Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Imaging Findings in Ectopic Pregnancy
-
Slides Pelvic Imaging in Early Pregnanc.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
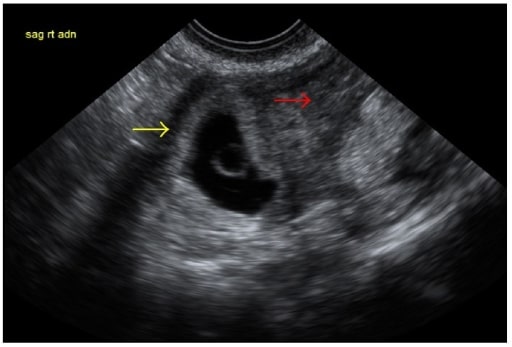
00:01 So what is an ectopic pregnancy? That is a pregnancy that's located outside of the normal uterine cavity and usually these results in a tubal location. 00:09 This can actually rupture and cause life threatening hemorrhage so these are very important to identify early on and patients usually present with lower abdominal pain in the case of an ectopic pregnancy. 00:20 So let's look at some imaging findings. 00:22 Ectopic pregnancies are usually presented as a heterogeneous adnexal mass and we'll look at some of these in detail. 00:30 You can have a tubal ring sign. 00:32 You can have what's called as pseudogestational sacs, you can actually have a sac within the uterus but it's not a true gestational sac. 00:39 One finding which is very commonly seen especially in early pregnancy is really just no identifiable pregnancy so in a patient that comes in with a positive beta HCG level knowing they are pregnant and we don't see any pregnancy identified anywhere, this is actually very common finding in ectopic pregnancy. 00:55 The patient may also present with a large amount of hemorrhagic fluid which can happen in the case of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. 01:02 So let's go into a little more detail with some of this. 01:05 So the tubal ring sign is actually an echogenic ring that separates the ectopic pregnancy from the ovary. 01:11 Occasionally, you can actually see an entire yolk sac and embryo as an ectopic pregnancy but often all you see is a mass like lesion. 01:20 A pseudogestational sac as I've mentioned is actually a cystic intrauterine structure which appears to be a gestational sac but doesn't contain any embryo. 01:30 It has a surrounding thickened echogenic endometrium or a decidual reaction as we saw earlier. 01:36 So this can be as somewhat misleading and it's important to see that even if you have what appears to be a gestational sac within the uterus you wanna make sure that you don't actually have another mass outside that could represent an ectopic pregnancy. 01:49 So this is an example of an ultrasound demonstrating an ectopic pregnancy in the right adnexum. So you have a pregnant patient that comes in with lower abdominal pain. 01:58 We have a sagittal image of the uterus here which doesn't show any kind of gestational sac. 02:04 On the image of the right ovary, we see a normal looking ovary here and then we have what appears to be an echogenic mass adjacent to the right ovary and this actually represents an ectopic pregnancy. 02:18 So again, no evidence of an intrauterine pregnancy in a patient that has a positive beta HCG level and a gestational age that represents about 7 weeks. 02:27 So at 7 weeks, we really should be seeing an embryo and possibly even a fetal heart rate. 02:32 So there are multiple locations of ectopic pregnancy. 02:36 Again, the most common is the tubal location as we mentioned right here, however, they can be interstitial which is right at the entrance of the fallopian tube into the uterus. 02:45 They can be cervical or down in the cervix and they can be at the distal end of the tube or in the fimbrial. 02:51 So multiple different locations and all of these really need to be evaluated for any kind of solid mass when performing an ultrasound looking for an ectopic pregnancy. 02:59 Ectopic pregnancies can rupture and they can result in very life threatening hemorrhage so it's important to recognize these early. 03:07 So how are ectopic pregnancy is treated if you do see an ectopic pregnancy on ultrasound? The first step is to call an OB-GYNE physician. 03:14 They can be treated medically with Methotrexate. 03:17 In this case the patient has to be stable, there can be no evidence of rupture of the ectopic, and this is usually about 90% effective in early, unruptured small ectopic pregnancies. 03:27 However, in a patient that doesn't meet those requirements the option is surgical treatment and this is really the only option available for a patient that has a ruptured ectopic pregnancy in which case they remove the fallopian tube especially the segment of the tube located at the level of the ectopic pregnancy and they try to reconnect the tube to preserve fertility if possible although occasionally that really isn't possible. 03:50 Another option is to do a salphingotomy or just an incision in the tube to remove the ectopic pregnancy and then again put the tube back together again. 03:58 The third option is actually ultrasound guided injection so Methotrexate or a potassium chloride can be injected into the gestational sac using ultrasound guidance.
About the Lecture
The lecture Imaging Findings in Ectopic Pregnancy by Hetal Verma, MD is from the course Abdominal Radiology. It contains the following chapters:
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Included Quiz Questions
Which statement is TRUE regarding the pseudo-gestational sac?
- It is surrounded by a thickened echogenic endometrium.
- It is a cystic extrauterine structure.
- There is always a yolk sac along with a visible embryo inside the sac.
- It is a heterogenous adnexal mass.
- It lies next to the echogenic ring in the ovary.
On ultrasound, an ectopic pregnancy is confirmed which is unruptured at 7 weeks gestation. What is the best treatment option for this patient?
- Methotrexate
- Salpingectomy
- Salpingostomy
- Ultrasound-guided potassium chloride injection
- Observation
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |