Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Labor Stage 1: Obstetric Anesthesia
-
Slides ObstetricAnesthesia Obstetrics.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
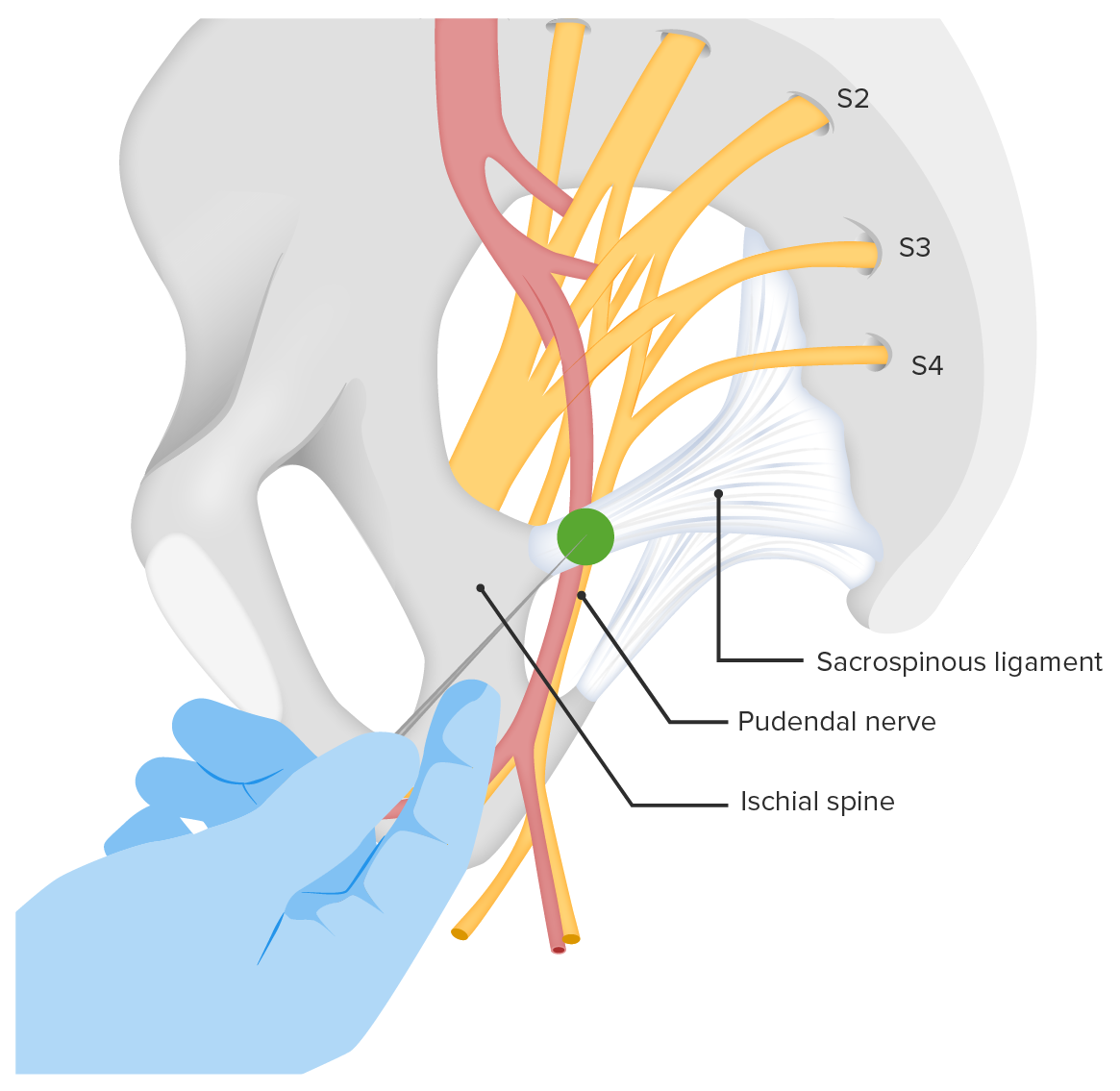
00:01 Now let's discuss Obstetric Anesthesia. 00:05 So we have a lot of options for managing pain in labor. 00:09 Let's take time to talk about each of these. 00:11 First is inhaled anesthesia. 00:15 So this is in the form of nitrous oxide also known as Laughing Gas. 00:19 It's inhaled intermittently in labor. 00:21 Mom is in control of that. 00:24 Pain relief however is minimal and is short lasting. 00:28 The side effects are nausea, dizziness and light headedness. 00:32 Nitrous oxide can be used for labor but not for cesarean sections. 00:39 Now let's talk about systemic opoid anesthesia. 00:44 So basically narcotics are given intravenously. 00:46 We have to be careful though because if they are given intravenously, that means that they go to the placenta and they can effect the fetus. 00:54 Pain relief is minimal and short lasting. 00:57 And they should not be given within 4 hours prior to expected to delivery. 01:02 Again because it is intravenous it goes to the placenta and the fetus can give the affects of the narcotic. 01:10 Maternal side effects are nausea, vomiting and drowsiness. 01:15 Fetal or neonatal side effects are fetal heart rate abnormalities or respiratory depression. 01:22 Now let's talk about local opoid anesthesia. 01:28 So this would be in the form of pudental nerve block as demonstrated here. 01:34 It could be used for operative vaginal delivery or repair of laceration or episiotomy. 01:39 So it's not typically used during the labor process. 01:42 And it cannot be used for cesarean sections as it would not provide anesthesia to the area needed. 01:47 But it can be used when you're using operative vaginal delivery. 01:51 It provides great pain relief along the nerve distribution. 01:55 Now you have to be cautious when you're doing a pudental nerve block because you can have potential hemorrhage if the pudental artery is accessed instead of the nerve. 02:04 Now, let's talk about regional opoid anesthesia. 02:10 So this is in the form of epidural or spinal. 02:13 So epidural anesthesia typically used for labor but it can be used for C-section. 02:19 During epidural placement a catheter is placed in the epidural space to inject medication. 02:25 It gives great pain relief from T8 to below but it can be spotty. 02:31 That means that patients can have what they call Hot Spots where they don't feel the pain relief in that area. 02:38 Now the maternal side effect of an epidural is hypotension. 02:41 This is particularly important specially for labor in patients. 02:45 With that hypotension patients can experience utero-placental insufficiency and that can affect the fetus. 