Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) with Case
-
Slides Gastroenterology 05 Esophageal Diseases.pdf
-
Reference List Gastroenterology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
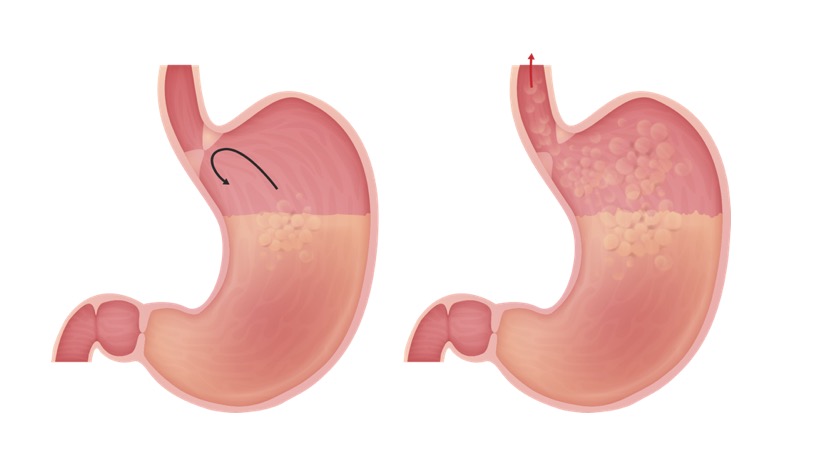
00:01 We'll move on to our next case now. 00:03 We have a 52-year-old man seen in clinic complaining of burning sensation in his chest for the past six weeks. 00:09 His symptoms are worse at night and after he eats a large meal. 00:14 He has tried over-the-counter antacids with some relief but still has symptoms. 00:19 And he has not had any difficulty swallowing or unintentional weight loss. 00:24 Vitals and physical exam are normal. 00:26 What is the best next step in treatment? So some key features of this case are that he has heartburn which is worsened by a lying flat and having large meals, he has tried some over-the-counter antacids such as H2 blockers which offer some relief, and he has no alarm symptoms of weight loss or dysphagia. 00:48 So let's talk a bit about gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD. 00:53 Here you can see a healthy stomach where the lower esophageal sphincter is closed during digestion. 01:00 And on the right side of this diagram, you see an example of gastric reflux where the lower esophageal sphincter is open and allowing the reflux of contents back up into the esophagus. 01:10 Patients may present with heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. 01:15 And the diagnosis is made by taking a good clinical history and see if they respond to an empiric trial of therapy. 01:23 In general, if you don't know the diagnosis you may do ambulatory ph monitoring to confirm your diagnosis. 01:31 Treatment is with initially recommending diet and lifestyle changes, and you may also offer pharmacologic treatment such a limited trial of an H2 blocker or a proton pump inhibitor. 01:44 So now let's talk about some alarm symptoms related to GERD. 01:48 You should always screen a patient with GERD for any alarm symptoms of unintentional weight loss, dysphagia, hematemesis, or melena. 01:57 If any of these things are present, you should refer that patient for upper endoscopy. 02:02 So now let's return to our case. 02:04 We have a 52-year-old man with heartburn exacerbated typically by lying flat and large meals, he has tried some over-the-counter antacids with some relief, and luckily he has no alarm symptoms of weight loss or dysphagia. So his heartburn is typical of GERD. 02:23 And because he has no alarm features, the next step in treatment should be recommending dietary and lifestyle modification and a trial of a proton pump inhibitor.
About the Lecture
The lecture Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) with Case by Kelley Chuang, MD is from the course Disorders of the Esophagus and the Stomach.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following symptoms is one of the alarm symptoms of GERD and is an indication for an upper endoscopy?
- Weight loss
- Heartburn
- Pressure sensation in the chest
- Chronic nonproductive cough
- Acidic taste in the mouth
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |