Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Theoretical Diagnosis and Treatment of the Knee
-
Slides Osteopathic Diagnosis of the Knee.pdf
-
Reference List Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
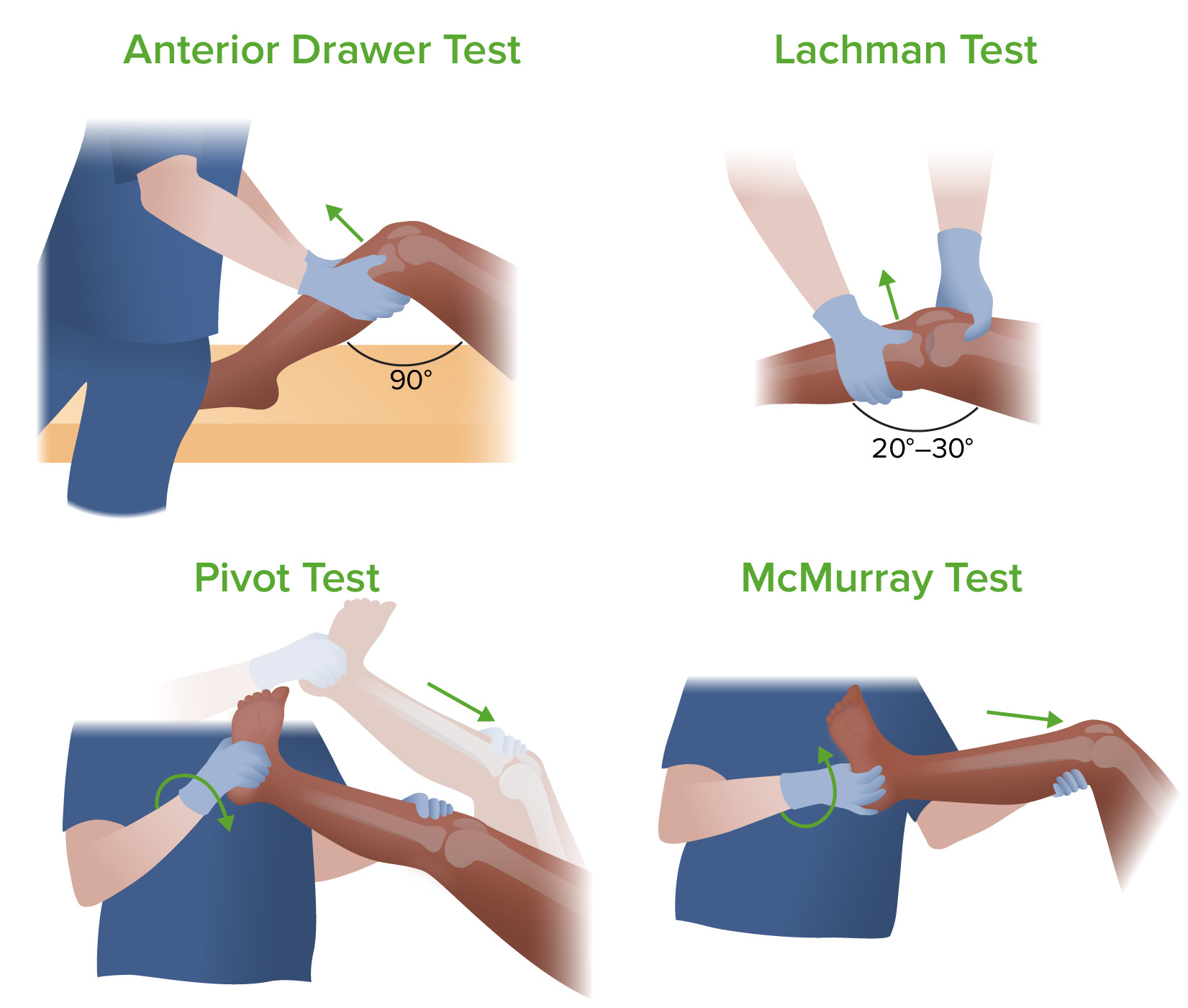
00:01 So with knee injuries, if we don't know what to do, if we just want to help the person feel better because there's nothing we can do, we generally prescribe RICE Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation. 00:16 We also found that supports and enhance proprioceptive sense helps a person self regulate and treat themselves better. 00:25 That's why knee braces or ace wraps which will give you 30 minutes to 2 hours of enhanced proprioceptive sense, a better knowledge of how your functioning is and allows you to function easier and flow smoother than you would've otherwise That's why when we have a person playing sports, you want to tape them up or wrap them up just before they go into the game. 00:51 otherwise, you're gonna lose some of the benefit. 00:53 We also often prescribe stretching, strengthening and stabilizing of the knee joint in order to enhance functioning. 01:01 When that doesn't work, we move to medications. NSAIDS do tend to decrease the amount of swelling NSAIDS do tend to decrease the amount of swelling and the symptoms from a overused or somewhat injured knee. 01:14 Acetaminophen doesn't decrease the swelling but it works with the brain level to stop you from thinking you have pain so you can continue functioning, continue playing and also give yourself time to heal. 01:25 Injections into the knee, more often take fluid out from an overuse injury than injecting in but on two to three occassions a year, somebody is using their knee in a bad way or has pain, you can give them steroid injections. 01:41 Lidocaine works on a short term basis for severe pain and there are these called supplements that you can get people to enhance the shock absorbency or gliding ability of the knee. 01:58 but those tend to give time limited benefit and do require multiple injections. 02:06 From the osteopathic medicine perspective, evaluating for somatic dysfunction of the knee and one joint above and one joint below are important. 02:15 noticing motor patterns, seeing if the knee is affecting the ankle functioning and the hip functioning and to promote homeostasis and fluid functioning of the musculoskeletal system When you have somebody come to you for knee pain, the demographics are gonna help a lot. 02:34 Children and adolescents are gonna have knee pain which is often overuse or growth. 02:40 It could be a patellar subluxation tendonitis or jumper's knee or Osgood-Schlatter from age or hormonally related. 02:47 Arthritis is possible but less likely, and you always have to worry about the outlier who may have a bony tumor or growth and osteosarcoma and exostosis, some kind of bony growth causing pain as well. 03:04 Patients younger than 45 also get patellar syndromes and are also at risk for trauma of both ligamentous and meniscal nature, although, less likely in kids. 03:19 And it's often common that hip pathology contributes to knee pathology. 03:24 People with abnormal angles or abnormal functioning will tend to develop knee pain as well Over 45 years of age, by far the most common problem is degenerative arthritis. 03:39 The knees worn out, you may have avascular necrosis, you may have a meniscal tear but it's wear and tear of the knee that causes it. 03:49 And also think of hip pathology - one joint above, one joint below can contribute to knee pain The angles of the knee and the hip and the ankle all should be taken into account. 04:04 When people complain about the knee pain, you can often localize it by asking more about history. 04:10 Is it the front of the knee? Which is more likely to mean that the person is involved or is it tendonitis? In the younger patient you'd worry about Osgood-Schaltter's. 04:19 Is it the back of the knee, where you could have ankle pain that's being referred higher or you can have a cyst in that area. 04:29 If the pain is medially, you worry about a chronic medial collateral ligament or you worry about the bursas being swollen from overuse. 04:38 If it's lateral pain, you worry about the lateral collateral ligament or a fibular head dysfunction When you wanna treat patellofemoral pain syndromes, first thing is rest. 04:49 If overuse is the most common cause, then rest of the knee is the most common treatment. 04:56 We also have ergonomic aids such as splints, bledsoe brace is gonna prevent overextension It's also going to give you an enhanced sense of functioning or proprioceptive awareness We also will treat with analgesics and taping and wrapping. 05:15 Physical therapy and OMM focuses on correcting abnormal mechanics and use and teaches people to protect their knees, how to use it, when injury is more likely and what they need to do to not get injured. 05:31 If the disease is severe and the pain is longstanding, it may take longstanding exercises to strengthen the quadriceps and the hamstrings. 05:40 and soft tissue techniques can give short term benefit as well as enhancing flexibility. 05:47 For the anterior knee, you wanna worry about osteochondritis dissecans as well, patellofemoral pain syndromes, acute articular cartilage injury, bony tumors, as a rare but we need to worry about, chondromalacia patella, patellar fracture or illiotibial band syndrome which is a common running injury that occurs. 06:11 Those are the major knee problems and again, when you have people complaining of knee issues, always examine the knee for biomechanics, for normal functioning, look one joint above, one joint below and see how the knee is affecting the whole body and concern that it may throw a person from neutral mechanics into non-neutral mechanics and have other effects further away. 06:38 You're gonna see a lot of knee complaints again, witnessing and sharing what's going on can be very helpful to earning a person's trust and helping prevent further deterioration or further issues later on. Thank you.
About the Lecture
The lecture Theoretical Diagnosis and Treatment of the Knee by Tyler Cymet, DO, FACOFP is from the course Osteopathic Diagnosis of the Knee Region. It contains the following chapters:
- Diagnosis and Treatment of the Knee
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome – Treatments
- Anterior Knee Pain – Differential Diagnosis
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is the most common cause of knee pain in patients older than 45 years?
- Degenerative changes or Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Avascular necrosis
- Meniscal tears/cruciate ligament rupture
- Hip pathology
- Tumors
Which of the following is used mostly commonly as first-line treatment for patellofemoral pain syndrome?
- RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) therapy
- Surgery
- NSAID/analgesics
- Taping
- Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine (OMM)
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
A very thorough explanation of differential diagnosis with knees and treatment