Os ácidos nucleicos são polímeros de nucleotídeos, moléculas orgânicas compostas por um açúcar, um grupo fosfato e uma base nitrogenada. Os ácidos nucleicos são responsáveis pelo armazenamento, replicação e expressão da informação genética. São “ácidos” pelos grupos fosfato que são de natureza ácida e “nucléicos” porque são armazenados no núcleo da célula. Os 2 ácidos nucleicos mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome frequentemente vistos em células eucarióticas são o ácido desoxirribonucleico ( DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure) e o ácido ribonucleico ( RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure). Embora quimicamente semelhantes, o DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure e o RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure têm funções biológicas específicas às quais as suas respetivas estruturas estão adaptadas.
Last updated: May 19, 2025
Contents
Os ácidos nucleicos são polímeros de nucleotídeos. Principais classes:
Os nucleotídeos são as unidades básicas de um ácido nucleico.
Composto de:
Açúcar de 5 carbonos:
Bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance nitrogenadas:
Os nucleotídeos são montados em polímeros de ácido nucleico pela adição de ligações fosfodiéster 5′-3′:
Nomenclatura de nucleotídeos:
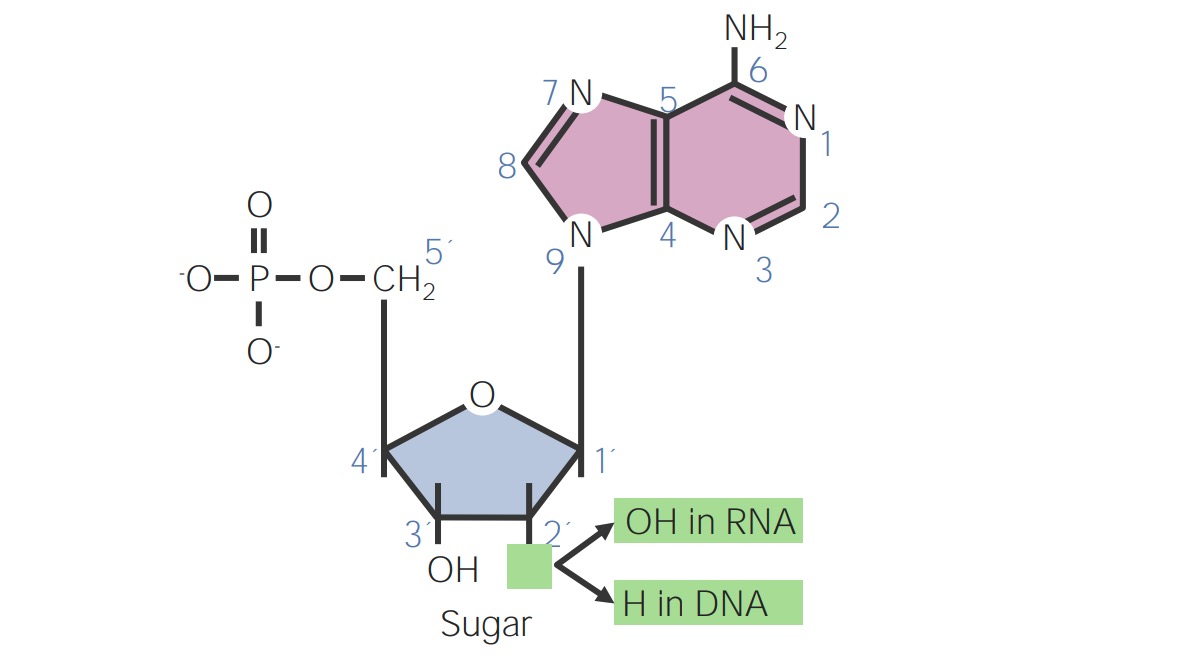
Estrutura de um nucleotídeo
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0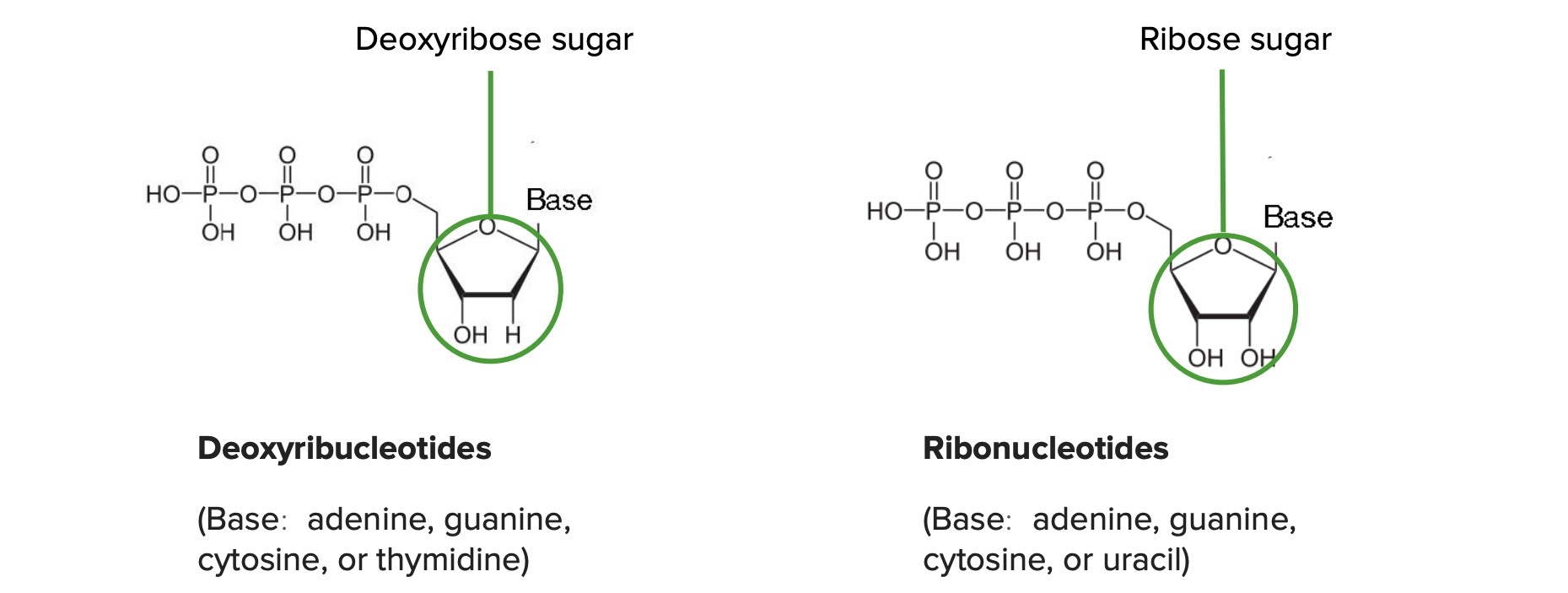
Diferença entre desoxirribonucleotídeos e ribonucleotídeos:
O carbono 2′ está ligado ao hidrogénio (H) no DNA e à hidroxila (OH) no RNA.
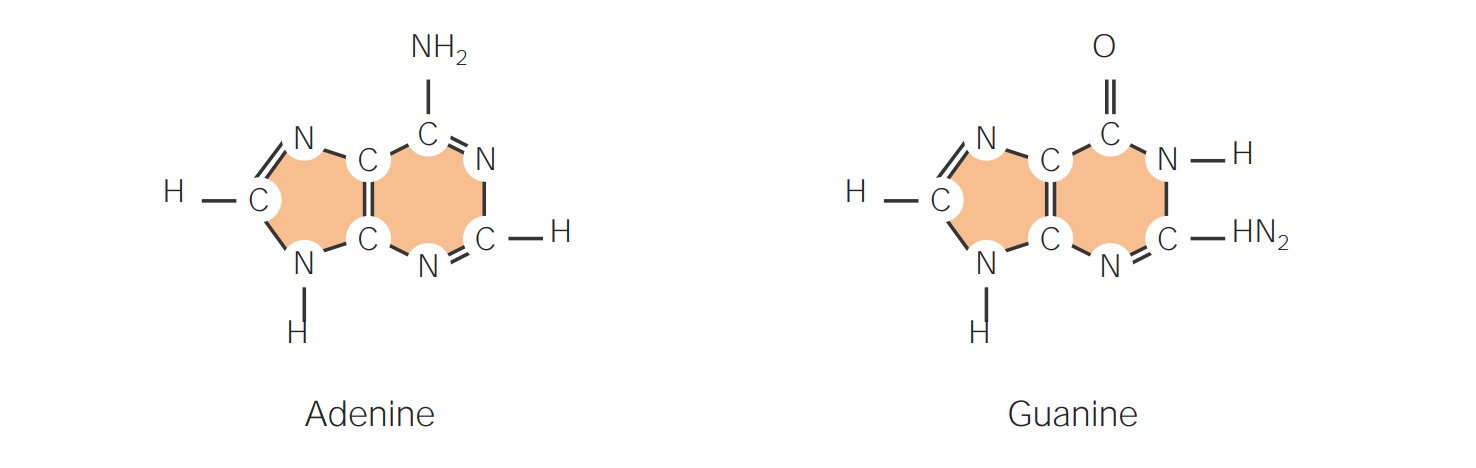
Estrutura de bases nitrogenadas: purinas
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0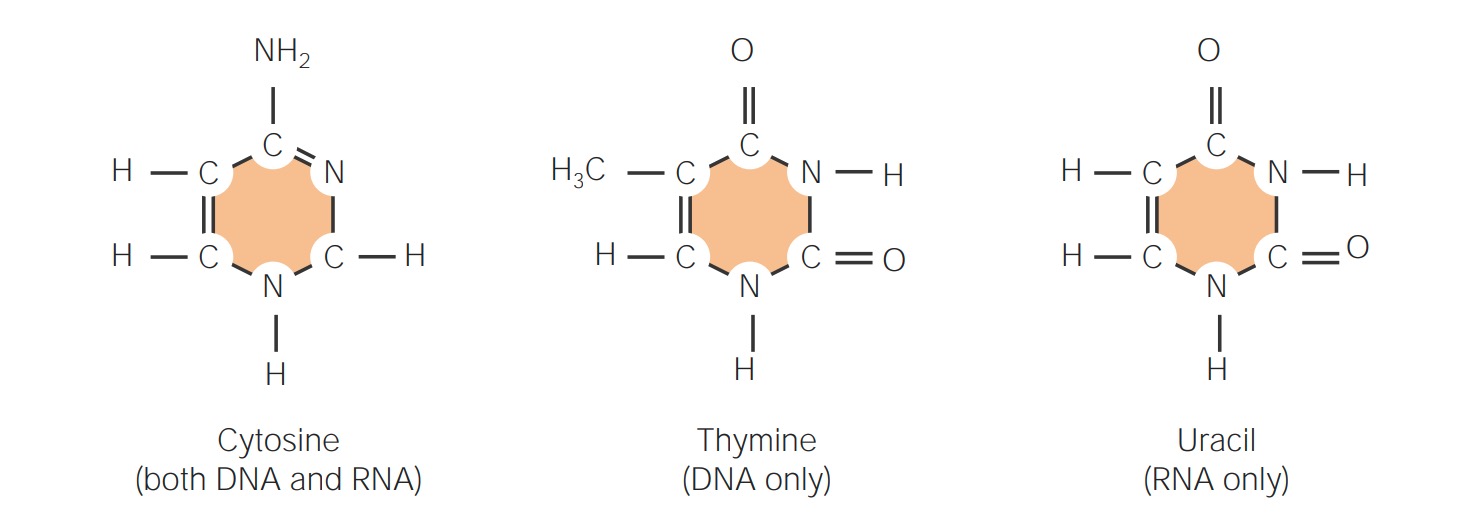
Estrutura de bases nitrogenadas: pirimidinas
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Estrutura de um ácido nucleico:
Observar as extremidades 5′ (P) e 3′ (OH) desacopladas.
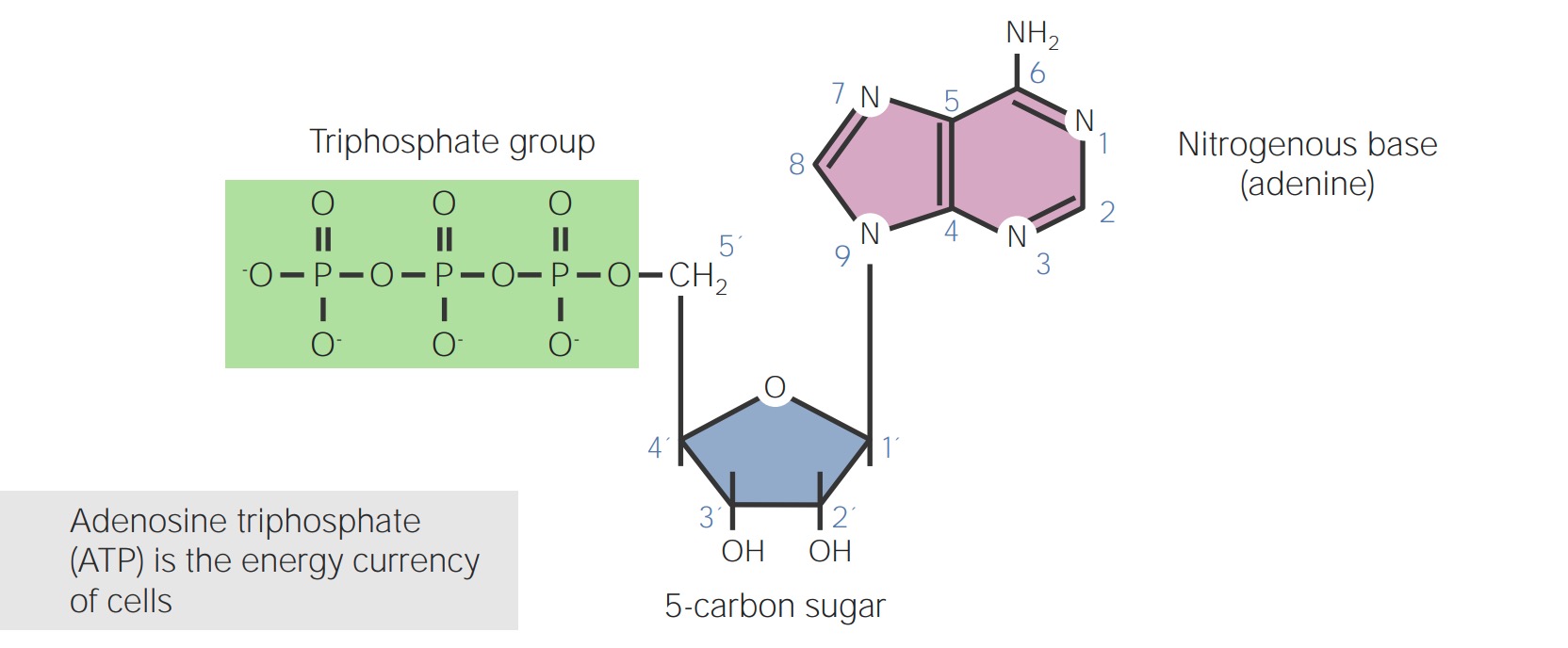
Estrutura do trifosfato de adenosina (ATP)
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0O DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure é o modelo genético para a vida, que contém os códigos para genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure.
RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure: biossíntese de proteínas, funções reguladoras, processamento e transporte
Existem diferentes formas de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure para fins especializados para as fases de replicação e tradução do material genético:
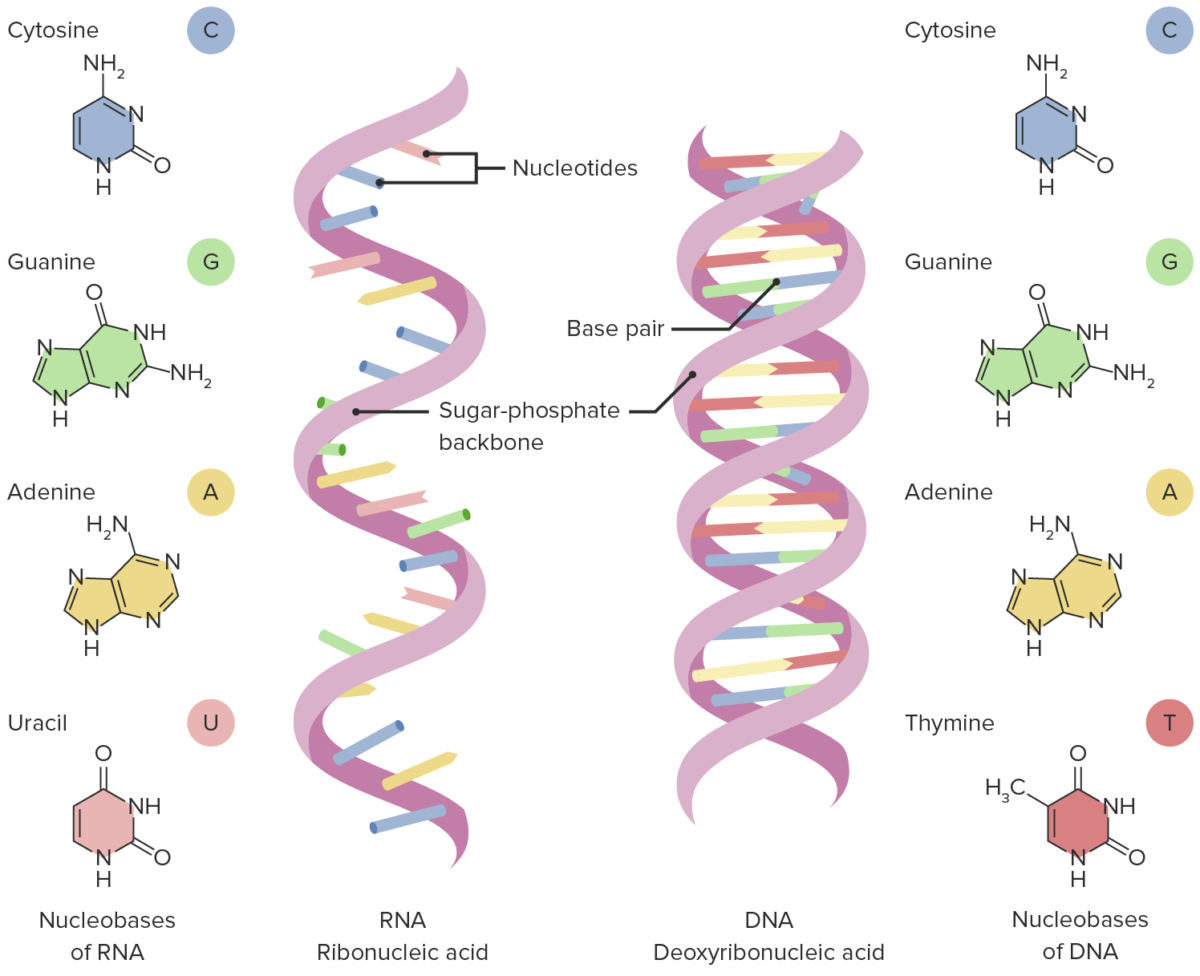
Estruturas de RNA e DNA
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0