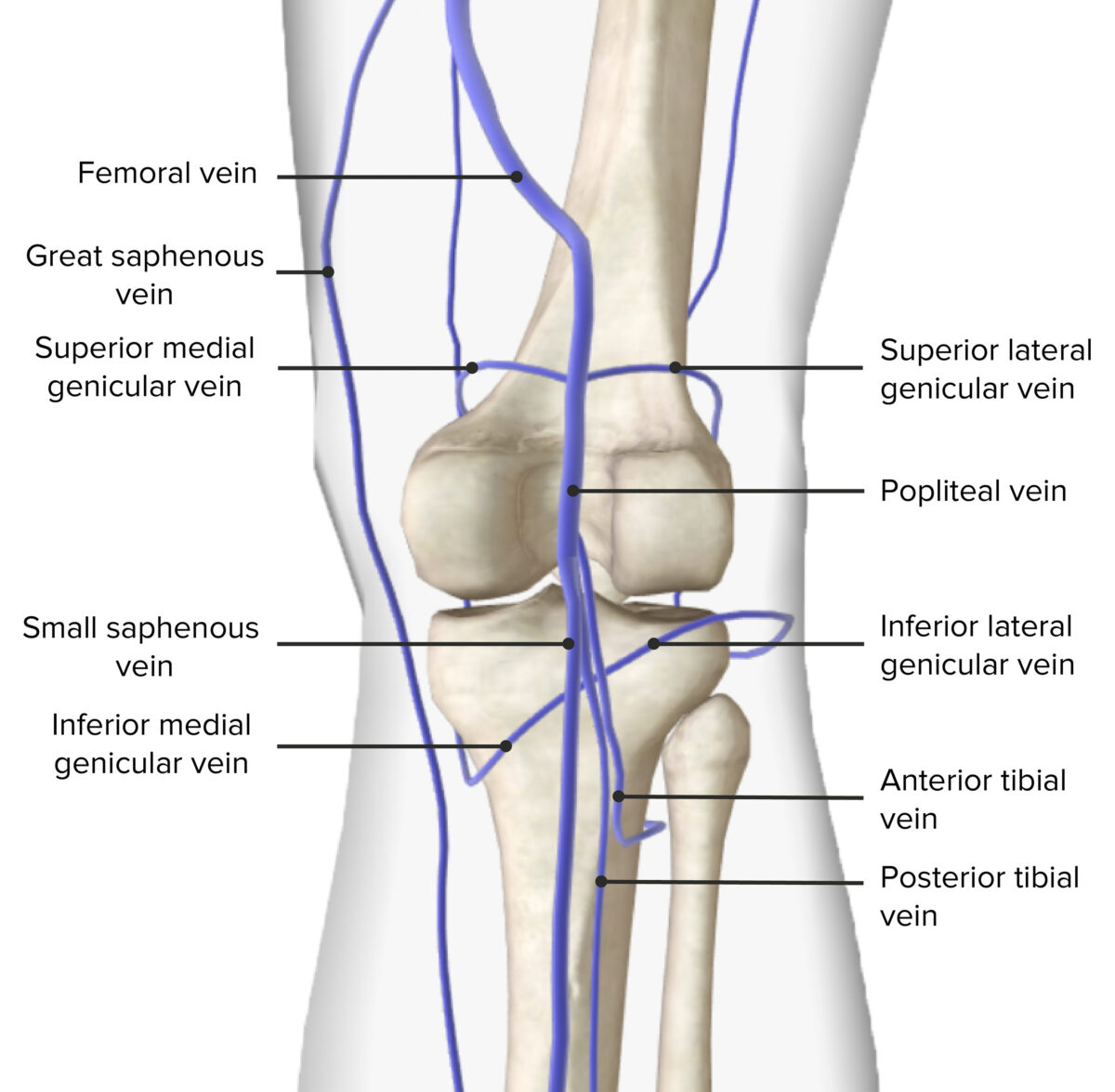
Drenaje venoso de la fosa poplítea
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria principales nervios de la fosa poplítea son las 2 ramas del nervio ciático, que es la mayor rama del plexo lumbosacro y se bifurca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ángulo superior de la fosa poplítea en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria siguientes:
Inervación de la fosa poplítea
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio.A continuación se presenta un importante concepto clínico relacionado con las estructuras que se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fosa poplítea:
Las siguientes afecciones tienen importancia clínica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum relación con la fosa poplítea: