Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Uterine Abnormalities
-
Slides Uterine Abnormalities.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
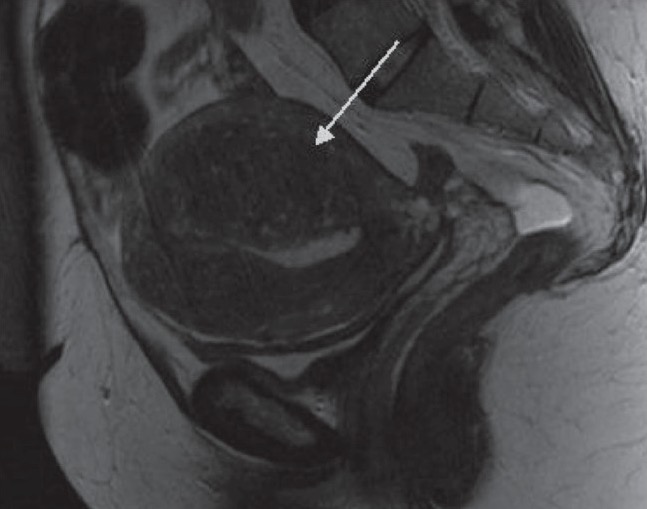
00:01 So in this lecture, we'll be talking a little bit about uterine abnormalities. 00:04 Imaging is used very frequently to evaluate for uterine abnormalities. 00:08 Most commonly is ultrasound. 00:10 So what are some common uterine abnormalities that you may see? Uterine fibroids are very commonly seen. 00:17 Occasionally, we may see adenomyosis and endometrial thickening is also a very common abnormality to find. 00:25 So let's look at all of these in a little more detail. 00:27 So, uterine fibroids are benign tumors of the smooth muscle cells of the uterus. 00:32 It's very common to see this especially in the reproductive years and mostly, they're asymptomatic. 00:37 However, they can cause pain, menorrhagia, and infertility and it depends on the size and location of the fibroids as to whether or not they cause any symptoms. 00:45 So some of the imaging findings of uterine fibroids on ultrasound is that it presents as a hypoechoic mass. 00:51 It may have calcifications and it may have cystic components or fat so they can be homogeneous. 00:58 However, if they contain calcifications or cystic components, they may be heterogeneous as well. 01:03 There are three different locations of uterine fibroids. 01:07 They may be submucosal which means that they're abudding the endometrium, and if they are, these can cause bleeding and infertility. 01:14 They may be intramural which are the ones that are least likely to cause symptoms and that means they are embedded completely within the myometrium or they may be subserosal and that means that they are abudding the outside surface of the uterus which can have a mass effect on adjacent structures and cause pain and abnormalities related to the mass effect on these structures. 01:35 So uterine fibroid is a heterogeneous, hypoechoic mass that arises from the uterine myometrium. 01:41 So let's take a look at a couple of examples. 01:43 This is a transvaginal sagittal image of the uterus. 01:46 We can see the outline of the uterus here and we can see here a portion of the endometrium. 01:55 So this area right here represents a uterine fibroid and this is intramural. 02:01 Although it has slight prominence posteriorly, the bulk of it is actually located within the myometrium. 02:07 This is an example of a subserosal fundal fibroid so it's a little bit difficult to see this uterus because it is a little bit distorted due to multiple fibroids. 02:16 We only see one discreet fibroid which is right here and you can see that this is the portion of the myometrium while the fibroid extends significantly outside of that portion indicating that it is subserosal. It's actually quite common for us to not be able to discreetly identify multiple fibroids. 02:32 They often have the same echogenicity as the surrounding myometrium. 02:35 So occasionally, when you have multiple fibroids, the uterus may appear distorted but you may not see individual fibroids. 02:42 So just the appearance of a heterogeneous distorted myometrium should tell you that this patient may have multiple fibroids. 02:49 It's important to remember that a fibroid that progressively enlarges in size or is greater than 8cm to begin with, should be considered suspicious for a sarcoma and the best way to differentiate between a fibroid and a sarcoma is an MRI. 03:02 This is an example of a patient that had a metastatic uterine sarcoma. 03:05 So sarcomas are very rare but they are malignant neoplasms of the uterus and they can metastasize. So as you see in this lung, there's a small nodule here which is from the uterine sarcoma. 03:17 Adenomyosis is somewhat rare condition of the uterus. 03:21 It's the presence of heterotopic endometrial stroma located within the myometrium. 03:26 The clinical presentation is often dysmenorrhea or menorrhagia. 03:30 And you can see here the small endometrial implants seen on this pathological specimen. 03:36 So the imaging findings of adenomyosis include an enlarged uterus if you have multiple implants that leads to an enlarged uterus. 03:42 The myometrium may have multiple cystic spaces and the posterior uterine wall appears widened on ultrasound and we'll take a look at an example. 03:52 This is really best visualized on ultrasound and MRI. 03:56 Again, CT is not a very good way to evaluate pelvic structures. 03:59 So this is an example of a patient with adenomyosis. 04:03 This is a sagittal transvaginal ultrasound image. 04:06 So again, here's the uterus here. 04:09 You can see the endometrium right here and you can see that the myometrium posteriorly is very thickened. 04:16 It really should be homogeneous all the way around. 04:19 So it should be about the same width anteriorly and posteriorly and you can see, this is probably almost double the width posteriorly as it is anteriorly. 04:26 You can also see a couple of small cystic spaces within the posterior myometrium which is again characteristic of adenomyosis. 04:34 So let's talk a little bit about endometrial thickening. 04:37 Endometrial thickening can be either focal or diffuse. 04:39 Focal endometrial thickening can be caused by a polyp, endometrial carcinoma or possibly a submucosal fibroid. 04:47 Diffuse endometrial thickening can often be seen in the normal secretory phase of a premenopausal woman but it can also represent endometrial hyperplasia or even endometrial carcinoma. 04:58 So this is an example of a patient with endometrial thickening. 05:01 It really is difficult to distinguish based on imaging alone because if this is a premenopausal female, this may represent a normal endometrium. 05:09 If there is any question of an abnormality, a sonohysterogram is often helpful to differentiat focal from diffuse and to help differentiate the location of a lesion which may then be biopsied. 05:20 In a postmenopausal female that has bleeding, this really is endometrial carcinoma until proven otherwise. 05:27 So in these patients, the patient really needs a hysteroscopy with biopsy. 05:30 Hysteroscopy is really the ideal way to biopsy the endometrium. 05:35 Endometrial atrophy also occurs occasionally in postmenopausal women and this is due to a lack of hormonal stimulation. 05:41 The endometrium is found to be less than 4mm in these women. 05:46 Approximately 4mm is the standard that you would expect in a normal postmenopausal female. 05:51 So when it goes under 4mm on a patient that has symptoms, you would definitely wanna consider endometrial atrophy. 05:57 It's the most common cause of postmenopausal bleeding, second to endometrial cancer. 06:03 So we've discussed some common abnormalities of the endometrium in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women in this section.
About the Lecture
The lecture Uterine Abnormalities by Hetal Verma, MD is from the course Abdominal Radiology. It contains the following chapters:
- Uterine Abnormalities
- Adenomyosis
- Endometrial Thickening
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is NOT true about adenomyosis?
- Submucosal lesions cause bleeding and infertility.
- It causes uterine enlargement.
- It causes cystic myometrial spaces.
- It is well visualized on ultrasound and MRI.
- The posterior uterine wall appears enlarged on ultrasound.
Uterine fibroids are…
- … mostly asymptomatic but can cause pain, menorrhagia, and infertility.
- …malignant lesions of the uterus.
- …commonly seen presenting in post-menopausal women.
- …seen as a hyperechoic mass with fibrous tissue.
- …developed from the glandular cells of the uterus.
A 36-year-old woman has a progressively enlarging uterine fibroid currently measuring 8 cm on ultrasound imaging. What is the next best step to rule out a sarcoma of the uterus?
- MRI
- CT scan
- Biopsy
- PET scan
- Repeat USG in 2 weeks
What is the normal endometrial thickness in a normal post-menopausal woman?
- ≤ 4 mm
- ≥ 6 mm
- 1 cm
- 1.5 cm
- 2 mm
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |