Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Gastritis with Case
-
Slides Gastroenterology 06 Stomach Disorders.pdf
-
Reference List Gastroenterology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
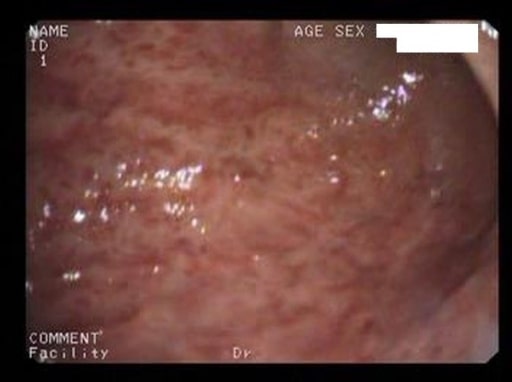
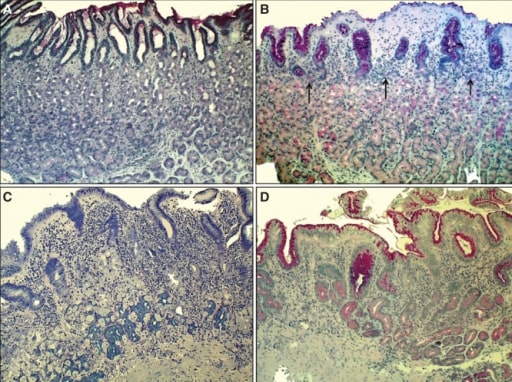
00:01 So now we'll move to our next case. 00:03 We have a 48-year-old man who presents to the clinic for follow-up. 00:07 He has had four months of epigastric discomfort and abdominal bloating after meals. 00:13 He has tried twice-daily omeprazole for the last three months without relief. 00:18 He has no weight loss, dysphagia, or odynophagia. He recently moved here from Mexico. 00:24 And two weeks ago, he underwent an upper endoscopy that showed erythema and erosions of the gastric mucosa. 00:32 One biopsy is taken shown here. His vitals are normal. 00:38 On exam, abdominal exam is benign. 00:41 So we're asked, what is the best next step in management? Before we answer that question, let's look a bit closer at this case. 00:49 So he has chronic epigastric discomfort after eating, he has already tried a greater than eight-week trial of a proton pump inhibitor, he importantly moved from a developing country, and he has some suspicious endoscopy results shown here that we'll go into a bit later. 01:10 So let's talk now about gastritis. Gastritis is the clinical term we use to refer to inflammation of the gastric mucosa. 01:20 When there is cell damage without inflammation, this is just called gastropathy. 01:26 So gastritis can result from multiple causes. It has a similar list of risk factors as peptic ulcer disease. 01:35 So things like NSAID, H. pylori, smoking, and alcohol can all cause gastritis. 01:41 It may also be an autoimmune condition, it can be results of infections, and it can also be due to granulomatous disease like Crohn's disease or sarcoidosis. 01:53 So here you can see two examples of biopsies from the gastric mucosa. 01:58 In panel B, you see a normal gastric mucosa. 02:02 And in panel A, you see multiple cells that are mononuclear infiltrating the gastric mucosa. 02:09 And this is what it looks like when patients have gastritis. 02:13 So the diagnosis of gastritis is made by upper endoscopy that should be done if patients continue to have symptoms after an adequate trial of a proton pump inhibitor or H2 blocker. 02:26 They should also be tested at some point for H. pylori or any other suspected infections. 02:33 Treatment is done by targeting the underlying cause. 02:36 So in summary, when you see a patient who's coming to you with gastritis, you should always remember to test for H. pylori, stop any offending agents, give them a trial of a proton pump inhibitor or H2 blocker, and then if they still have symptoms after eight weeks, refer for upper endoscopy. 02:56 So now let's go back to our case. 03:00 We had a 48-year-old man coming in with chronic epigastric discomfort after eating, he has already tried an adequate trial of PPI, he interestingly moved from a developing country, and his endoscopy results that we discussed earlier now show gastritis as you can see multiple lymphocytes infiltrating into the mucosa. 03:21 What is the best next step in diagnosis? So since this patient is from a region where H. pylori has high prevalence, he should have had gastric biopsies done to rule out H. pylori. 03:35 But since this is not shown in the example that we are given, you should check for an H.pylori stool antigen.
About the Lecture
The lecture Gastritis with Case by Kelley Chuang, MD is from the course Disorders of the Esophagus and the Stomach.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is the best next step after 8 weeks of proton pump inhibitor trial without improvement of chronic epigastric discomfort?
- Endoscopy with biopsy
- H2 inhibitors
- Continue proton pump inhibitors
- Colonoscopy
- Abdominal ultrasonography
Which of the following is the most important risk factor for gastritis?
- H. pylori infection
- Proton pump inhibitor use
- H2 inhibitor use
- C. difficile infection
- Diarrhea
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |