El sistema respiratorio se encarga de eliminar el volátil ácido dióxido de carbono (CO2), que se produce a través del metabolismo aeróbico. El cuerpo produce aproximadamente 15 000 mmol de CO2 al AL Amyloidosis día, que es la mayor parte de producción diaria de ácido; el resto de la carga ácida diaria (solo unos 70 mmol de ácidos no volátiles) se excreta a través de los LOS Neisseria riñones. Cuando se produce hiperventilación, se expulsa el exceso de dióxido de carbono y se produce alcalosis respiratoria. Los LOS Neisseria riñones responden disminuyendo el bicarbonato sérico (HCO3–) mediante el aumento de la excreción de HCO3– o la disminución de la excreción de H+. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan un aumento de la frecuencia respiratoria, disnea, mareo y, potencialmente, síntomas psicológicos. El diagnóstico implica unos antecedentes exhaustivos, examen físico y gasometría arterial. El tratamiento se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de las anomalías subyacentes, la estabilización de los LOS Neisseria pacientes con sufrimiento agudo y, potencialmente, una pequeña dosis de benzodiacepinas de acción corta.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La alcalosis respiratoria se refiere al AL Amyloidosis proceso que da lugar a una disminución del nivel de dióxido de carbono (CO2) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre.
| Etiología | Ejemplos |
|---|---|
| Fisiológica (no patológica) |
|
| Inducida por hipoxia |
|
| Medicamentos |
|
| Procesos intracraneales |
|
| Etiologías psicológicas |
|
| Otros procesos |
|
Los LOS Neisseria trastornos ácido–base se clasifican según la alteración primaria (respiratoria o metabólica) y la presencia o ausencia de compensación.
Observar el pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance, la PCO2 (presión parcial de CO2) y HCO3– (bicarbonato) para determinar la alteración primaria.
Cuando se produce una acidosis Acidosis A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. Respiratory Acidosis o una alcalosis, el cuerpo intenta compensarla. A menudo, la compensación dará lugar a un pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance normal.
La alcalosis respiratoria es un proceso que provoca una disminución del nivel de dióxido de carbono.
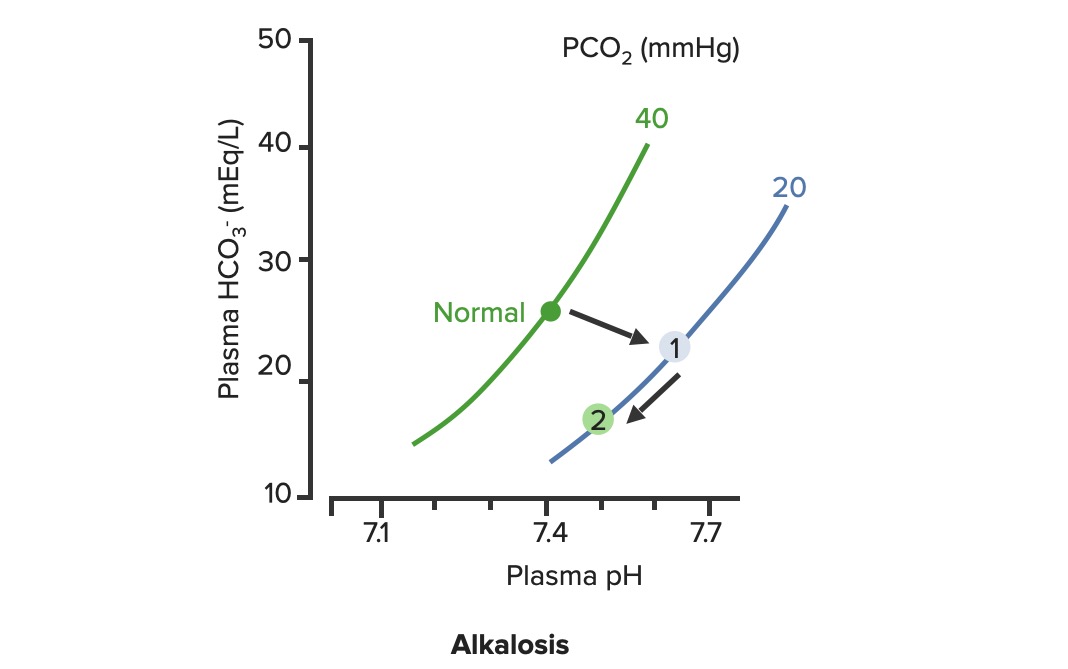
Compensación renal de la alcalosis respiratoria:
En la alcalosis respiratoria, la PCO2 disminuye, desplazando la curva de PCO2 hacia la derecha (1). A medida que los niveles de HCO3– son disminuidos por los riñones, el pH mejora a lo largo de la línea de PCO2 (2)
La alcalosis respiratoria aguda frente a la crónica se define por el grado de compensación renal.
El diagnóstico de una alcalosis respiratoria suele requerir unos antecedentes y examen físico exhaustivos, así como una gasometría arterial.