02:52 And the fetus will manifest having that hypotension by having late decelerations. 02:59 So spinal anesthesia. 03:00 This is injected into the spinal fluid and it's used for C-sections. 03:05 It gives great relief from T10 to below. 03:07 So a little bit lower than an epidural and it last from between 2 to 4 hours. 03:13 Again the maternal side effect is hypotension and bradycardia. 03:17 And with that again, the fetus can start to have late decelerations as a manifestation of utero-placental insufficiency. 03:27 Now let's talk about general anesthesia. 03:31 So general anesthesia is reserved only for emergency C-sections. 03:35 Typically with C-section again we use an epidural or we use spinal anesthesia. 03:40 And even in some emerging cases we can still use epidural or spinal. 03:45 However, if it is an extreme emergency situation we would need to do a C-section. 03:51 General anesthesia is usually reserved for emergency sections or non-emergency sections where there is a contraindication to epidural or spinal anesthesia. 04:00 Contraindications for spinal anesthesia include intracranial masses or a history of extensive back surgery. 04:08 A lot of times moms can have vomiting and that can result in aspiration pneumonitis. 04:12 Specially if mom has any food in her stomach or has not been in PO for 8 hours. 04:19 Fetal side effects of general anesthesia, respiratory depression.
About the Lecture
The lecture Labor Stage 1: Obstetric Anesthesia by Veronica Gillispie, MD, MAS, FACOG is from the course Intrapartum Care. It contains the following chapters:
- Obstetric Anesthesia
- Regional Analgesia – Epidural and Spinal
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following are the typical side effects of nitrous oxide analgesia?
- Maternal nausea and lightheadedness
- Fetal respiratory depression
- Maternal hypotension
- Late decelerations on fetal heart tracing
- Uteroplacental insufficiency
Which of the following is a typical risk of epidural analgesia during labor?
- Hypotension
- Postpartum hemorrhage
- Fetal respiratory depression
- Maternal nausea and vomiting
- Maternal aspiration pneumonia
Which of the following is the best definition of spinal analgesia?
- Injection of analgesia directly into the spinal fluid for regional analgesia used during cesarean sections.
- Administration of a slow flow of analgesia via a catheter into the epidural space in the spine only used during cesarean sections.
- Administration of a slow flow of analgesia via a catheter into the epidural space in the spine which can be used during normal labor or cesarean sections.
- Administration of opiates into the pudendal nerve to create a local nerve block used in operative vaginal deliveries.
- Injection of analgesia directly into the spinal fluid for regional analgesia used during normal labor.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |