Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Ovarian Tumors
-
Slides Ovary Female Repro.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
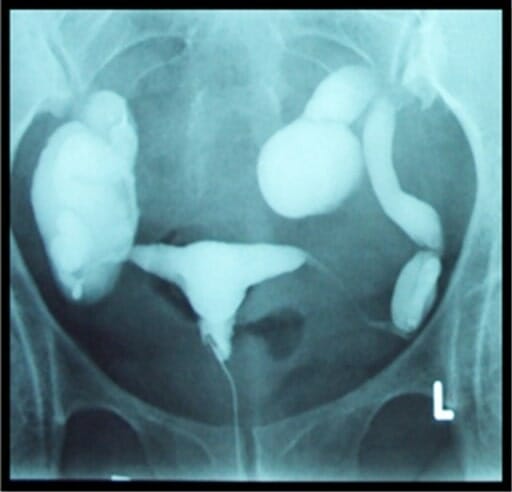
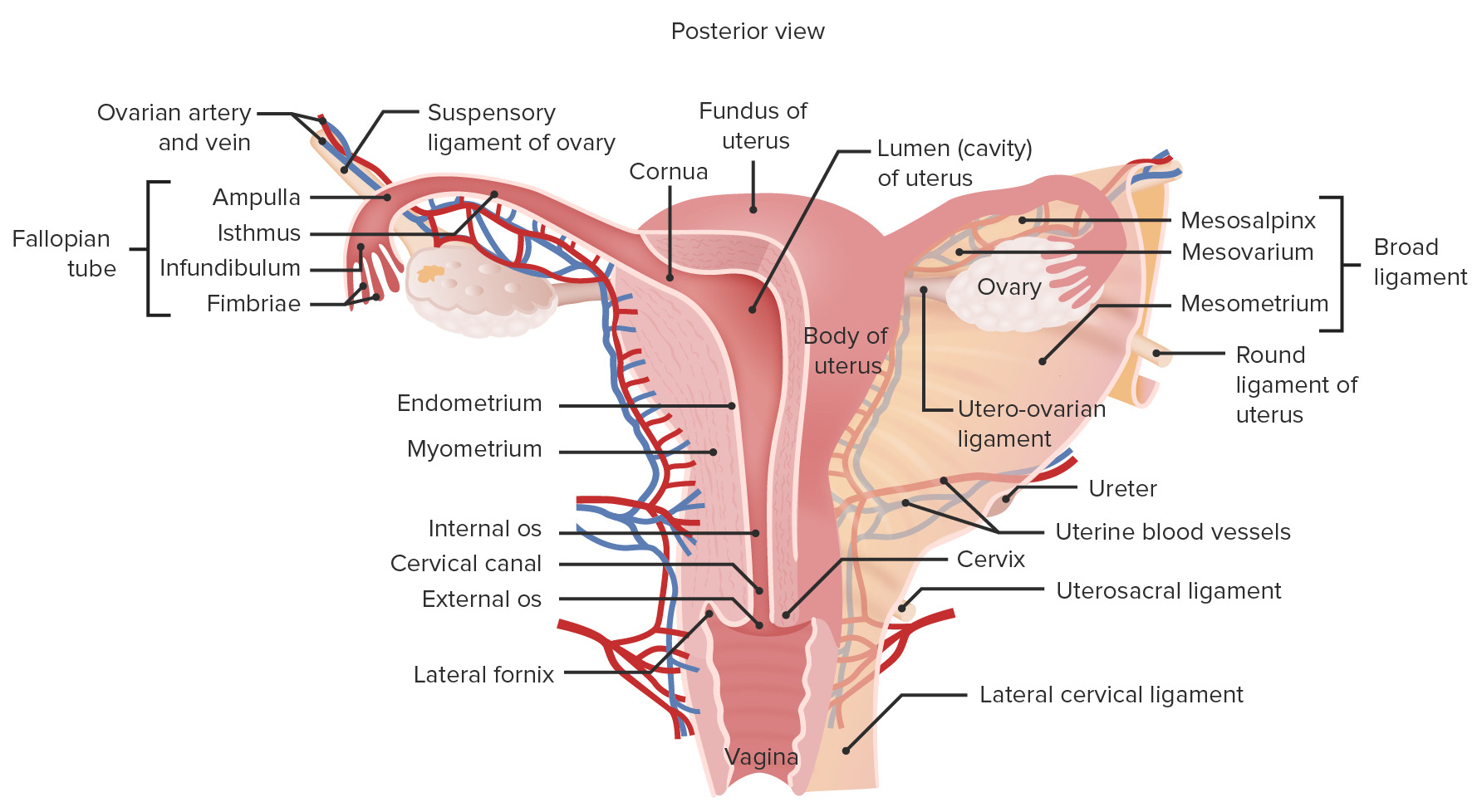
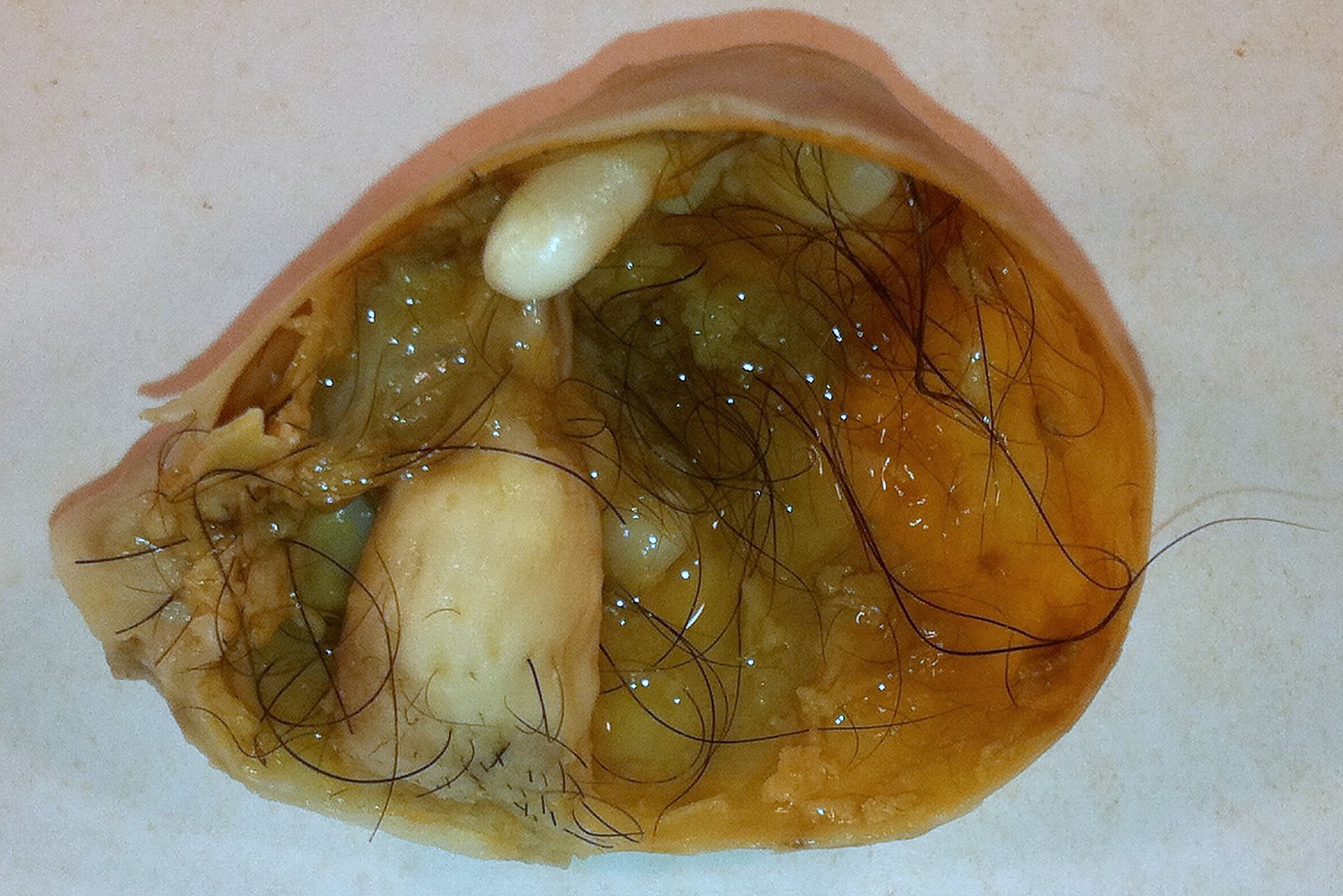
00:01 Here, we’ll take a look at ovarian tumors. 00:04 With ovarian tumors, 6% of cancers in female are ovarian tumors. 00:11 By the time we’re done with this, I'll give you a proper organization and I’ll tell you where to focus with ovarian tumors because it is a lot of information. 00:18 There’s no doubt about that. 00:19 But if you have proper organization, trust me, it doesn’t seem so bad. 00:25 Eighth most common form of cancer of women in the United States. 00:30 Usually detected late. 00:32 Why? Well, because the patient is pretty much asymptomatic. 00:36 And by late, well, we had this discussion earlier, neoplasia – Just to make sure we’re clear – that ovarian tumor and cancer, it may begin early at the age of 40 or 45. 00:49 That’s pretty early. 00:51 What do you think the median age of presentation is in the U.S.? Sixties. 00:56 Wow! Yeah. 00:57 That’s almost 20 years of an active tumor in the ovary. 01:01 I don’t care how benign it’s been. 01:03 If it remains active for 20 years, of course it then becomes malignant and kills your patient. 01:10 Look at this. 01:11 Fifth most common cause of cancer death overall. 01:16 One, two and three in a female. 01:18 Remember, one, lung. 01:19 Two, breast. 01:20 Three is going to be colorectal. 01:22 Five, right up there. 01:24 Amazing! Pathogenesis: Responsible for almost half of deaths from cancer of female genital tract, ovarian tumor. 01:35 What we’ll do here, and I’ll show you a picture, is to then categorize and organize. 01:40 I would prefer to show you the picture so that you’d clearly see where your emphasis will be and should be with ovarian tumors. 01:49 Risk factors before we get to the organization. 01:52 Risk factors: Nulliparity. 01:54 Family history. 01:55 BRCA1 and BRCA2.
About the Lecture
The lecture Ovarian Tumors by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Ovarian Diseases.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following patients is at highest risk for ovarian cancer?
- G0P0 50-year-old woman with a mother and sister with breast cancer
- G1P2 30-year-old woman with no past medical history
- G3P3 30-year-old woman with a mother diagnosed with breast cancer at age 80
- G1P1 40-year-old woman with no past medical history
- G2P2 25-year-old woman with an aunt diagnosed with ovarian cancer at age 70
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |