Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hypothyroidism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
-
Emergency Medicine Bord Thyroid Emergencies.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
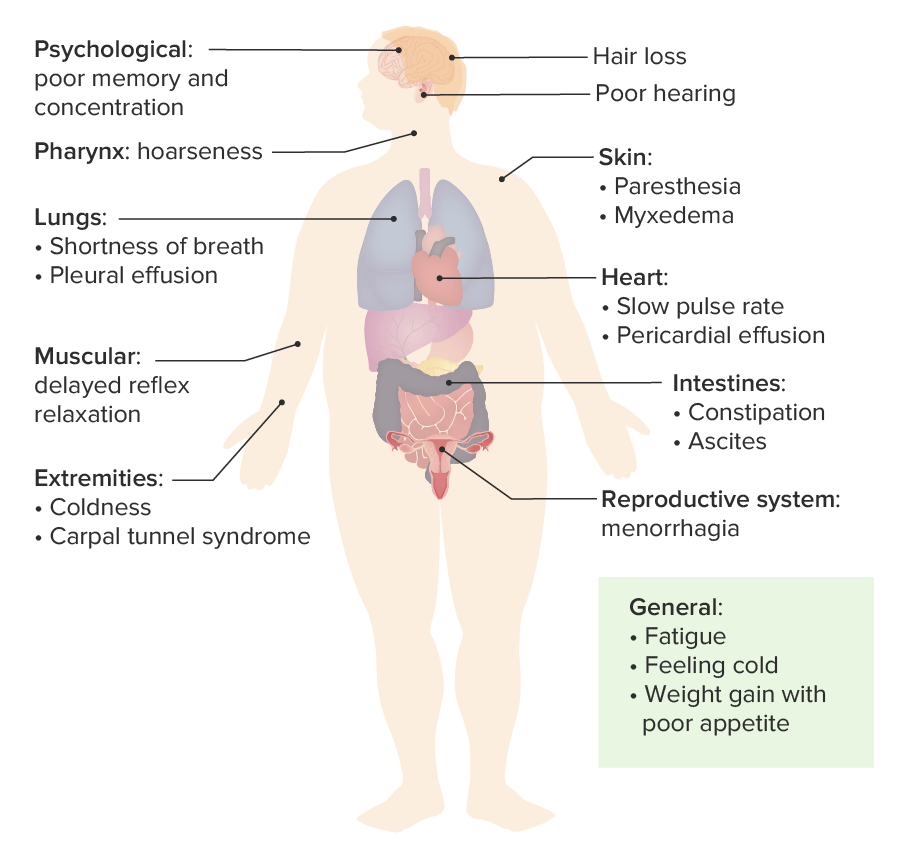
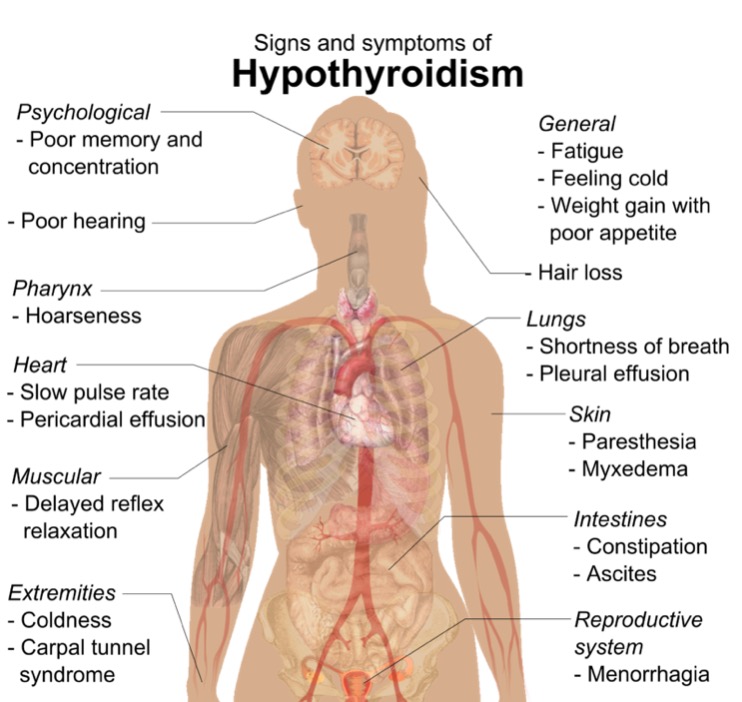
00:01 We’re gonna move on now and we’re gonna talk about hypothyroid. 00:05 So hypothyroidism is when the thyroid gland fails to produce an adequate amount of thyroid hormone. 00:11 Now this can be due to primary hypothyroidism which is due to gland failure itself and this is a big majority of the cases, this is 99% of the cases, the gland itself isn’t making what it’s supposed to. 00:24 Autoimmune disease related to Hashimoto’s. 00:27 Patients can also have infiltrative disease into their thyroid. 00:32 Pregnancy can cause hypothyroidism and the gland not to function adequately and then congenital hypothyroidism. 00:40 There’s also a secondary hypothyroidism which is due to lack of stimulation of the gland so this is coming from further open that feedback pathway, so from the pituitary gland or from the hypothalamus. 00:51 Now the symptoms here can be very varied. 00:54 They can be vague to overt organ failure when patients have hypothyroidism. 00:58 Now hypothyroidism affects about 1 to 2% of women in the United States. 01:04 Patients can have fatigue or weakness. 01:07 They can have cold intolerance, so they’re gonna be the person in the room who’s alaways cold, who’s looking for a jacket or a blanket to put on. 01:15 They may experience weight gain. 01:17 Elevated blood pressure, a slow heart rate, dry skin. 01:21 Now this is the body in a decreased basal metabolic state. 01:26 So whereas hyperthyroidism, your body is revved up. 01:29 You have increased sympathetic stimulation, this is your body slowing down. 01:33 This is your body gaining weight, your heart rate slowing down, you’re feeling cold. 01:40 Now myxedema coma is a severe life threatening stage of hypothyroidism. 01:46 So this is the equivalent of thyroid storm in a hypothyroid state. 01:50 It can be precipitated by sepsis, stroke or myocardial infarction. 01:55 Just looking at the patient profile, the classic thing that you’re gonna see is an older woman classically in the winter who has a known history of hypothyroidism. 02:05 Potentially, may have had their thyroid removed and be chronically on thyroid replacement. 02:10 Hypothermia, the temperature is usually less than 95.9 Fahrenheit or less than 36 degrees. 02:18 Now if the temperature is very dangerously low, so less than 90 degrees Fahrenheit or 32 degrees Celsius. 02:24 That’s a pretty poor prognostic sign and as temperature has been as low as 24 degrees Celsius reported. 02:31 Patients will also have altered mental status. 02:35 They may be lethargic or confused. 02:37 They may also be agitated. 02:39 They may have a seizure potentially. 02:42 The blood pressure may be low. 02:44 Refractory to volume resuscitation, so if you have a patient who has a low blood pressure, you’re giving them fluids, it might not necessarily get better. 02:52 Again, the body is slowing down so the patientis gonna have slow and shallow respirations. 02:58 Because of that they may develop hypercapnia, the carbon dioxide levels may increase, they might become hypoxic and they’re at a high risk for respiratory failure. 03:08 Patients may also have sinus bradycardia, the QT interval may be prolonged and they may have ventricular arrhythmias. 03:14 And then the classic myxedema facies which is basically puffy eyelids and lips, the tongue might be large, the nose might be broad. 03:23 And there also may be evidence of severe chronic hypothyroidism, so they might have the changes and the issues that we talked about or the hypothyroid diagnosis. 03:35 Often times there’s an acute precipitating illness here and possibly may be related to drug toxicity and may have associated hyponatremia. 03:44 So how do we diagnose this? So we put together our clinical picture and we have to maintain a high level of suspicion for it. 03:51 So we’re looking for a high TSH level, so the TSH is really elevated. 03:56 The body is trying to say secrete the thyroid hormone but the gland is not doing it. 04:01 The T4 levels are low, the T3 levels are low. 04:05 You’re gonna wanna get an EKG to assess for any kind of arrhythmia and you may also see elevated liver function test. 04:12 Now what do we wanna do for hypothyroidism? First and foremost we wanna replace the thyroid hormone, we wanna give thyroxine. 04:20 In myxedema coma, you wanna replace the thyroid hormone rapidly so you wanna give it IV. 04:26 You also wanna provide the patient with supportive care so you wanna give them fluids, you wanna warm them up again using a Bair Hugger or warm fluids or some kind of irrigation, especially in cases of severe hypothermia. 04:39 So for the most part, most hypothyroid patients who don’t have myxedema coma but have some element of hypothyroidism can be treated as an outpatient. 04:50 If your patient has myxedema coma, that’s a patient who requires ICU level of care. 04:55 So the conclusion here is that thyroid hormone secretion is based on a negative feedback loop. 05:00 Symptoms of thyroid emergencies can be vague, so you have to maintain a high level of suspicion for these conditions. 05:07 When you have a thyroid emergency, look for an underlying cause such as sepsis or cardiac events. 05:14 And then treatment for thyroid emergencies consist of supportive care and then either decreasing or increasing depending on what’s going on the amount of thyroid hormone.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hypothyroidism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment by Sharon Bord, MD is from the course Endocrine and Electrolyte Emergencies. It contains the following chapters:
- Hypothyroidism
- Sympthoms of Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroidism: Diagnosis and Treatment
Included Quiz Questions
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism?
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- Pregnancy
- Thyroid surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Pituitary tumor
What is the most serious complication of hypothyroidism in an adult?
- Myxedema coma
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Goiter
- Infertility
- Cognitive decline
Which of the following statements regarding thyroid emergencies is NOT true?
- Management for hypothyroidism is aggressive fluid replacement to prevent myxedema.
- Thyroid hormone secretion is based on a negative feedback loop.
- For rapid replacement of thyroid hormones, IV administration is indicated.
- Myxedema warrants an ICU admission.
- The underlying cause for thyroid emergencies must be identified for appropriate management.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Simple, concise lecture regarding hypothyroidism. Discussed - patient population, S/S, diagnostics, and treatments.