As anemias sideroblásticas são um grupo heterogéneo de distúrbios da medula óssea caracterizados pela acumulação anormal de ferro nas mitocôndrias dos precursores eritróides. O ferro acumulado aparece como grânulos numa distribuição em forma de anel à volta do núcleo, dando origem à característica morfológica de um sideroblasto em anel. As anemias sideroblásticas podem resultar de defeitos hereditários na síntese do heme ou podem ser adquiridas no caso do alcoolismo, envenenamento por chumbo, fármacos ou deficiência de vitaminas. A anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types é comumente microcítica com contagem de reticulócitos baixa a normal. Os níveis séricos de ferro estão geralmente elevados. Um exame de medula óssea que mostre sideroblastos em anel estabelece o diagnóstico. O tratamento envolve a getsão da doençs subjacente, evitando fármacos e/ou toxinas causadoras e flebotomia em casos de sobrecarga de ferro.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
As anemias sideroblásticas são um grupo heterogéneo de distúrbios da medula óssea caracterizados pela acumulação anormal de ferro nas mitocôndrias dos precursores eritróides.
A distribuição do ferro é em forma de anel em volta do núcleo, manifestada pelos precursores (sideroblastos em anel) na medula óssea.
Distúrbios Congénitos:
Adquirido:
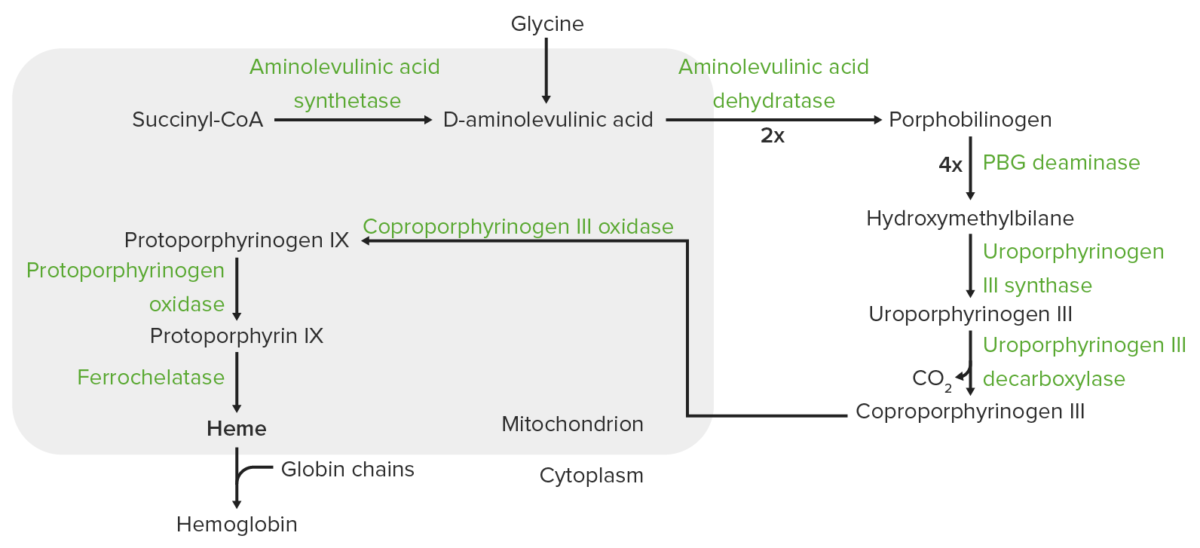
Síntese do grupo Heme:
A síntese do heme é um processo que ocorre nas mitocôndrias e no citoplasma.
Na mitocôndria, a succinil-CoA combina-se com a glicina para formar o ácido aminolevulínico (ALA).
Esta reação é catalisada pela sintase do ácido aminolevulínico (ALAS2 nos eritrócitos). O ALA sai para o citoplasma, onde 2 moléculas de ALA condensam-se para produzir porfobilinogênio (PB). As etapas subsequentes levam à formação do coproporfirinogênio III, que é transportado de volta para a mitocôndria. A oxidase facilita a conversão do coproporfirinogênio III em protoporfirinogênio IX, que então é convertido em protoporfirina IX. O ferro ferroso é inserido na protoporfirina IX, formando o heme (catalisado pela ferroquelatase).
Defeitos na síntese do heme:
Defeitos na biogénese do cluster ferro-enxofre (CFE):
Defeitos na síntese de proteínas mitocondriais:
Disfunção na eritropoiese:
A apresentação clínica varia de acordo com a doença de base.
Características gerais da anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types:
Pacientes com deficiência de vitamina B 6 podem apresentar:
Pacientes com intoxicação por chumbo podem apresentar:
Outros:
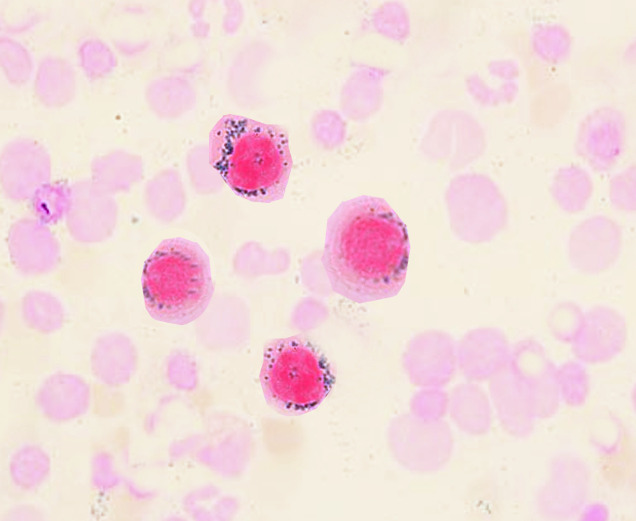
Sideroblastos em anel
Imagem : “Ringed sideroblastd” por S. Bhimji, MD. Licença: CC BY 4.0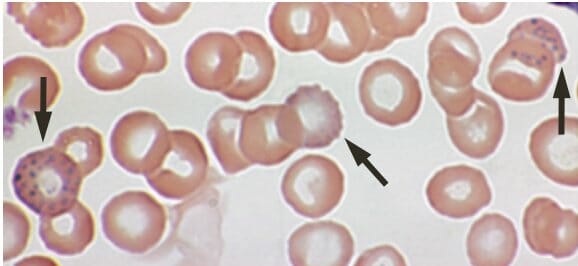
Envenenamento por chumbo:
Pontilhado basofílico num esfregaço de sangue periférico de um indivíduo de 53 anos com anemia e queixas de fadiga e obstipação
| Achados no hemograma | Diagnóstico | Nível de ferro | Historial médico |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types com MCV < 80 | Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types sideroblástica | ↑ Nível de ferro | Alcoolismo, SMD |
| Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types por deficiência de ferro | ↓ Nível de ferro | Perda de sangue | |
| Talassemia | Nível normal de ferro | Dependente da gravidade ( anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types assintomática a grave) |
As opções de tratamento dependem da etiologia e incluem: