La enfermedad por descompresión, conocida informalmente como "la enfermedad del buzo", es una afección causada por la compresión y la descompresión de los LOS Neisseria gases contenidos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo durante el descenso y el rápido ascenso durante el buceo. La presentación clínica de la enfermedad por descompresión puede ser inespecífica y variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables, con un tiempo de aparición que puede variar desde inmediatamente hasta 12 horas después de salir a la superficie. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente. El tratamiento consta de terapia de soporte temprana y un tratamiento de recompresión hiperbárica realizado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un centro especializado.
Last updated: Apr 4, 2025
La enfermedad por descompresión comprende diversos síntomas causados por las burbujas de gas que salen de la solución en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo luego de ascender tras una inmersión profunda.
Según la gravedad de los LOS Neisseria síntomas y la localización de las burbujas de gas:
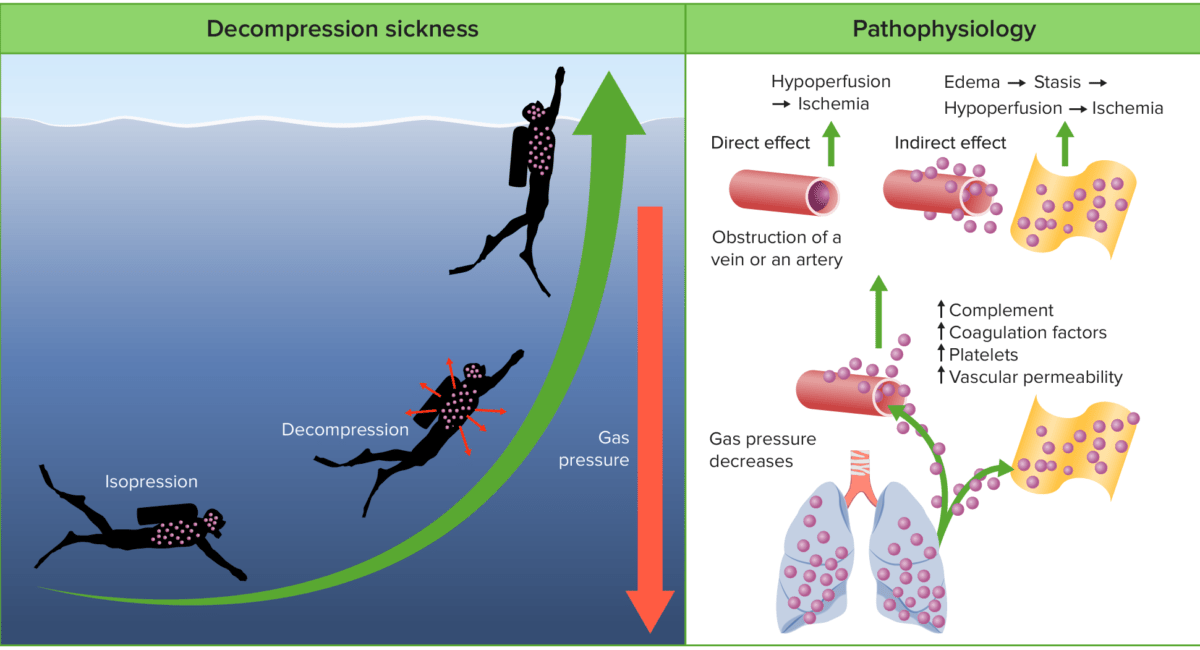
Fisiopatología de la enfermedad por descompresión:
Durante el descenso, el aumento de la presión hace que los gases se disuelvan en los tejidos y la sangre del cuerpo. Durante la descompresión, los tejidos se sobresaturan con estos gases, dando lugar a la formación de gas libre. Estas burbujas de gas pueden filtrarse en los capilares pulmonares en pequeñas cantidades. Sin embargo, en grandes cantidades, los gases pueden provocar una obstrucción vascular directa, la activación de las plaquetas y de las cascadas de coagulación, fugas capilares y respuestas inflamatorias.
| Neurológicas: cerebral |
|
|---|---|
| Neurológicas: médula espinal |
|
| Neurológicas: vestibulococlear | |
| Neurológicas: periférico | Alteración sensitiva no dermatológica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de parches |
| Musculoesqueléticas | Dolor Dolor Inflammation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las articulaciones (“las curvas”) |
| Oculares |
|
| Pulmonares |
|
| Cardiovasculares |
|
| Cutáneas |
|
| Linfáticas | Edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema de tejidos blandos |
| Constitucionales | Fatiga y malestar |
El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
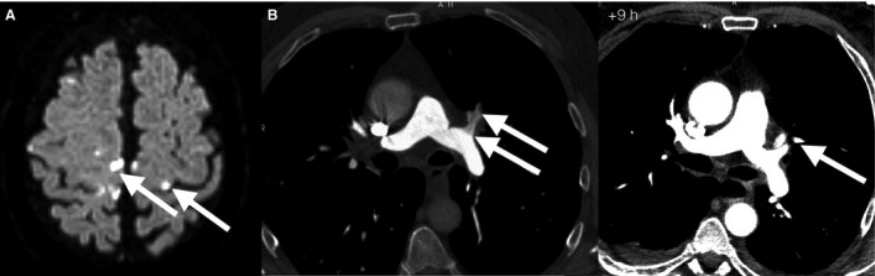
Varón de 61 años con experiencia en buceo que se presenta con un diagnóstico de enfermedad por descompresión:
(A) RM de la cabeza que muestra múltiples tromboembolismos cerebrales.
(B) TC del tórax 6 horas después de los primeros síntomas que muestra múltiples tromboembolismos pulmonares de las arterias segmentarias.
TC de seguimiento del tórax 9 horas después: no hay tromboembolismo pulmonar de las mismas arterias segmentarias.
El objetivo principal de la terapia es disolver las burbujas y recomprimir el gas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria fluidos corporales.
Las siguientes afecciones aumentan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran medida la probabilidad de desarrollar enfermedad de descompresión: