Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Estradiol and Progestin Effects
-
Slides Female Hormones Endocrine System.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
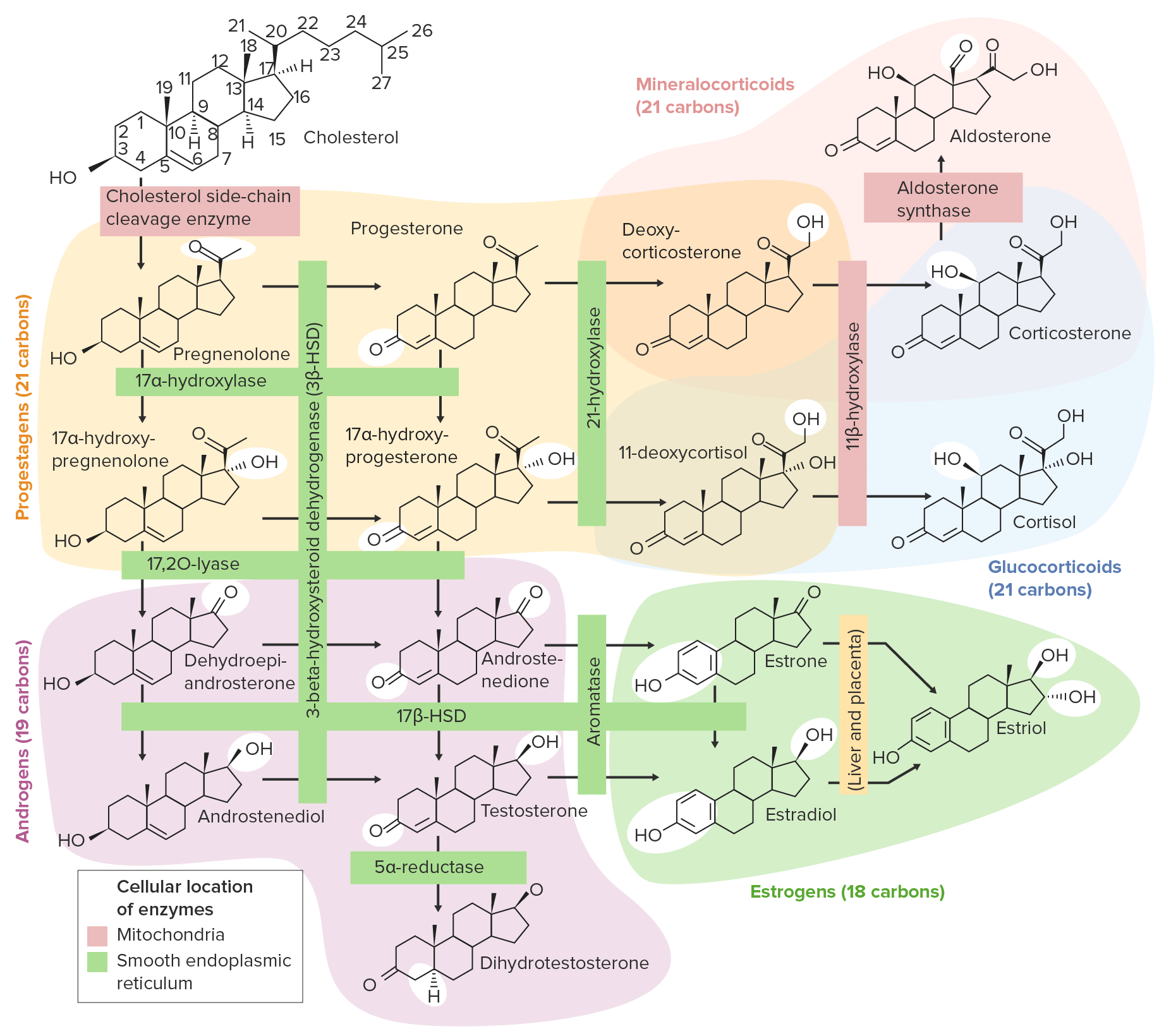
00:00 What are the peripheral effects of estradiol? Estradiol increases bone growth by osteoblast. 00:11 It increases most all progesterone responses. So if you have estradiol present and progesterone, progesterone is going to do more work than it can just by itself. It increases a lot of lipid-profile related items like it decreases your LDL protein but it increases your HDL protein. In the reproductive organs, it's going to stimulate uterine growth, fallopian tube growth, breast growth as well as secretions of the cervix and increasing the receptors on the granulosis cells. One thing I will point out here is that oftentimes after a woman has no longer has cycles or becomes menopausal, she does lose more bone mineral density. One of the reasons this occurs is because of lower levels of estradiol. Progesterone has a number of effects on its own. Progesterone affects milk development and some of the breast tissue that is going to help for that process to work. In the reproductive organs, you get increase in endometrial secretions and secretions become thicker. There is also a decrease in endometrial growth. Finally, there is a small increase in body temperature associated with progesterone and therefore these items you can think about of being directly related to the endometrium and to the breast.
About the Lecture
The lecture Estradiol and Progestin Effects by Thad Wilson, PhD is from the course Reproductive Physiology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is increased by high plasma levels of progesterone?
- Endometrial secretions
- Milk production
- High-density lipoproteins
- Bone growth
Which of the following is the mechanism of effect of estradiol on bone?
- Increased growth
- Increased mineralization
- Increased remodeling
- Increased parathyroid hormone
- Increased calcitonin
Which of the following is a result of progestin on the body?
- Increased endometrial secretion
- Increased lactation
- Increased endometrial growth
- Decreased body temperature
- Decreased endometrial secretion viscosity
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |